Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
What Is Contextual Advertising and How It Is Used: The Basics of PPC

Any minor inconvenience on the purchase journey may divert visitors from obtaining a product. That’s why online retailers and other entrepreneurs speed up their websites, enhance UI/UX by optimizing on-site search or navigation, and implement new technologies.
Website promotion revolves around one question: "Do you want to see quick results or ensure long-term growth?" Depending on the answer, you may focus on search engine optimization (SEO) or pay-per-click advertising (PPC). You may prioritize only one of these methods, but it’s better to balance them by simultaneously investing in SEO and PPC.
This guide will focus on PPC — a fast website promotion method. You’ll know the peculiarities of contextual advertising and why it’s on the rise nowadays.
Google Ads and AdSense: How Does It Work?
Types of Contextual Advertising
Contextual and Behavioral Advertising: Difference
Importance of Context in Advertising
Why Is PPC Gaining Popularity?
Contextual Targeting in Advertising: Pros and Cons
Role of Artificial Intelligence in PPC
How to Launch a PPC Campaign: Step-by-Step Guide
- 1. Initiate the Campaign
- 2. Choose the Target Audience
- 3. Get Down to Content Targeting
- 4. Match Pages with Ad Specifications
What Is PPC and Why It Is Important?
- Competition in the field: you may have to pay a higher fee to get a chance of winning over a competitor with the same score.
- A click-through rate: a likelihood that a viewer will click your advertisement. The more clicks you get, the higher the click-through rate becomes. It means a lower fee for placing an ad and a higher return on investment (ROI).
- The landing page experience: what happens after users click the ad, whether they get valuable and relevant information, can navigate the website, or use the on-site search.
Suppose the ad costs $2 per click but generates $50 orders. The company earns a lot in this case.
Every PPC advertising platform wants its consumers to be happy. So they give the best positions to advertisers who build relevant, intelligently targeted pay-per-click campaigns. They also charge such resources less, resulting in greater earnings for your company.
A web admin or search engine earns from PPC by displaying the ad and directing traffic to another website. The website owner who publishes the ad on another website, on the other side, gains visitors and sales. So it's a win-win situation where website owners can monetize their work, and businesses can show targeted ads and expand their reach.
PPC stands apart from SEO in various ways, including:
- It relies on regular payment. The visitors aren't organic as in the case of SEO but cost you money for every click.
- It works when you pay for it. The website doesn't build authority or advance in search results. You stop paying, and the website returns to its original place.
- It shows instant results. Unlike SEO, with the need to wait for about six months, PPC contributes to increased traffic from the first seconds after the ad appears.
- It doesn't require website optimization. SEO is about evaluating the website's performance and enhancing the user experience. Web admins should consider more than 200 Google ranking factors to appear as high on the list as possible. They are website speed, mobile friendliness, content quality, etc.
The ultimate goal of PPC is to gain visitors. PPC success depends on the number of viewers and the relevance and attractiveness of the ad copy.
There is no clear winner in the PPC vs. SEO battle as they pursue different goals. Business owners should invest in both channels to gain the maximum profit.
Google Ads and AdSense: How Does It Work?
First, you need an account on Google Ads — an advertising system based on auctions. There are auctions that are conducted in real-time; users input requests and determine the best-matching ad.
The choice depends on various factors. For example, the ad should contain quality and relevant keywords. Moreover, the amount the advertiser is ready to pay for the ad also matters. A short version of the process looks like this:
- The ad enters the auction.
- Google Ads considers your keywords, landing page, and expected click-through rate.
- The system assigns you a Quality Score from one to 10.
- Google Ads multiplies this score by your maximum bid to calculate the Ad Score.
- If your ad gets th e highest score, you see it in search results.
Another crucial tool for advertising is Google AdSense. It lets publishers join Google to provide advertising opportunities for Google Ads users. Bloggers can get paid for impressions (based on the total page views) and clicks.
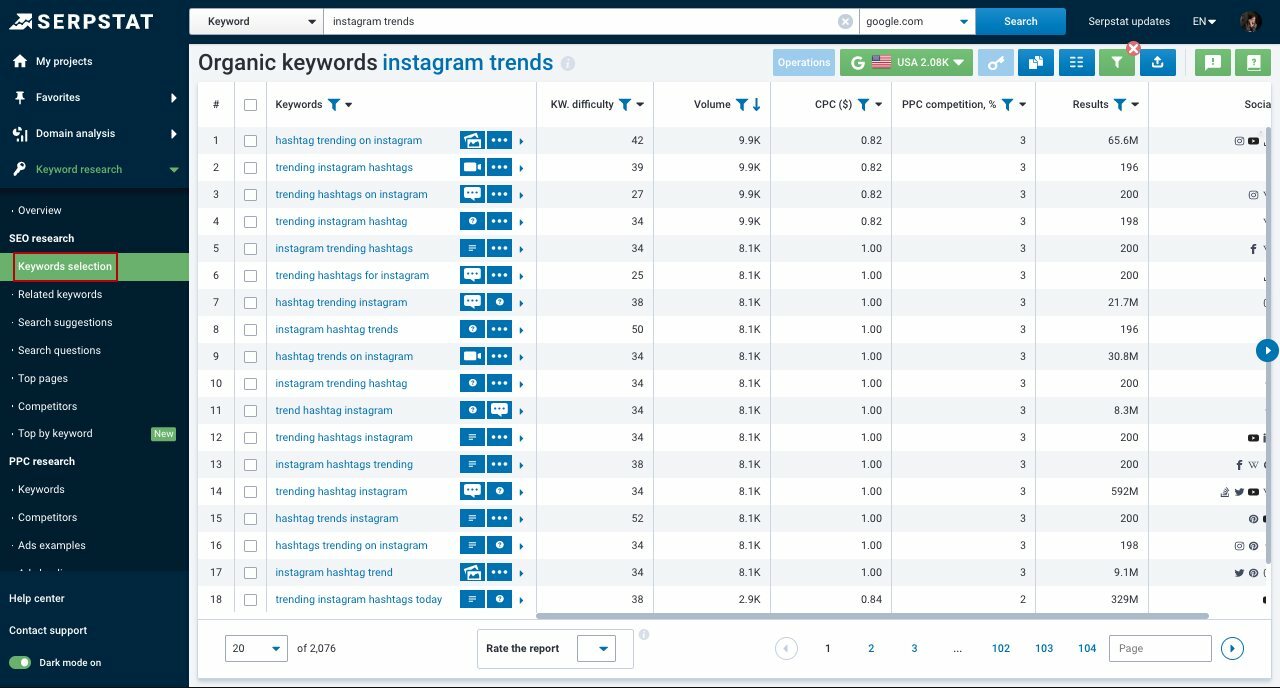
Simply go to the service's homepage, and enter your parent keyword into the search bar. Serpstat will then generate a list of related or similar keywords in organic and paid searches, along with their keyword difficulty, volume, Cost Per Click (CPC) value, and PPC competition.
