Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
5 SEO Tips to Increase Your Organic Traffic in 2023

Still, it’s important to keep in mind that organic traffic, unlike paid traffic sources, is a marathon, not a sprint. It takes time for your best organic traffic practices to see results, but once you’ve established your strategies well, they work for you with minimal user input.
Today we will dive into a few of the most popular traffic sources and 5 steps one can follow to increase organic traffic.
Importance of Organic Traffic
How to Get Organic Traffic?
5 Ways to Optimize Organic Traffic
#1: Use Effective Headings and Titles
#2: Optimize Your Content for Searches
#3: Create Click-Driving Meta Descriptions
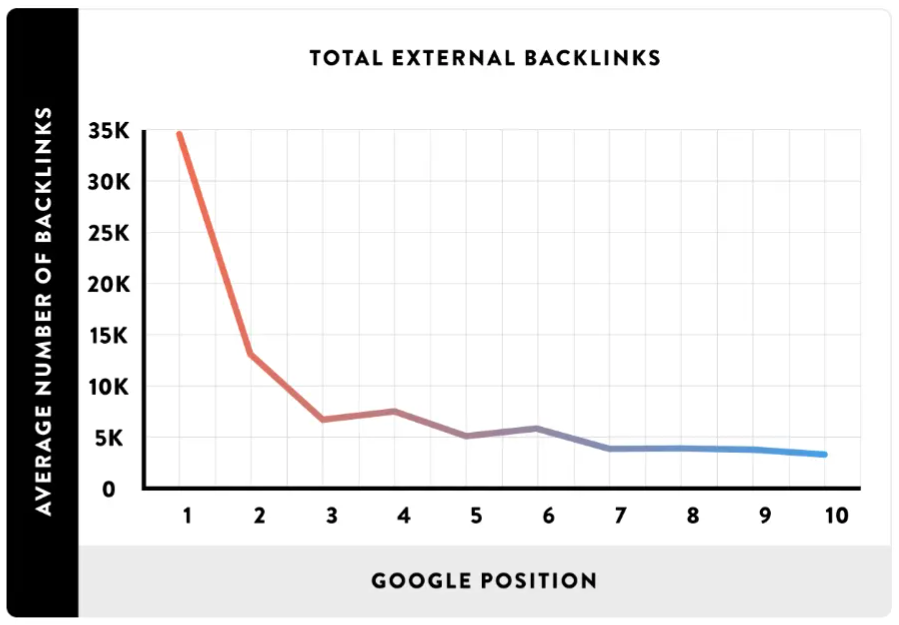
#4: Develop a Diverse Backlink Profile
#5: Increase Your Website’s Speed
Key Takeaways
What Are Traffic Sources?
Traffic is commonly sorted into a few key categories, including direct, organic, paid search, social, email, and referral traffic, each of which works in a specific way.
Among all these traffic sources, direct and organic traffic are the two most important, but for this article, let’s focus on organic traffic.
Importance of Organic Traffic
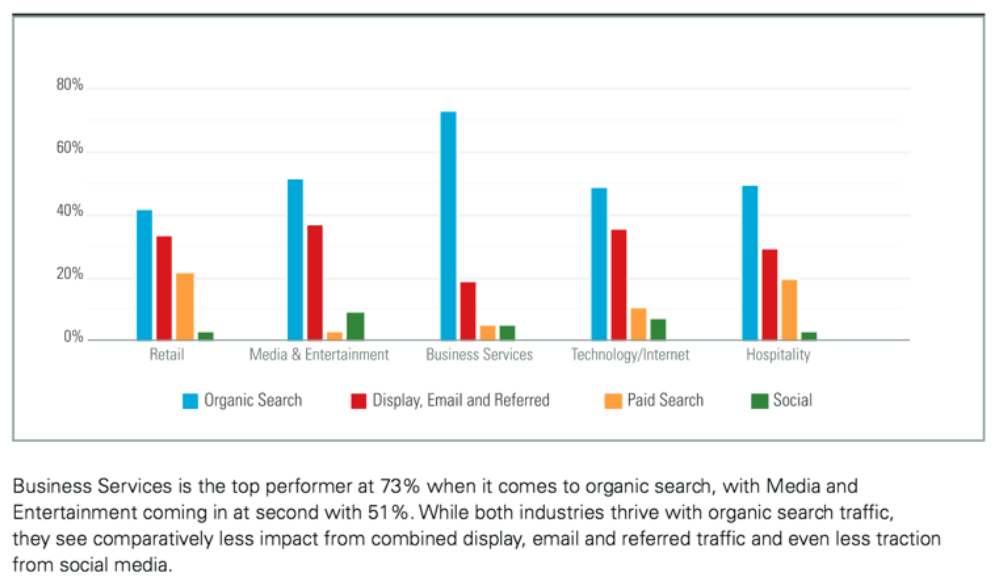
Organic traffic comes into play when the users accessing your content input specific queries into their search engine. The terms they use to define their query cue search engines like Google to hunt for articles that seem most relevant. The unpaid articles that pop up first on your search results page are the ones that search engines determine to be the best match for your needs, and that’s how your organic traffic is born.
