Tutorial
Keyword clustering
Keyword clustering is the process of grouping a set of keywords in such a way that keywords in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. The level of similarity/differentiation depends on the set parameters.
Why do you need keyword clustering?
- grouping keywords by meaning to a page, section or site directory;
- optimizing your site with automatic analysis of the semantic core;
- creating clusters of the keywords for specific directories and page sections;
- creating a site structure by distributing keywords into clusters;
- expanding topics for which there are few keywords.
The most fundamental drawback of existing keyword clustering tools is that the resulting clusters may either contain keywords without a strong semantic similarity or the analyzed
The first issue arises while using Weak cluster type, the second is caused by Strong type. Also, both these clustering types share a common drawback — the
Unlike many competitors’ solutions, Serpstat clustering tool doesn’t set a cluster center — a keyword with the highest search volume which is compared with other keywords to detect the number of matching URLs in SERP, and Serpstat is looking for connections among all clustered keywords.
Let’s look in detail at the main settings of the tool.
In fact, there are only two of them: Strength and Cluster type.
Strength:
- weak — tells the system that in order to be combined into a cluster, the keywords must have at least 3 common URLs in top-30 search results for a keyword
- medium — the keywords must have at least 8 common URLs in top-30 search results for a keyword
- strong — sets 12 common URLs as a condition for keywords merging into a single cluster.
The next clustering parameter choice is cluster type:
- soft cluster type — tells the system that a cluster can be created if at least one pair of keywords 
- hard cluster type — requires all keywords in a cluster to have 3, 8 or 12 common URLs in top-30 search results for a keyword (the requirement for the number of common keywords is defined on the previous step where you selected weak/medium/strong clustering). The resulting clusters contain synonymous keywords with a high semantic similarity. At the same time, this clustering method produces lots of clusters as the keywords can be merged into a cluster only if they are closely related.
Strength shows how closely a keyword is semantically related to the cluster’s topic on a scale from 0 to 100.
Upon clustering completion, a portion of the initial set of keywords can be seen in the "Unsorted keywords" directory. These are objects that haven’t been added into any cluster. One reason for this can be that the keywords have no semantic similarity to the topic of the analyzed keyword set and should be removed from the dataset. An alternative solution is to create separate pages for these keywords or move them to one of the created clusters if you believe they belong there.
Which clustering method is right for you?
The decision should be based on the semantic similarity of the objects from your dataset.
If the keywords are initially closely related, for example, sneakers of different brands, you may want to choose "Strong"+"Hard" or "Strong"+"Soft" so that only the closest synonyms are combined into a cluster. You’ll get lots of clusters to use for separate pages or specific categories.
In the case of various products and services, for example, a keyword collection for a multi-product store or medical center with a full range of health-care services, it’s worth selecting "Weak"+"Soft". The choice of "Strong"+"Soft" will produce more clusters and a possibility to get more topic-specific clusters.
Setting up a clustering project
(1) Go to the "Keyword clustering, Text analysis" block in the side menu, and (2) click "Add a new project" button:

Set preferable settings before clustering the keywords.
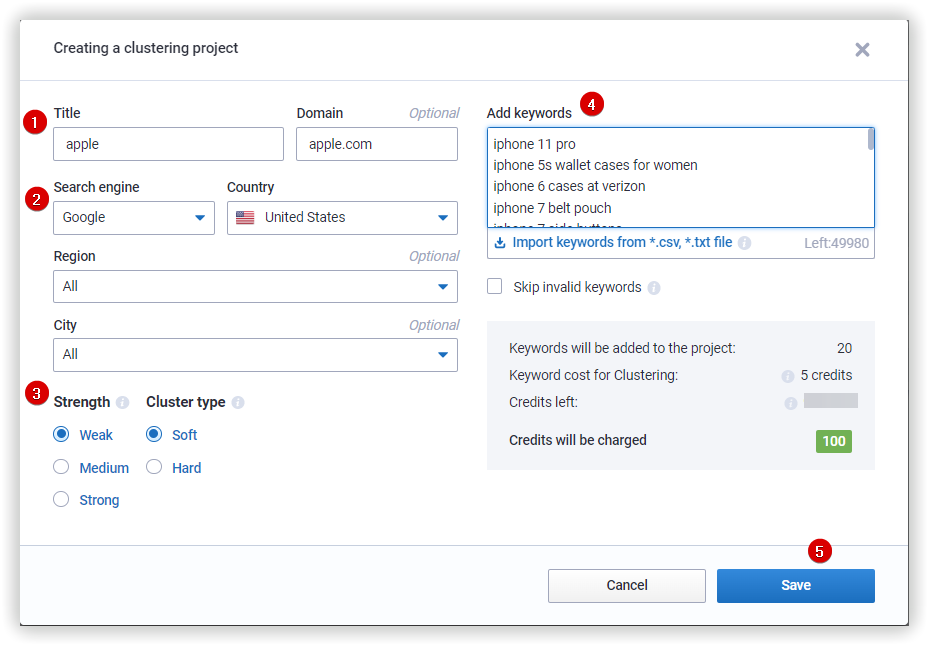
- Name your project and input a domain name (optional).