It also has "Search Questions," where you can see what people are asking about a particular keyword, which is great to see how you can add new keywords and improve your PPC campaign.
Types of Contextual Advertising
Advertising systems analyze keywords on the page and match them with the ad. For example, you may read a travel blog and see an advertisement from a booking agency. Such ads may come in three forms:
- Texts with calls to action (CTA) and an in-built link;
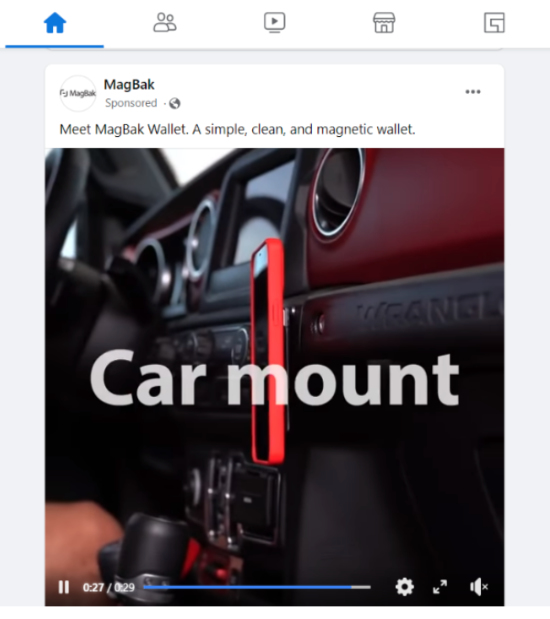
- Static images with a CTA button;
- Videos containing links to the website.
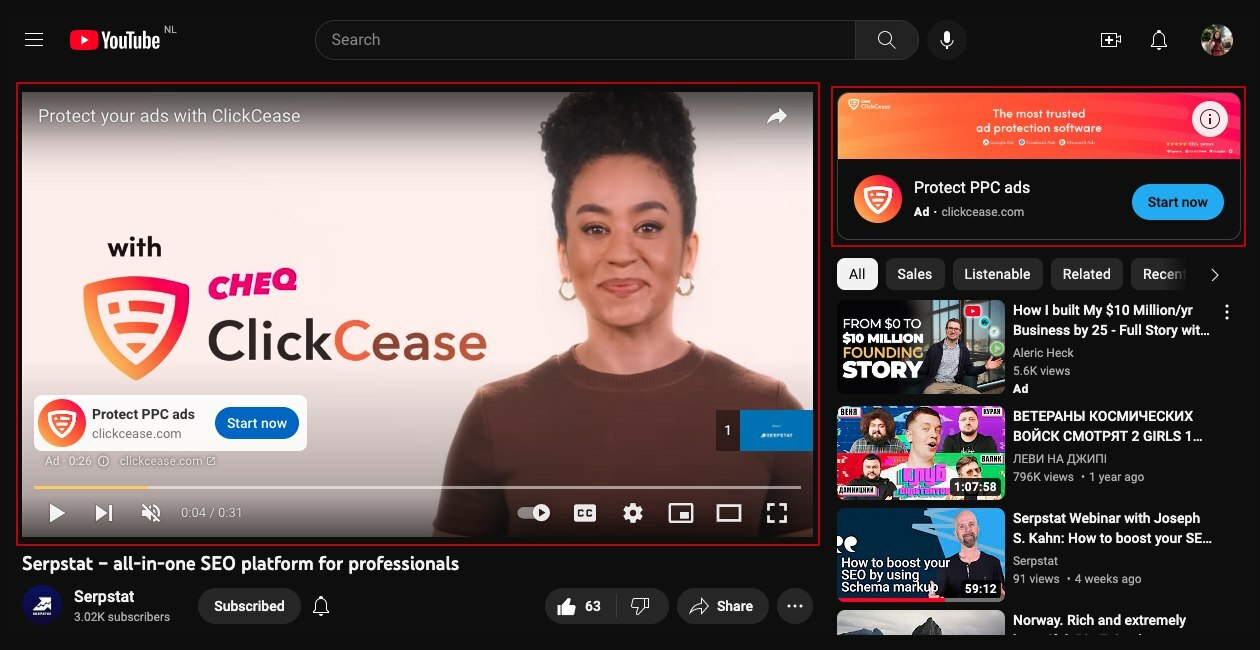
- Search engine ads. They appear right below the search bar after users click the “Search” button. Search engine ads are the first links viewers see before organic results. They are marked as an “Ad” for users to understand their purpose and contain a title, description, website link, and extensions.