It's important to keep in mind that your search engine doesn't match a user query word-for-word. Instead, it takes the user’s search intent into consideration to present them with a SERP (Search Engine Results Page) that satisfies their query’s intent.
On the other hand, there is organic traffic — a high-impact, low-cost, long-term solution that requires little maintenance once established.
SEO strategies are constantly changing, so you can never fully step away from the traffic-generating processes, but with organic methods, you’re much closer to an automated system than you ever could be with a PPC system in place.
Some top-ranking sites pay upwards of $100,000 per month on SEO to hit their targeted keywords and beat their competition. So to even have a chance of ranking with them, you must be involved in SEO strategies.
But the beauty of powerful SEO practices is that you don’t have to have a massive SEO budget to outrank your competitors. Because as David Farkas, the founder and CEO of The Upper Ranks, puts it, “if you dominate search results, it’s easier to dominate your market.”
When your content is on the first page of a Google, Bing, or Yahoo search results page, it’s an incredible advantage because there is no way for your competition to duplicate how you got your results. They can’t reverse-engineer your content experience to benefit themselves as they can with PPC. Hence, until other articles outperform you with keywords, relevance, or search intent matching, you’ll continue to rank higher on SERPs than competing sites.
Additionally, once an article reaches a high rank on any given search engine, it becomes much more challenging to bump it off the first page because the more people click on it, the more relevant it will continue to be.
How to Get Organic Traffic?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) plays a key role in organic traffic. The more you optimize your site with specific search terms, the better you rank on search engines.
Let's now discuss five actionable ways you can follow to optimize your organic traffic today.
5 Ways to Optimize Organic Traffic
Primarily, you can do this by using effective headers and titles and optimizing your content from quality to relevance to variety within the body of your articles. You can also use tailored meta descriptions, well-developed backlink profiles, and increased website speed to ensure that your pages are optimized to gain you the most organic traffic they can, thereby improving your search engine visibility and individual page rankings.
Let’s dive into each of these systems to understand better how you can make them work for you.
#1: Use Effective Headings and Titles
Titles tagged with the “<title> HTML” tag work to define your article. They serve as the most concise description of your page’s content and are one of the first things search engines like Google analyze when determining which articles to rank higher on a SERP.
It’s essential to be strategic when it comes to your titles to make them compelling not only to search engines but also to individual users. A few key things to keep in mind when you’re drafting your page’s title include:
- Don’t use more than 70 characters. Anything more than that will be cut off on Google’s search results page, preventing users from reading the full title.
- Always include the main keyword you want your page to rank.
- Make your titles catchy with words and phrases that will draw readers in.
- Try titling your articles with numbered lists or “How to’s” to draw readers in (i.e., “5 SEO Tips to Increase Your Traffic” or “How To Automate The Work Of An Internet Marketer”).
- If you have room, add your company’s name at the end of your title heading to increase brand awareness.
Headings should be broken down into <h2> tagged primary subheadings with your secondary keywords written in the title to improve rankings. Then, you can use <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, and <h6> subheadings to further split up your content.
Theoretically, it should look something like this:

#2: Optimize Your Content for Searches
Optimizing your content starts with ensuring you have compelling titles and headings because those are the two-page elements that Google and other search engines will pay the most attention to in the beginning. Then, you’ll want to develop original, high-quality content with the most relevant information and feature it across several content types.
