FAQ
FAQ Serpstat
About Serpstat
Search analytics
1. Missing domain/URL data in the Domain Analysis/URL Analysis module.
Possible reasons:
• The domain/URL does not rank in the top 100 Google or top 50 Bing search results. Serpstat collects data only within this range.
• Keywords for which a website is ranking in the top 100 are not present in Serpstat database. Why? A special algorithm automatically adds keywords to the database, and the reason for their absence may be low keyword volume.
How to get more data for a domain/URL?
Write to our support chat, and we will help you add keywords on your topic to the Serpstat database. You can also do it yourself with the Batch Keyword Analysis tool.
2. There is no data for a keyword in the Keyword Research module.
We don't have the keyword in our database because the keyword may have a low volume. You can search for a keyword with a more general meaning and check out a list of related keywords. For example, instead of searching for "buy iphone 10 green near me", you can search for "buy iphone" and filter results by the words "green" AND / OR "near me."
If a keyword has a high volume but is absent in our database, write to our support chat. We will check the reason for its absence and help you add it to our database. You can also add new keywords yourself using the Batch Keyword Analysis tool.
The keyword list is all the keywords of a domain; they are the basis for creating a common structure and site pages. The core is words by which the user finds a specific page of the site, depending on the search query. Proper compilation of the keyword list will help the site get into the top search engine results.
There are different methods for collecting keyword list:
-Use the keyword list of a competitor;
-Collect keyword intersections of multiple competitors;
-Use keywords that competitors use in advertising;
-Receive similar keywords;
-Collect search suggestions.
Here are a few options for collecting semantics using Serpstat:
1. Go to the Website analysis / SEO analysis / Domain vs Domain section. In this report, you can compare up to 3 domains simultaneously, analyze the semantics, and, in particular, the unique keywords of competitors. This will allow you to look at what key phrases your competitors are moving forward and decide whether it is necessary to expand your semantic core with these words.
If you are interested in this particular niche, the same report is in the PPC (contextual advertising) section.
2. Using the section Keyword analysis / Content marketing / Search questions, you can find the most popular queries based on the keyword you are analyzing. Also, understand what topics can be covered on the site, responding to user requests on the Internet, thereby increasing traffic to your site.
3. The Website analysis section has an excellent report on Keywords in the SEO analysis section. You can look at the domain's ranked keywords, filter the report, and export it with your competitor's semantics.
4. If you use Keyword selection and Related Keyword reports in the Keyword research section, you can collect all synonyms and phrases that are close in meaning to the search word, which will help expand your domain's keyword list.
I want to share with you useful articles from our blog, there are some great examples and interesting information on this topic:
How to collect a semantic core for a site
How to find new keywords and expand semantics
How To Collect A Semantic Core For Contextual Advertising And Get Maximum Outreach
1. To analyze a list of keywords in bulk, use Keywords batch analysis.
Available parameters: Volume, Cost, Keywords Difficulty (KD), Competition in PPC, and the number of results.
Team and Agency plans: add up to 100 000 keywords in one project and create up to 20 projects.
Registered users: one project and ten keywords are available.
2. Another way for batch analysis is Serpstat API.
Subscription and credits
After paying for a pricing plan, your subscription will automatically be renewed according to the selected paid period (1 month or a year) until you cancel the subscription. Check the information about the payment history in the "Bills" section.