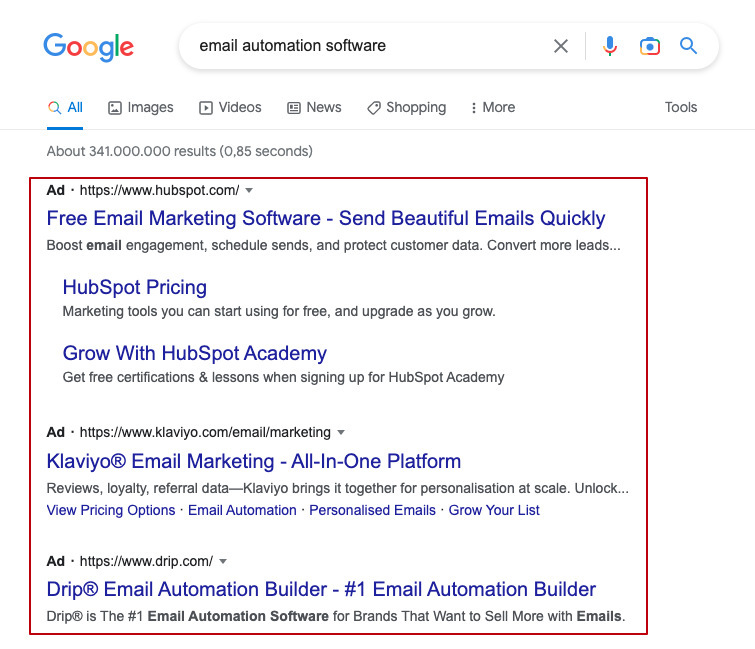
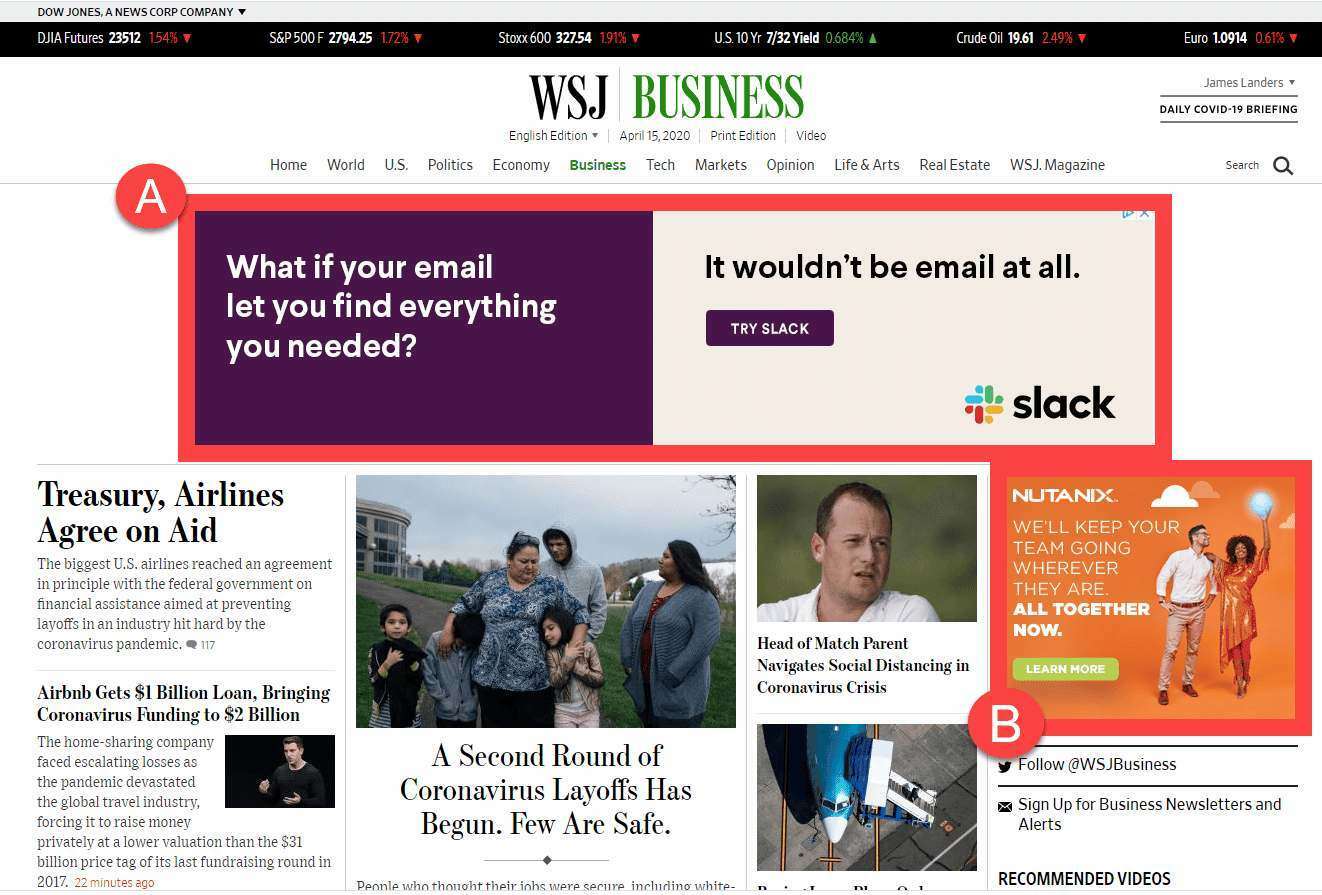
- Display ads. You can see them on websites, apps, and Google-owned resources like Gmail and YouTube. The most typical format of such ads is banners with product images or interactive elements.
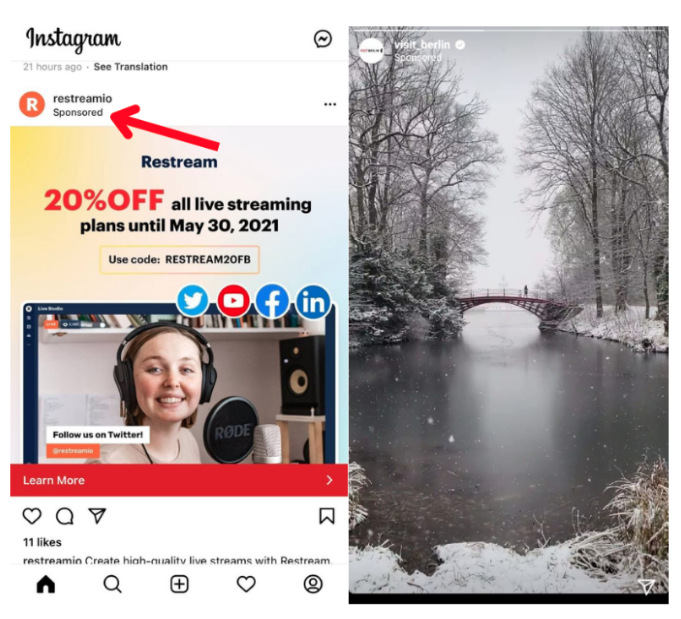
- Social media ads. Social media are a valuable source of potential customers. They let you display products to wider audiences and target groups based on their age, preferences, location, etc.