- Create High-Quality Original Content
It's important to remember that while it's nice to produce a lot of blog posts and articles, it's even more vital that everything you make is of the highest possible quality. More than anything else, quality determines your authority on a subject and can decide whether a user revisits your website.
You should always:
- check for spelling, punctuation, and grammar errors;
- break up your text into manageable sections;
- include relevant images, graphics, and other visual content;
- reference appropriate statistics.
Further, you must feature 100% original content. It helps to differentiate your website from others and gives you a competitive advantage regarding SEO and your online visibility with SERP rankings.
And, yes, in a world of clickbait-y, copycat content, producing your original content is challenging and requires a lot of research, time, and creativity. Still, there are tools available that can help you succeed. For example, Google Analytics can help you see what your audience's interests are so that you can generate ideas targeted to them.
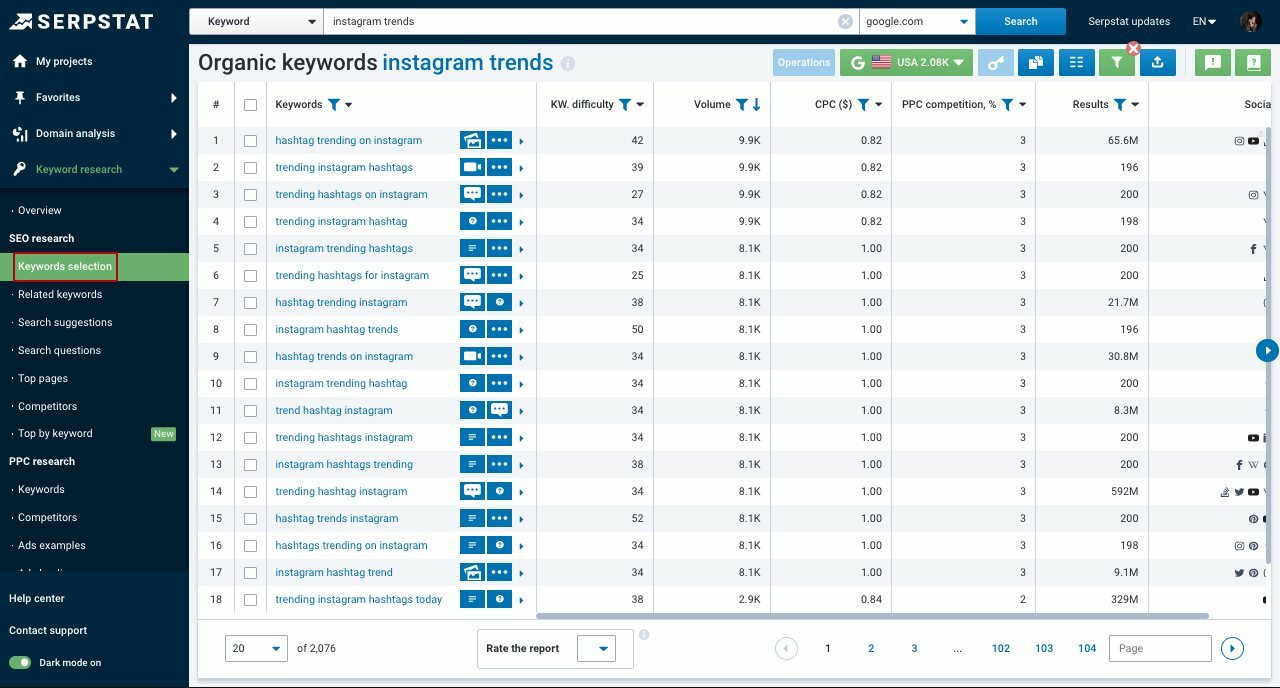