To cancel the subscription, go to "Settings" or "Bills" and turn off the Recurring billing. 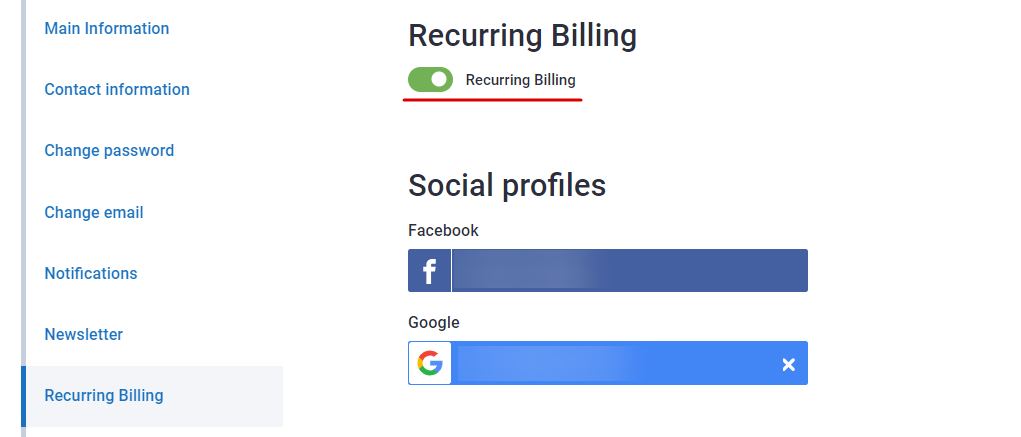
The subscription will be active until the end of the paid period and switch to a freemium version afterward.
Still have questions? Contact the tech support chat.
Possible reasons for payment errors:
1. Lack of card funds.
2. CVC/CVV is incorrect.
3. The card expiration date is invalid or wrong.
4. The debit card requires a PIN. Some debit cards require a PIN to be entered. Such cards can’t be used for online purchases.
5. Cross-border restrictions. There may be restrictions for using a card outside the country where it was issued.
6. A card can be used only for specific payment categories such as healthcare or travel.
7. This card has an online limit, or online transactions are not available for the card.
8. Timed out session. Some payment systems set time restrictions for the payment process. If you didn’t have enough time for an operation, please try again and finish it before the session expires.