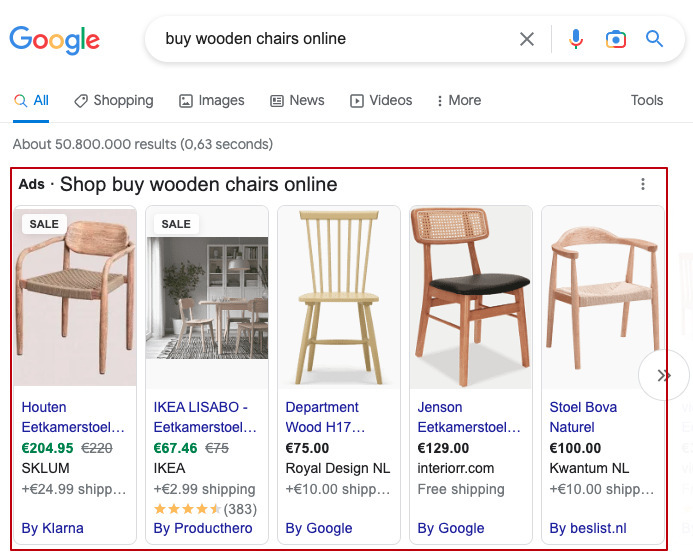
- Shopping ads. As the name suggests, you need to be an online retailer to use this type of advertising. Shopping ads appear in search engines in dedicated sections or above organic results and on third parties. They contain product images, price, name, and other attributes for higher engagement and CTR.
- Application ads. Such advertising promotes apps so you can find them in app markets, search engines, and third parties.
- In-game ads appear when the game is loading or when users play.
Contextual and Behavioral Advertising: Difference
- Contextual Advertising
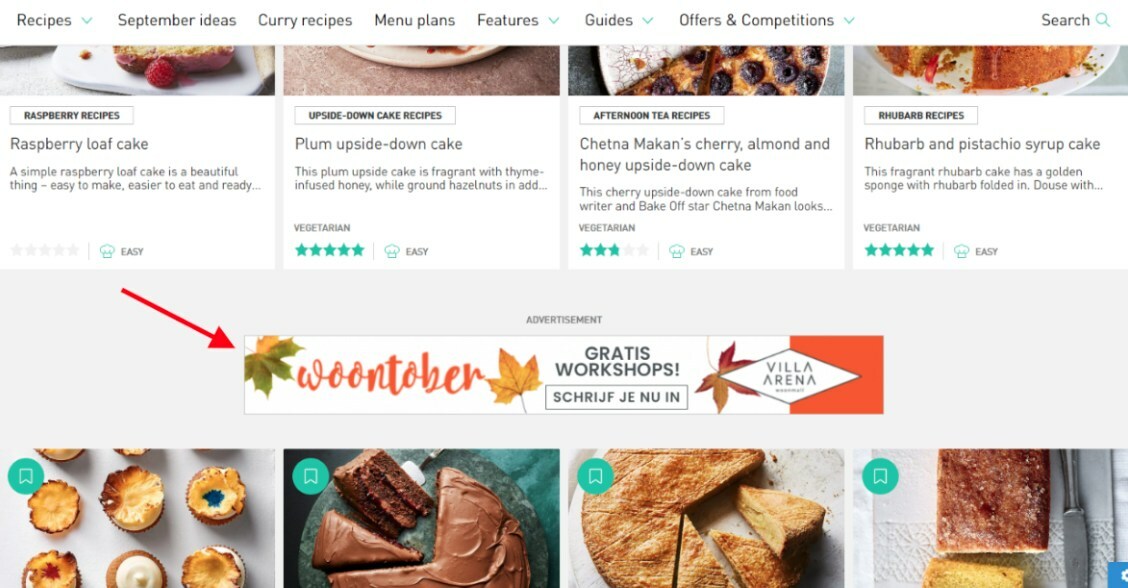
Suppose you browse cake recipes and see the ad for mixers. It’s probably contextual targeting, as making a cake requires you to have a mixer. So the ad viewers on this page are the best audience. The item and the content are related.
Below is an ample example of contextual advertising on the Delicious Magazine website. The page contains the cake recipes and the ad for a free interior workshop from the Villa ArenA website.
- Behavioral Advertising
A case in point is the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary website. If you see an advertisement for shoes you previously viewed or added to the cart, it’s behavioral retargeting.
The bottom line is that both promotion types have pros and cons. You may leverage both simultaneously to have the desired result without choosing one over the other
Importance of Context in Advertising
The user’s past behavior doesn’t always reflect the relevant information about their interests. Why? Because behavioral data expires and becomes outdated. Customers may lose interest in the viewed goods. Ever-changing customer demands require you to understand what interests them at this particular moment and cater to their needs with highly relevant and timely ads.
Constantly evolving laws may also present an issue for companies. Struggling with compliance regulations, public opinions about privacy, and policies about using cookies may slow down marketing activities or even lead to unnecessary spending. Context helps avoid problems with the lack of cookies.
According to the IDC report, failed data activities take up 44% of data specialists’ workdays worldwide. They have to leverage several tools, collecting, analyzing, and using data scattered around numerous documents and spreadsheets. So productivity suffers. These issues lead to advertisers changing their approaches to collecting data. One of them is contextual advertising. You don’t have to leverage customer clicks and views by relying on context.
Why Is PPC Gaining Popularity?
Google had planned to phase out third-party cookies in January 2020. However, it postponed the deadline. Recent information shows marketers won’t be allowed to follow customers online using third-party cookies after 2023.