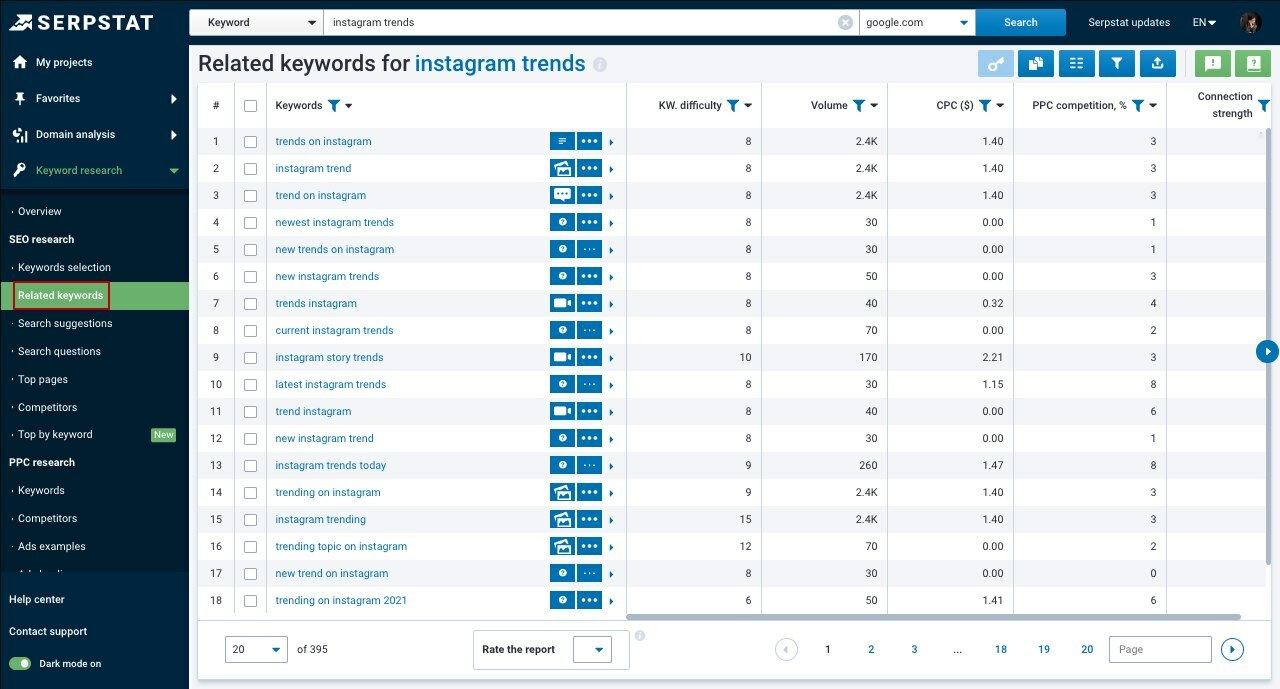
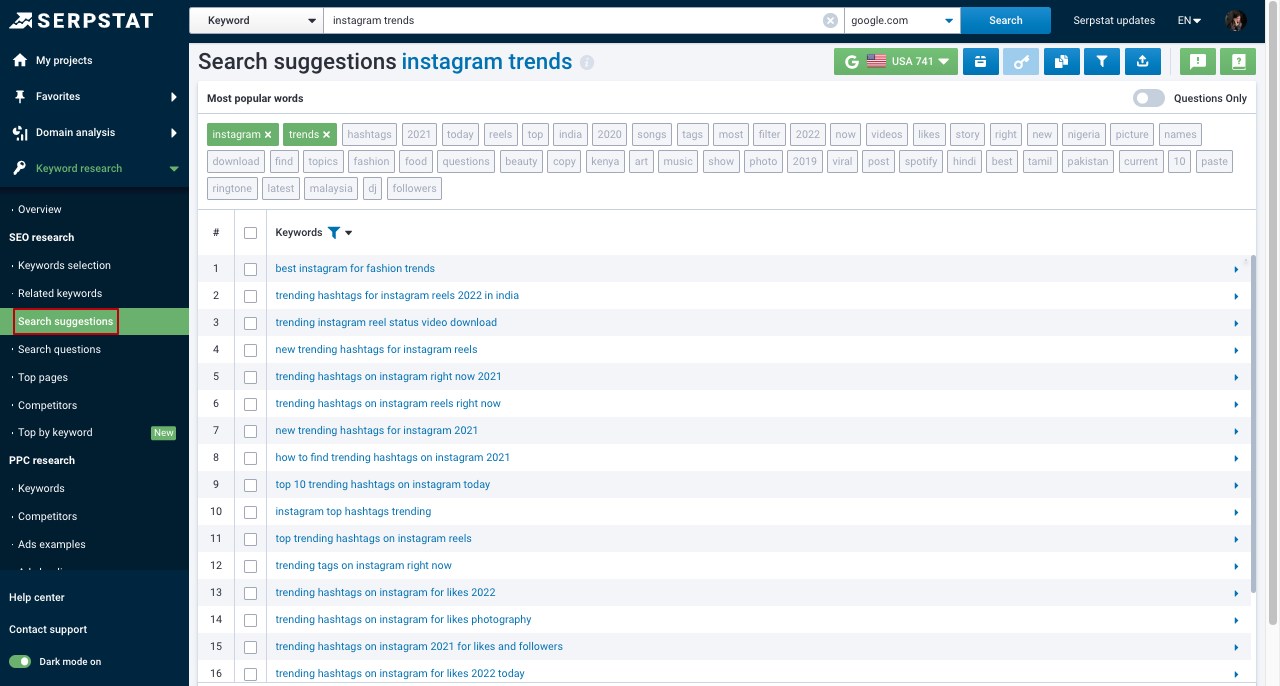
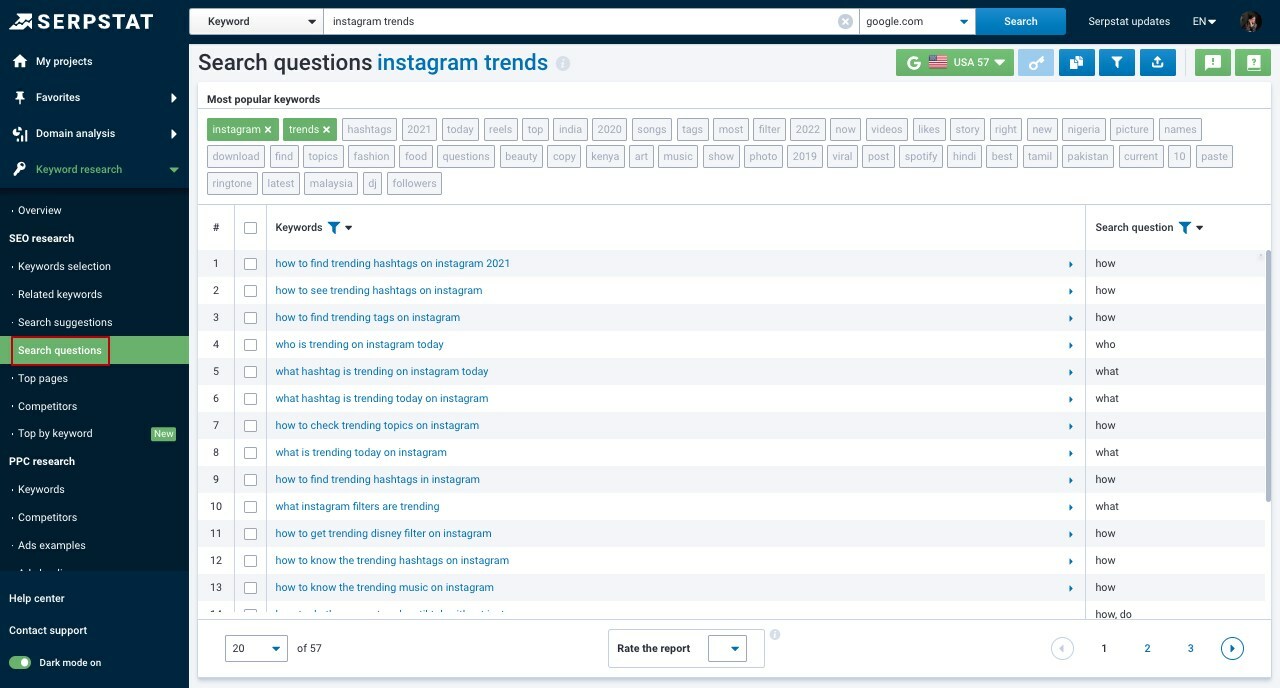
The tool fetches all search terms containing your set keywords. You can see different reports, including:
- "Keywords Selection" report – organic keywords associated with the researched one that domains are ranking for in Google's top-100 results.
- "Related Keywords" report represents all search queries that are semantically related to the searched keyword. This is where you can check and use new variations of the queries.