*If you are not sure which restrictions are set for your card, please contact your bank to specify these details.
In case you face any difficulties during the payment process, don't hesitate to get in touch with us via online chat or at support@serpstat.com
To check your subscription credits, go to "My account".
The section contains information about your profile, pricing plan, the number of credits left, and the date of credits renewal.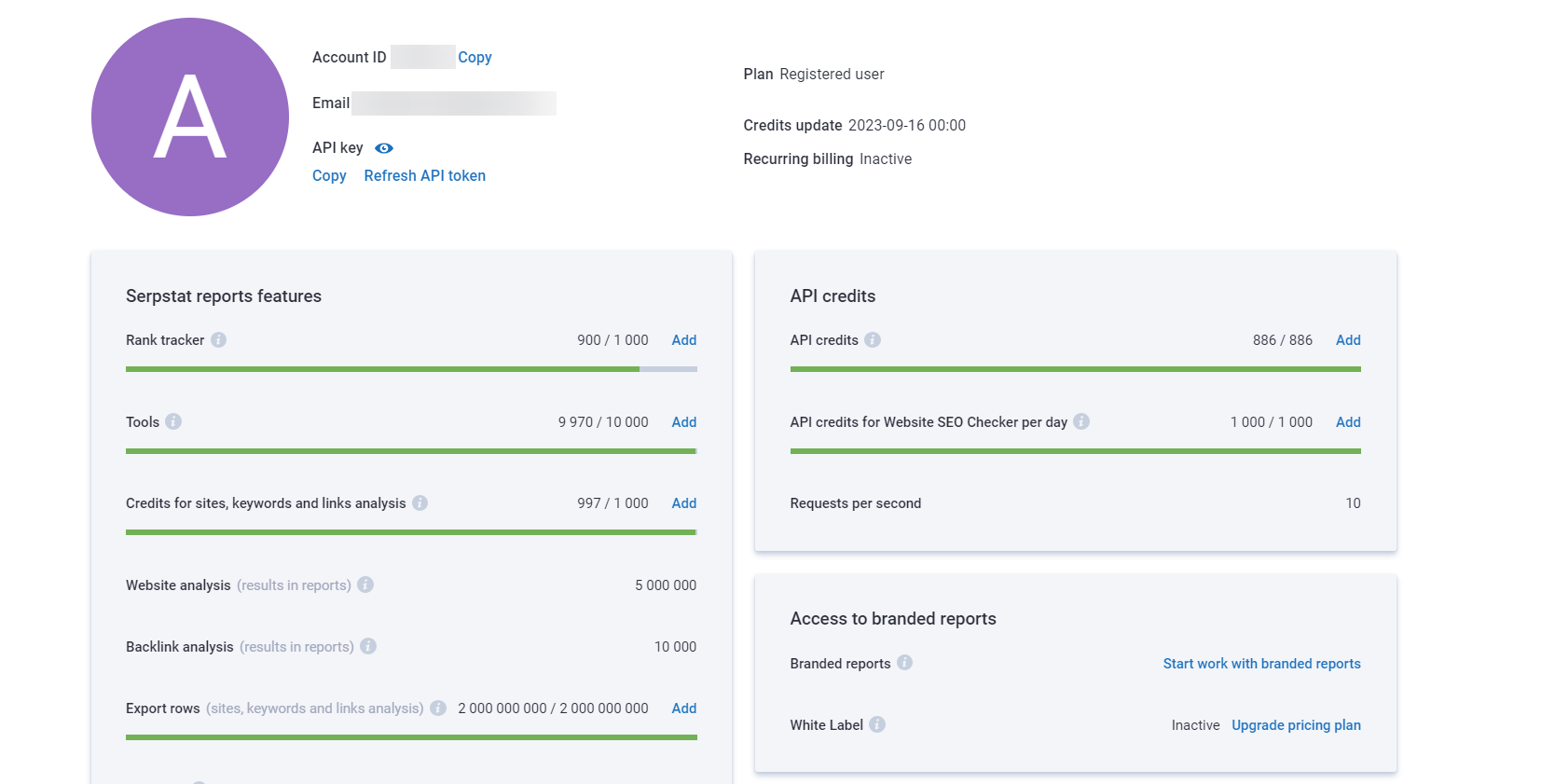
If you run out of credits, you have two options:
- Wait for the credits renewal.
- Buy additional credits.
1. The credits renewal date is indicated in My account.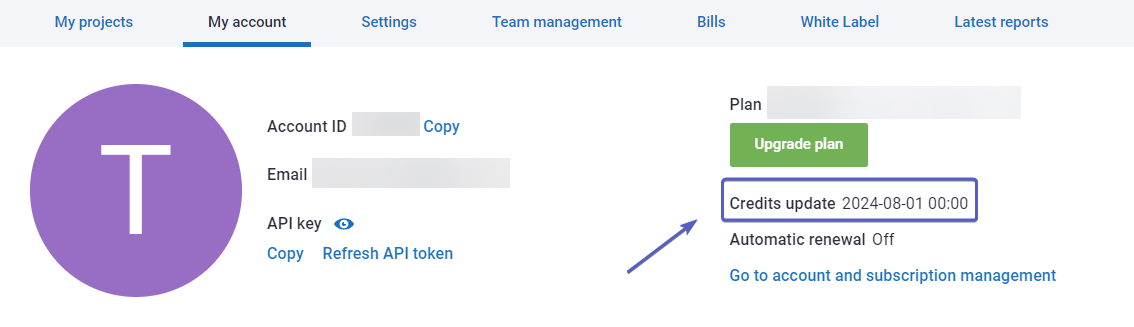
2. To buy additional credits, go to the My account and click the "Add" button near the credits number.
Or use the "Buy additional credits" button in the sidebar:
The support chat will be opened, where your manager will clarify the details.