People seek more privacy online. This fact also doesn’t help businesses promote their products and services effectively. How can they target the needed customer groups without knowing their preferences?
The potential end of cookies will make it impossible for marketers to target people across various websites. Privacy-first advertising also reduces the amount of available customer data. What’s the solution? Turn to contextual advertising.
As Brook Shepard, Forbes Council Member, writes in his article, “A return to a contextual advertising model can indeed be a good fit for advertisers when the privacy concerns are limiting the mechanics of some digital advertising tools.” This type of promotion is a better choice for advertisers willing to adapt to cookie-less environments and ever-changing consumer needs. While behavioral advertising may seem more profitable, contextual advertising doesn’t mean a decline in sales.
With all things considered, contextual advertising may be a tried-and-tested idea because:
- it proved its effectiveness;
- it protects user privacy;
- it saves marketers from breaking the law;
- it enables increased personalization without being intrusive.
Contextual Targeting in Advertising: Pros and Cons
Let’s dive deeper into the pros and cons of adopting contextual advertising in your company.
6 Pros of Contextual Advertising
Behavioral targeting relies on numerous data. What websites do consumers open? What buttons do they click? By enabling cookies, you can answer all these questions only when people allow it. However, consumers have become more reluctant to share their personal information by the day.
According to a recent Startpage survey, 72% of Americans are “very concerned” to “extremely concerned” about the use of their data. Contextual advertising works even with disabled cookies, providing ways for audience targeting and spending money wisely.
When tons of data enter the system, your data collection, analytical tools, and employees come into play. It means lots of time and resources that small and medium businesses may not have. That’s why behavioral targeting, with all its advantages, may not be a cost-effective solution for you. It’s not the case with contextual advertising.
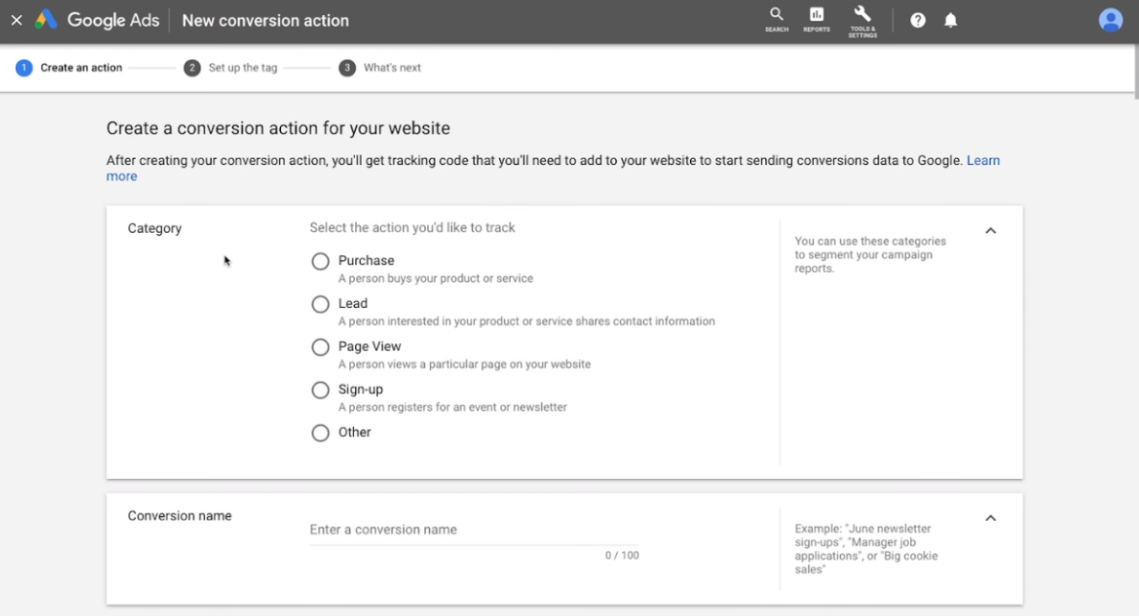
You don’t need special skills to create an ad in Google Ads. It has a user-friendly interface and even suggests keywords for the ad. All you need to do is to come up with an idea, title, and text, download an image, and set goals.
We come across hundreds of marketing messages every day. Banners, emails, and push notifications from brands compete for our attention and try to convert us into customers. That’s where you need personalization to stand out from the crowd.
Studies show that even small steps in this direction can significantly impact. A Forrester research states that immature personalization strategies boost sales by 6% and customer loyalty and engagement by 33%.
Showing the ad in the relevant context aims to assist users when they need it most. It’s much better than bombarding them with unnecessary offers.
Providing relevant content to users based on their location and weather is another way to boost conversions. While the weather may seem unimportant, you can learn much about a consumer’s behavior by looking at this information.
Suppose you notice an upcoming heat wave. Depending on your store, display ads for sunscreen, sprinkler systems, or ice cream. The same applies to how one forecast influences purchase behavior in different regions. Say, subtropical Florida and continental Minnesota.
You have complete control over the campaign to change any element:
- text and titles;
- target conditions;
- lists of positive and negative keywords (which keywords the system should exclude when choosing the ad).
These parameters determine the place of an advertisement. You can choose not to participate in a campaign or hide a specific ad whenever you want, for instance:
- You find it ineffective or confusing to users.
- There is no need to display it during this season.
On the contrary, it’s impossible to immediately change the situation in SEO or viral advertisements.
Brand reputation is as important as legal safety. When targeting consumers by their behavior, you may soon find your ads on undesirable places like an adult or extremist websites. Yes, you may exclude this website from your advertising, but some ads may sneak there. These ads may damage your reputation, showing you as a website with weak security policies.
Contextual advertising may prevent businesses from getting into these situations. It considers keywords and topics, giving you more leverage to place ads on the needed websites. As a result, users will be less likely to encounter your ads where they don’t anticipate (or desire) to view them and where you don’t want them to.
3 Cons of Contextual Advertising
Numerous clicks on the ad lead to increased website traffic.