- "Search Suggestions" report shows the queries offered to users under the search bar.
- "Search Questions" report is where you can see all question forms of search suggestions. These are questions that include a selected keyword that users are looking for an answer to.
Would you like to make the most out of Serpstat Keyword Research tool?
You can simply try how it works by yourself!
Click the button below to get a free 7-day trial :)
- Feature Relevant Content
If you only draft content on out-of-date, irrelevant topics, users will have no reason to access your site, and search engines will have no motivation to promote your articles among their top-ranked results. Similarly, suppose you draft content that becomes outdated with time. In that case, it will also fall off ranked recommendations if you don't regularly update it to reflect the appropriate changes in technology, news, or whatever else.
Remember: search engines prefer shiny, new articles far more than older, potentially outdated ones. Maintain a high ranking on SERPs by regularly refreshing and repurposing your content.
- Play with Different Types of Content
Several variations are available, and each has many benefits that can help push your ranking to the top of your SERPs, and the better your mix of content is, the more your audience will return to read what you have to say.
A few key content types include:
- product reviews;
- buyer's guides;
- newsletters;
- shopping galleries;
- how-to's;
- case studies;
- e-books;
- blogs;
- white papers;
- infographics.
#3: Create Click-Driving Meta Descriptions
It’s important to note that meta descriptions are not as significant to Google’s ranking algorithm as other page elements, like the title and headers. Still, they are vital to your audience in serving as a preview of your content.
By writing compelling, descriptive meta descriptions, you increase your chances of drawing in new readers by 5.8%, so let’s look at a few essential tips you can follow to write the best meta descriptions for your content and click rates.
- Keep it Casual
- Be Concise
Remember, meta descriptions have a character limit of 120 words before your search engine cuts off the rest of the text, so make the most of that word count and be strategic about the language you use.
- Use Keywords
We believe that one more toll will be of use to you – Keyword Trends. This is a new tool that shows the most popular queries for a selected city and country in real-time. So, this is the way you can identify the most trending keywords and use them on a site, increasing traffic.
- Include a CTA
- Don’t Copy Yourself
But by creating brand new meta descriptions, you increase your SERP visibility chances in the long run.
#4: Develop a Diverse Backlink Profile
But developing a diverse backlink profile isn’t the easiest feat. To do it right, you’ll need to have backlinks on several different pages across a wide range of outside websites, including reference pages, directories, news sites, and blogs.
There are a few key strategies you can implement now to develop your backlink profile:
- Create high-quality content that websites will want to link to.
- Use top referral sources from your website.
- Form partnerships with websites you send outbound links to.
- Use Google Search Console's Top Linking Sites report to see what content you already have backlinks on and use that to develop similar content.
- Work with SEO tools to find out where your competitors have backlinks and use their sources to develop backlinks for your site.
- Build backlinks off of your competitor's broken links.
- Create useful infographics that others will want to reference.
#5: Increase Your Website’s Speed
What’s more, Google and other search engines find them annoying as well and don’t rank them as highly across their search results pages to give their users a better online experience. So even if you follow all the other tips in this article, if you have a slow-loading page, Google won’t rank you highly.
There are a few different reasons why your website may be running slowly, including:
- Poor-quality website hosting platforms.
- Too many HTTP requests.
- Increased code density.
- Large image and media resolution sizes.
- Excessive amounts of ads.
- Outdated CMS tools.
- Lack of a proper CDN.
Fortunately, there are a few easy fixes that can have you up and running faster than before with a minimal amount of work.