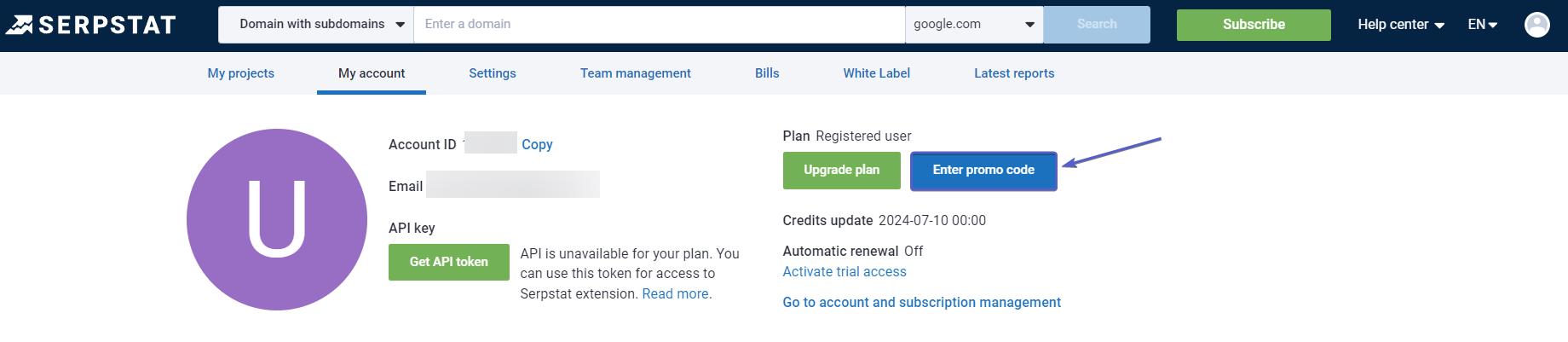
To activate the promo code, follow the instructions below:
1. Go to your "Profile".
2. Enter the coupon in the appropriate field:
Customer service
To delete your account:
1. Go to your Profile.
2. Then Security and delete your account manually or just contact us via online chat on our website.
Still have questions? Contact the tech support chat.
SERP crawling
The pricing starts with $0,001 per query for more than 1 000 000 queries per month, and $0,0013 per query if you have less than 1 000 000 queries per month.
To get the total price for the necessary number of queries, please use the pricing plan calculator on the SERP crawling page.
If you make a request in the SERP crawling tool to get data from a Google SERP, and this SERP has a block with common questions, this block is displayed in the report. The data is pulled into the report automatically and does not require additional actions. Use the questions in this block to create relevant content and meta tags.
1 keyword is a minimum number of keywords for parsing.
Keyword difficulty
Keyword clustering
Considering the formed cluster, you can see the following indicators:
1. Volume — how often users search a keyword per month.
2. Every keyword from a cluster has its connection strength. It provides a hint of how close that keyword is to the cluster's topic on a scale from 0 to 100%.
3. Homogeneity shows the semantic consistency of a cluster of a scale from 0 to 100%.
4. If you specified a domain while creating a project, we'll look at your website's pages and display the page which is the closest to the cluster's topic in the URL field. If you didn't input a domain, you can add a domain manually when launching text analysis.
5. To see the list of page-competitors in top-30 search results for keywords from a cluster you can click to the "Show metatop" button. The more relevant pages to the cluster’s topic will be ranked higher in the meta-top.
1. Development of the site structure.
Clustering helps to compose the structure of the site by breaking keywords from the semantic core into semantic groups.
2. Determination of target keywords to promote specific pages of the site.
You will determine the keywords by which you can promote the corresponding pages of your site.
3. Drawing up a technical assignment for a copywriter.
Clustering will automatically group keywords for articles into clusters that can be used for a technical assignment to a copywriter.
4. Separation of requests for commercial and informational types.
With the help of clustering, you will determine which keywords should be used on certain pages of the site. For example, commercial queries are on the homepage or category pages, and informational queries are for articles.
5. Semantic core analysis.
If there are too many information queries in the collected semantics for an online store, and there are few clusters with commercial queries, you need to expand the semantic core.
6. Search for unique keywords that are not included in any cluster.
Clustering allows you to define unique keywords that do not fall into any cluster.
You can get even more information about the tool in our article:)
There are 2 settings in the tool:
- cluster type;
- strength.
1. When choosing "Strong" cluster type, all keywords in one cluster will have the same URL in the top.
When choosing "Weak" cluster type, to combine all keywords into one cluster, it is sufficient to have a set of common URLs for at least one pair of keywords.
The number of common URLs for keywords in one strong or weak cluster types determines the parameters of the strength.
2. With "Weak" strength — 3 common URLs in the top, "Medium" — 8, "Strong" — 12.
The choice of the clustering mode depends on the keywords that you want to cluster.