Nevertheless, buying something on the website is still a long way to go. So you may spend money on clicks without any chance of getting the money back. Even more, competitors may click your ads, making you pay for these actions.
The price for ads varies across industries and seasons. For instance, you promote the same product throughout the year for one price. Let it be ice skates. The price for their ad will rise in winter due to the skyrocketing rates on this topic. And what if someone uses ad blockers? You may not reach the ideal customer in this case.
It may be hard to influence the ad position in the highly-competitive sphere. The more contenders you have, the more you need to pay to win the auction and display the ad. Even in the case of winning, the system may place the ad at the bottom of the page, on the second page, or wherever your potential customer may overlook it.
Plus, the abundance of ads may irritate users. It reduces the chance of a conversion.
Contextual advertising may not fit all businesses. For example, Google restricts the promotion of:
- alcoholic products in some countries;
- prescription drugs;
- tickets to events from uncertified sellers.
Similarly, contextual advertising may be too expensive or ineffective for small or local stores or specific products.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in PPC
Modern AI-based solutions with machine learning algorithms take this analysis to the next level. The AI-powered deep analysis tries to predict human behavior.
So, what would a brain do when manually choosing where to position an advertisement? The correct answer to this question helps ensure that your advertisement appears on time, is suitable, and interests users.
Additionally, a relevant ad gives customers a more tailored experience. It’s especially beneficial due to the increasing importance of personalization for conversions.
Statistics show that 71% of consumers want to receive a personalized experience. Not giving it to them disappoints 76% of shoppers. Chances are they’ll prefer to buy in another store that provides this opportunity.
How to Launch a PPC Campaign: Step-by-Step Guide