- Choose a search engine and country; region and town are optional.
- Choose strength and cluster type.
- Add a list of keywords or import them from a file (csv, txt). The size of the imported file must not exceed 30MB.
Add only valid keywords that don't contain:
- Duplicates.
- Special characters.
- Search operators.
- Spaces at the beginning or at the end.
- Double spaces.
- Digits as keywords.
- Keywords longer than 80 characters. - Click the "Save" button to create your project and start the clustering process.
The clustering process may take some time. The result of clustering will look like this:
We land on a Project page with a list of clusters — groups of semantically related keywords, where:
1. The number of clusters created in this project is displayed in brackets next to the name of the "Clusters" column.
2. By pointing the cursor at the cluster and clicking on the pencil, you can change the name of the created cluster.
3. The number of keywords in each cluster.
4. The "Add cluster" button allows you to create a new cluster (enter a name and press Enter).
5. Unsorted keywords are pinned, and they are always in the upper part (they are not involved in sorting clusters).
In the right window you will find a list of all keywords of the selected cluster and its parameters.
1. Volume — how often people search this keyword per month.
2. Connection strength — provides how close that keyword is to the cluster's topic on a scale from 0 to 100%.
3. Homogeneity shows the semantic consistency of a cluster (from 0 to 100%).
4. If you specified a domain while creating a project, we'll look at your website's pages and display the page which is the closest to the cluster's topic in the URL field. If you
5. Metatop is a list of major competitors in SERP for keywords from a cluster. The higher a page’s rank in the meta-top, the more relevant it is to the cluster’s topic:
Each cluster has a drop-down menu:
1. The "Add keywords" button opens a window where you can add some keywords to the existing cluster.
2. Click "Delete keywords" button to delete checked keywords from the cluster.
3. The "Move to unsorted" button moves the selected keywords to the "Unsorted keywords" directory.
4. If you need to move seleсted keywords to another cluster click "Move keywords to..", and also you can move selected keywords to a new cluster — just create it here:
5. The "Delete cluster" button deletes the cluster from your project.
In the right corner, you can check how many credits you have left.
Keywords search to find specific keywords among all clusters.
Next, there are buttons with the following functions:
- text analysis can be launched for any of the clusters. To do this, press the "TA" button, which will open a pop-up for selecting clusters;
- the "Refresh clustering" button restarts the current clustering results;
- open the "Project settings" to change the current settings, but after that, you need to restart clustering for the project to get the updated data;
- export is available in various formats separately for the whole project or a certain cluster (open the needed cluster and for the export select "Cluster"):
* CSV Open Office, Libre Office
* CSV Microsoft Excel (CP1251) — only for the whole cluster
* XLSX Microsoft Excel (up to 10K)
* XLS Microsoft Excel (up to 10K)
Sort information in ascending/descending order by clicking the column title.
How are credits charged?
How the credits for Clustering are spent:
1 keyword = 5 credits.
Number of keywords * 5 = number of spent credits.
For example: When you add 20 keywords to the project, you spend 100 credits:
20 * 5 = 100 credits.
Please note: Credits for Clustering, Text analysis, Domains batch analysis and Keywords batch analysis are comm.
Click the "?" button to open this tutorial for the Keyword clustering tool.
Learn more about the tool in the article "How To Group Keywords Automatically With The Serpstat "Clustering" Tool"
If you still have any questions, you can go to our FAQ or contact the tech support chat.
If you'd like to get advice on Serpstat's features, order your free 30-minute demo.