If the keywords are from the same topic, and they are already related in meaning, then it is better to choose "hard" exact clustering with "Strong"+"Strong" parameters. Thus, only synonymous keywords will be combined into clusters.
If keywords are from different topics, then it is better to choose a softer clustering with "Weak"+"Weak" parameters. For example, let's say you want to cluster the collected semantics for a multi-item online store or online shop. In this case, there will not be many clusters, but they will be formed according to separate groups of goods or topics of the online magazine.
Selecting "Strong"+"Weak" parameters will give you more clusters than "Weak"+"Weak". In this case, according to the obtained clusters of keywords, it will be possible to promote individual pages or write articles.
Learn more about the strength and cluster type from our blog article.
Still have questions? Contact the tech support chat.
Each cluster has a drop-down menu:

1. Add keywords — opens a window where you can add some keywords to the existing cluster.
2. Delete keywords — deletes checked keywords from the cluster.
3. Move to unsorted — moves selected keywords to the "Unsorted keywords" directory.
4. Move keywords to... — moves keywords to the other cluster.
5. Delete cluster — deletes the cluster from your project.
Text analysis
For the Clustering or Text Analysis tools 1 keyword = 5 credits.
For example, 1000 credits allows you to cluster 200 keywords, i.e. 200 keywords * 5 credits = 1000 credits.
After Clustering for the same keywords, you can launch Text Analysis, which will require another 1000 credits.
Please note that credits for Clustering, Text analysis, Domains batch analysis and Keywords batch analysis are general per month.
Serpstat Text analysis divides the text space of pages into three main areas: Title, H1, Body.
Then text analysis is carried out and recommendations are provided on the use of keywords.
The general assessment of the page relevance to keywords from the cluster is carried out separately. The analysis process can be simplified as follows:
1. Serpstat compiles a list of keywords that appear in Title, H1, Body of the top 15 results for analyzed keywords.
2. The tool groups pages similar in topic (commercial with commercial, articles with articles and information materials, videos with videos, etc.)
3. Selects recommendations for the landing page and analyzes its relevance in relation to keywords.
4. When creating the Text analysis tool, we abandoned the recommendations on the number of occurrences of words and phrases in the page content, preferring the relative indicators of the importance of the phrase as a percentage.
The Text analysis can be performed in two ways:
- Вased on URL
- Цithout URL (when you need general recommendations prior to setting up a page).
1. The TA report based on URL contains:
- page’s relevance scores to keywords from a cluster;
- words that should be placed into Title, H1 and Body;
- keywords' indicators: LSI Rank, Chance; Status;
- suggestions on whether you need to increase/decrease the number of words in the Body section (recommendations are provided based on the average number of words on competitor pages).
2. Text analysis without URL will provide suggested keywords for Title, H1 and Body along with their LSI Rank, Chance and percentage ratio of a recommended word’s lemma to the total number of unique keywords on corresponding sections of pages from the metatop.

1. Proximity level — a score on a scale from 0 to 100% that displays how close a keyword is in terms of semantic similarity to the cluster topic.
2. Relevance — a relative score that shows how well your page is optimized for the keyword compared with top pages from the SERP. Hover over the color strip to view a minimum, average, and maximum relevance score for the keyword among your competitors and your relevance to the keyword as well.

1. Recommendation words — words suggested for your Title if you see a Not included mark under the Status column. We display words’ lemmas in recommended words, but you can use these words in any form tailored to your text intent.
2. LSI Rank — word’s importance for Title on a scale from 0 to 100%. It’s calculated as a ratio of the recommended word occurrences to occurrences of other words from the "bag of words” we collected from Titles of competitor's URLs.
3. Chance — the percentage of competitors from the analyzed group that has the word in the title.
4. Status — the column may have three values. Included - the word is present in the Title on the landing page. Not included - the page doesn’t have the word in its Title. Overspam — the word is used too many times in Title compared to other pages from the analyzed group; it’s worth removing some excessive word occurrences. If you didn’t specify the target URL, we’ll show the usage of the word’s lemma, in Title competitors’ pages in the percentage ratio of the overall number of unique words from their Titles - this feature will be useful for content marketers and copywriters.