Let’s discuss setting up a contextual advertising campaign in Google Ads since Google AdSense is one of the most effective contextual advertising programs available. Here’s how it goes on the Google Display Network.
1. Initiate the Campaign
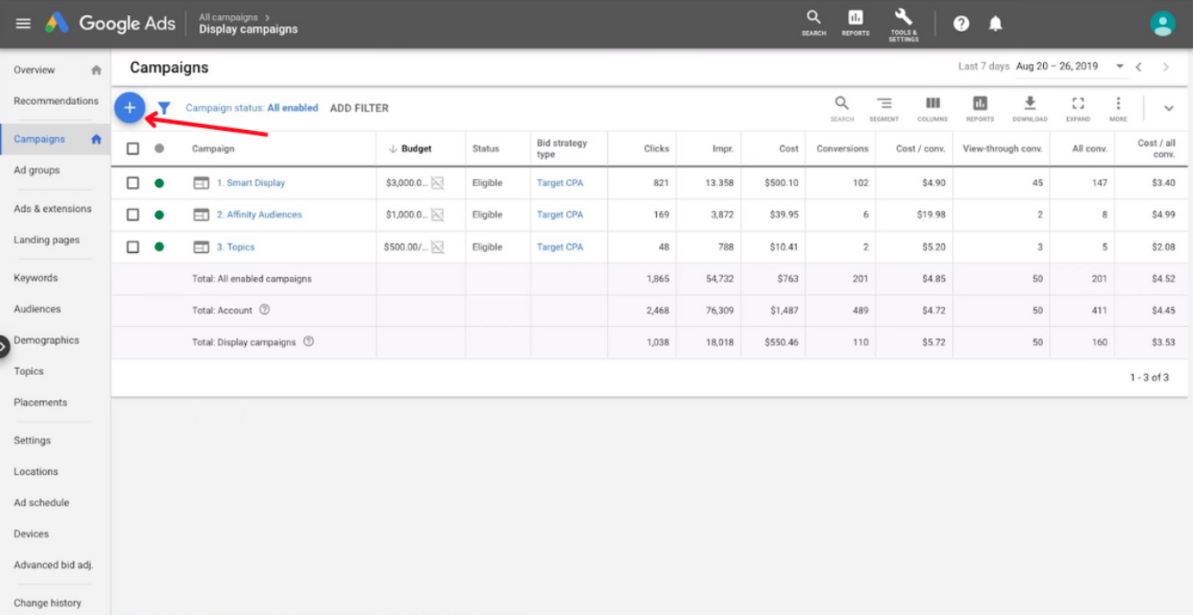
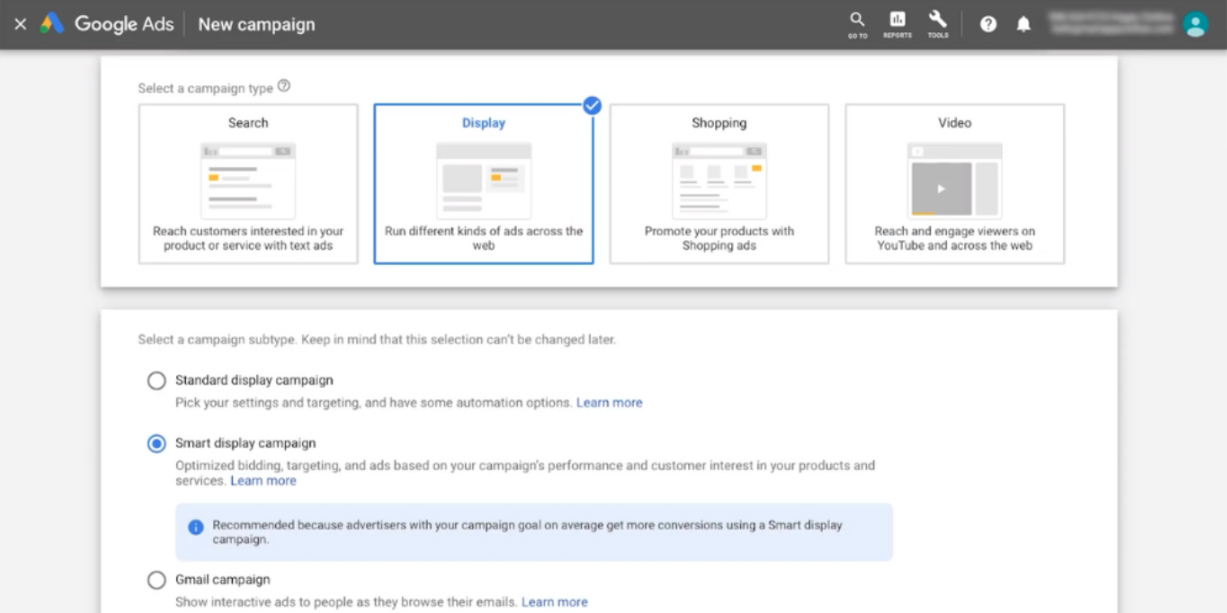
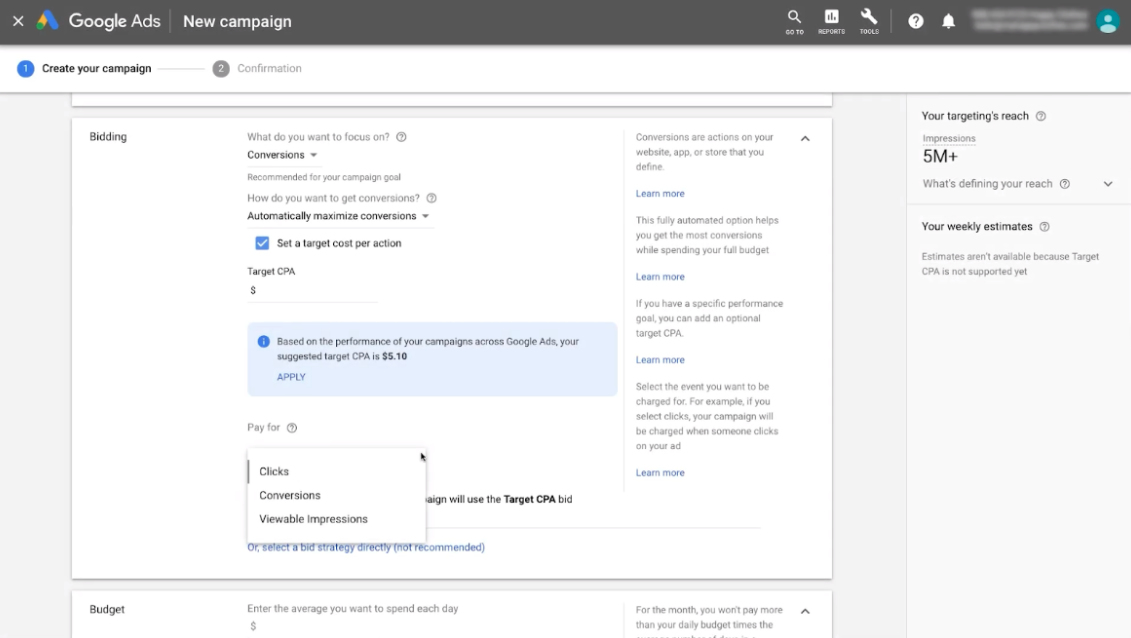
2. Choose the Target Audience
Select the groups and demographics after setting up your campaign to display the ad to them. You can choose how to build an audience based on several important factors, such as:
- affinity, which enables you to target individuals according to their long-term interests;
- intent, a sign that they are considering making a purchase;
- remarketing, which lets you target potential customers who have already interacted with your brand.
All these criteria apply to contextual advertising. But you must analyze what works best for your potential customers and fits the websites where the ad will appear. Consider demographics as well. For example, there are age-specific products you want to display to a particular group. The reason to exclude others is lower chances of converting them into purchasers. It may be an anti-age cream that customers younger than 40 shouldn’t see.
3. Get Down to Content Targeting
This box has three options: placements, topics, and keywords. Topics and keywords help networks evaluate web pages to determine the relevant content for display ads. You can combine all three ways of content targeting to ensure maximum relevance.
- Topics
Let’s assume you sell skincare products. Your case may include “beauty products” or “skincare” and become more narrowly focused, such as “moisturizers,” “cleansers,” “masks,” etc.
You can pick broad, narrow, or both categories. Combining two types can be a helpful strategy. General topics increase brand exposure, while more specialized ones show better conversions.
- Keywords
Google advises adding five to 50 keywords, including negative ones, to ensure the best matching of the ad with the website content. When selecting keywords, remember that there are options to specify the targeting strategy. You can target users interested in the keywords or display the ad within the content containing those keywords.