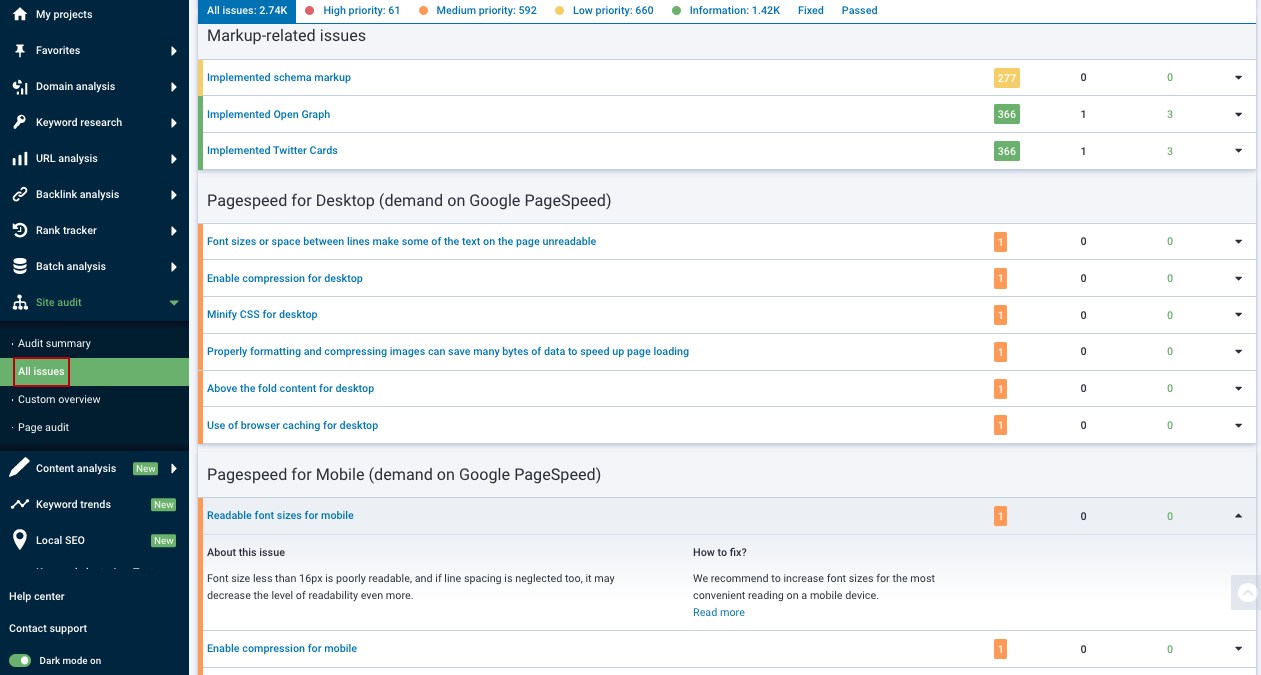
Checking your website's loading speed would be a much easier task if you use the Site Audit tool from Serpstat. Not only that, the platform will show you all the technical issues that exist on the site, as well as the possible ways to fix them.
Want to learn how to fix on-site issues and boost your Google rankings with the Site Audit tool?
Follow the link below, and sign up for a free 7-day trial
- Reduce Image Resolution
Image compression tools are readily available online through resources like Adobe Photoshop.
- Reduce Your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript Presence
Web developers can do this by cutting unnecessary lines of code, spaces, punctuation marks, and other characters that clog up your pages. Then, they can compress the remaining information if the files exceed 150 bytes in size to make for faster web page load times.
- Use an Appropriate CDN
So if you are a website based in America with a strong user presence in England, you can use a CDN to host your site in the appropriate European region to reduce your webpage’s load time in England.
Key Takeaways
But the good news is that once you start implementing these strategies, keeping up with them becomes second nature, and they’ll work for you much longer than you work on them.
Organic traffic strategies are a long game when it comes to traffic gathering. Still, by the time they start working for you, you will have saved much time and money. You’ll have a well-developed audience of targeted users who are more likely to engage with your content, increase your click rates, and bump you up on your SERPs.
Remember, if all these strategies seem overwhelming, focus on successfully implementing them one at a time. The more comfortable you become with each one, the sooner you can graduate to the next, and soon enough, you’re sure to have one of the top-ranked pages across your favorite search engines.
Speed up your search marketing growth with Serpstat!
Keyword and backlink opportunities, competitors' online strategy, daily rankings and SEO-related issues.
A pack of tools for reducing your time on SEO tasks.
Discover More SEO Tools
Backlink Cheсker
Backlinks checking for any site. Increase the power of your backlink profile
API for SEO
Search big data and get results using SEO API
Competitor Website Analytics
Complete analysis of competitors' websites for SEO and PPC
Keyword Rank Checker
Google Keyword Rankings Checker - gain valuable insights into your website's search engine rankings
Recommended posts
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.