API
The number of charged credits per request is 1 per row (the method removes as many limits as you get rows in the API response).
An example of a method response in the API Help.
Site audit
The page is closed to scanning or a specific user-agent in robots.txt settings.
1. Allow scanning for all crawlers:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
2. Disable scanning for all but the Serpstat robot:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /
User-agent: Serpstatbot
Allow: /
2.1 Select Serpstatbot as user-agent in the Audit settings.
3. Run an Audit without robots.txt.
Every website is like a live organism, and all live organisms are permanently changing. They grow, become older and disappear at some point of time. Keeping this metaphor in mind, let's move to the technical part.
These are the reasons of page number changes that are not related to Serpstat audit or any other auditing tool:
- the number of the pages on your website changed (increased or decreased) since the last crawl;
- your website had some technical issues during the crawling;
- your website is not ready for increased load;
- you use a kind of anti-DDoS protection mechanism that prohibits crawling;
- some pages do not have incoming links from the other pages of your website, so there is no way for the crawler to get there;
- there are some non-existent pages that are not yet dropped from the search results of search engines.
What you can do here is try one of these:
1. If you want exactly the same pages to be crawled every time, run the audit in “Page list” or “Sitemap” mode in Audit settings > Credits and speed > Scanning type. This will give you the maximum control over what should be crawled and what should not. But be sure to check that the pages in the list or in the sitemap stay the same.
2. If you want exactly the same number of crawled pages independent of what pages are crawled, set the number of pages to crawl in Audit settings > Credits and speed > Pages to scan.
3. Disable “Automatic speed control” and set the audit speed to the minimum in Audit settings > Credits and speed > Scanning speed. This will reduce the load and might help to get rid of 50X errors.
4. Explore the result of the site: search operator to understand what pages are indexed by the search engine.
This can be due to the fact that the Audit was completed by scanning a different number of pages. SDO score depends on the number of scanned pages. The more pages we scan the more issues we can find. The more issues we find the less SDO would be.
1. Determine why a different number of pages are being scanned.
2. Scan again.
We check for the presence of certain attributes, if at least one attribute from the list is not affixed — this will be flagged as an absence of markup.
1. schema.org
- itemscope
- itemprop
- itemtype
More information here.
2. Twitter Card
- twitter:card
More information here.
3. Open Graph
- meta property="og:title"
- meta property="og:type"
- meta property="og:url"
- meta property="og:image"
If the structured data of the site is written as JavaScript scripts, then you need to enable the "Scan pages for JavaScript" option so that the Audit will check them:
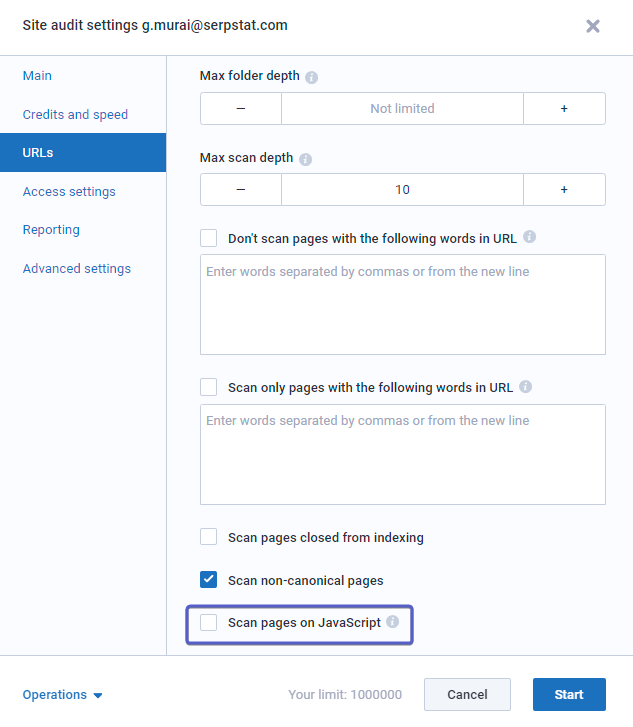
More information here.