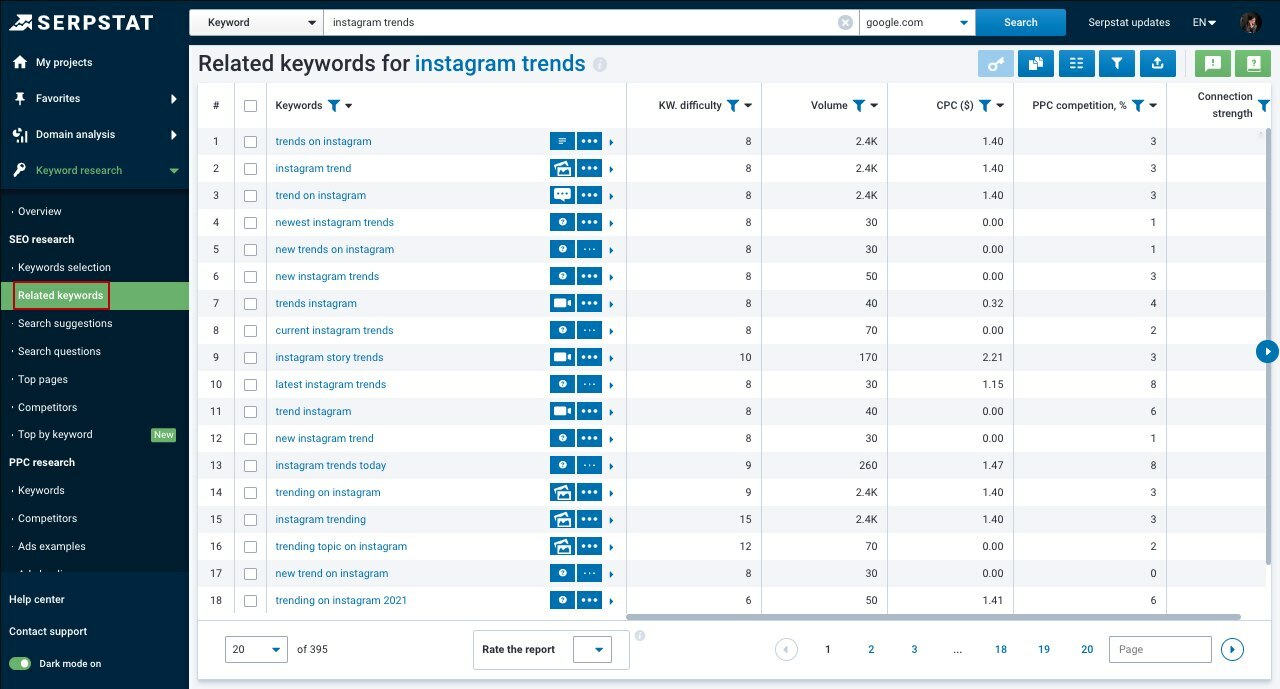
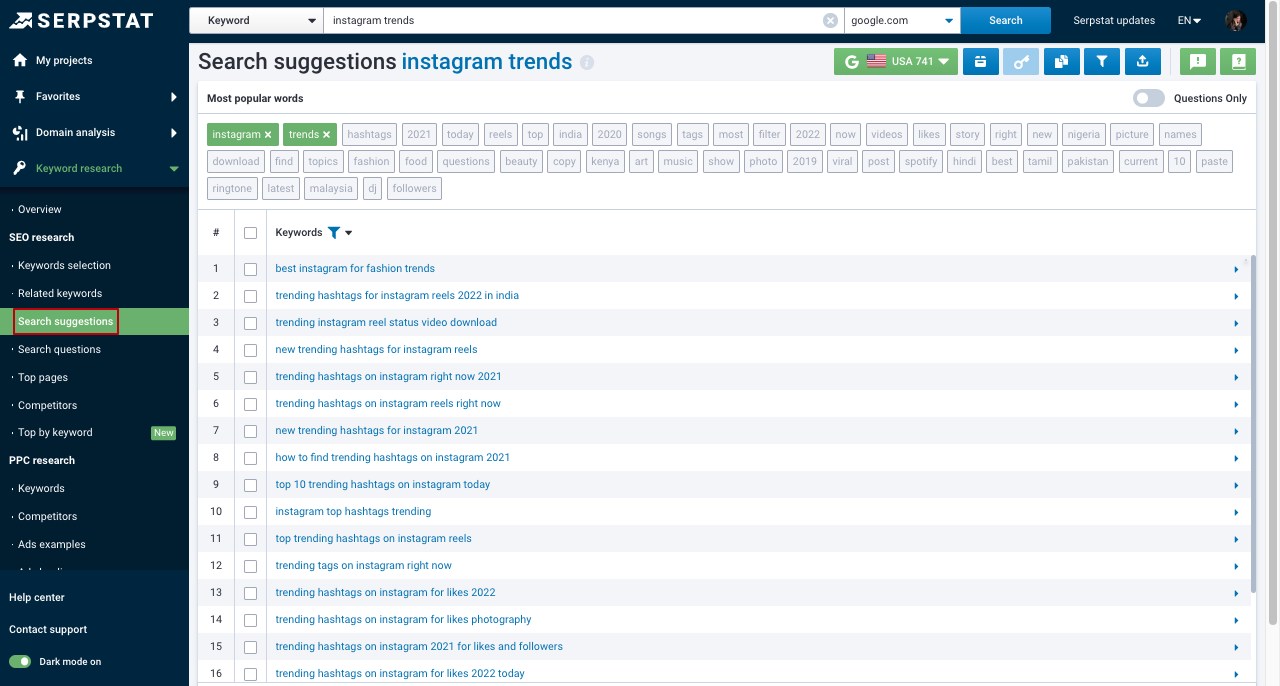
✔️ The "Related Keywords" report shows all search queries that are semantically related to the searched keyword. This is where you can check and use new variations of the queries.
✔️ The "Search Suggestions" report represents the queries offered to users under the search bar.
✔️ The "Search Questions" report is where you can see all question forms of search suggestions. These are questions that include a selected keyword that users are looking for an answer to.
- Placements
4. Match Pages with Ad Specifications
If you target topics and keywords in the same group, the latter is decisive for Google. The reason is that they narrow the topic, which may be too broad for choosing an ad.
However, you may specify whether the system should display the ad to a broad or specific reach. Broad reach dwells on your topic. Specific reach entails placing ads based on keywords and at least one topic. After the analysis, the system sets the ad contextually.
Key Takeaways
However, it may not be the case soon. As third-party cookies will no longer exist, advertisers must find other ways to target their potential customers. That’s where contextual advertising comes to the stage.
Contextual advertising is all about relevancy. It’s similar to ads in magazines where context matters. Systems analyze keywords, website topics, and other factors to choose the best-fit ad for this environment. As a result, the ad doesn’t seem intrusive and provides value to users. Plus, it doesn’t leverage personal data, being more secure for consumers.
We believe that contextual advertising is the future of advertising. While existing on the market for some time and being left out by some businesses, contextual advertising may soon come back.
Speed up your search marketing growth with Serpstat!
Keyword and backlink opportunities, competitors' online strategy, daily rankings and SEO-related issues.
A pack of tools for reducing your time on SEO tasks.
Discover More SEO Tools
Tools for Keywords
Keywords Research Tools – uncover untapped potential in your niche
Serpstat Features
SERP SEO Tool – the ultimate solution for website optimization
Keyword Difficulty Tool
Stay ahead of the competition and dominate your niche with our keywords difficulty tool
Check Page for SEO
On-page SEO checker – identify technical issues, optimize and drive more traffic to your website
Recommended posts
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.