Due to too many requests from the Audit, the user’s server considered this an attack and banned the IP addresses.
Your server might block the requests from Serpstat because of multiple requests. This is a common mechanism to prevent some malicious activity like DDoS attacks. There are two ways to handle this.
1. Reduce the scanning speed in the Audit settings.
2. Add Serpstat IP addresses to the whitelist.
2.1. You can find the complete list of IP addresses here.
2.2. Contact your webmaster or hosting provider to add the IP to the whitelist.
2.3. Use the instructions for adding IP addresses to whitelists from popular cloud hosting:
An audit ends on the host page if it does not contain links to other pages. This most often happens if the user's site is a SPA.
1. If you have a multi-page website, make sure that the source code of the host page contains links to other pages of the site.
2. If you have an SPA site, use the recommendations to optimize it.
Rank tracker
Manual update will help you update the key phrases you need at any time.
1. Go to the Keywords report.
2. Select the regions for which you want to withdraw positions.
3. Select the required keywords using the checkbox on the left (you can select all or several).
4. Click Update Positions.
Still have questions? Contact the tech support chat.
1. Positions dynamics.
On the graph, you can trace the entire history of the domain's transfer in search results.
2. Snippets.
Snippets for the tracked domain in SERP with the highest position. The color shows the change of the snippet.
Title, URL, Description are displayed in the snippet.
3. Keyword Storm.
The value of the storm in % shows how much the search engine results for a given keyword have changed in a selected search region.
The dynamics are shown next to the previous value. If the project had only one check, then the block with the storm is not displayed. The value can range from 0% to 100%.
0% - no domain has changed its position;
0−40% - normal change in position;
40% −80% - serious changes are occurring in the ranking algorithm.You need to check the storm for other keywords.
100% - none of the domains remained at their previous position.
Most likely, there was some kind of update in the search engine. It is necessary to monitor the news.

1. Filter by tag.
After sorting, all the data in the report will be built relative to the selected group of phrases using tags.

2. Filter by region.
If many regions have been added to the project, it is possible to check the domain positions for each of them separately

3. Filter by date.
In the report, you can view the entire history of the position, starting from the date of its creation.

4. Dropdown with competitors.
If you added competitors to the project in the search results and want to track their position by the added keywords, you can select them from the dropdown in the Keywords / Positions report.

1. The Tool has 1 search engine:
- Google.
2. 4 types of SERP:
- Desktop Organic
- Phone Organic
- Phone Paid
- Phone Paid
We check the context separately from the organics so as not to mix the results, since we usually show the best position.
3. Country.
The list of countries become available after selecting a search engine and depends on it.
The note:
There is a list of countries Google doesn’t work with https://support.google.com/google-ads/answer/6163740?hl=en
4. Region.
The list of regions is displayed after selecting a country and depending on it.
The region field is available only to Google and is not required.
The peculiarity of Google is that we can check the delivery of search region settings at different levels. Those. Both at the level of the country, region, and at the city level.
5. City.
The list of cities become available after selecting a region in the previous field (optional).
6. Language.
The list of languages becomes available after selecting a country.
The language is automatically set depending on the selected country as the official language or the most popular language, if several are used in the country. If there is no default language, then we put English.
Backlink analysis
- the text is equal to an empty line). It can be a text link that is only visible in the code, an image, a button"}" data-sheets-userformat="{"2":899,"3":{"1":0},"4":[null,2,16777215],"10":1,"11":4,"12":0}">We do not use such a concept. We have the concept of "Anchor without text": this is a link that does not have an anchor ( - the text is equal to an empty line). It can be a text link that is only visible in the code, an image, a button
Batch analysis
Number of domains * number of metrics = numbers of credits.
1 metric = 1 credit
Metrics for analysis are parameters chosen in settings, such as keywords, visibility, Domain rank, ads, backlinks, etc.
Example: 1 domain * 20 metrics for analysis (9 metrics for analytics + 11 metrics for links) * 1 base = 20 credits.
Regions are not considered for Links analysis.
Analysis of 2 bases = 40 credits: 11 credits for link analysis + 9 credits for domain analysis * 2 bases.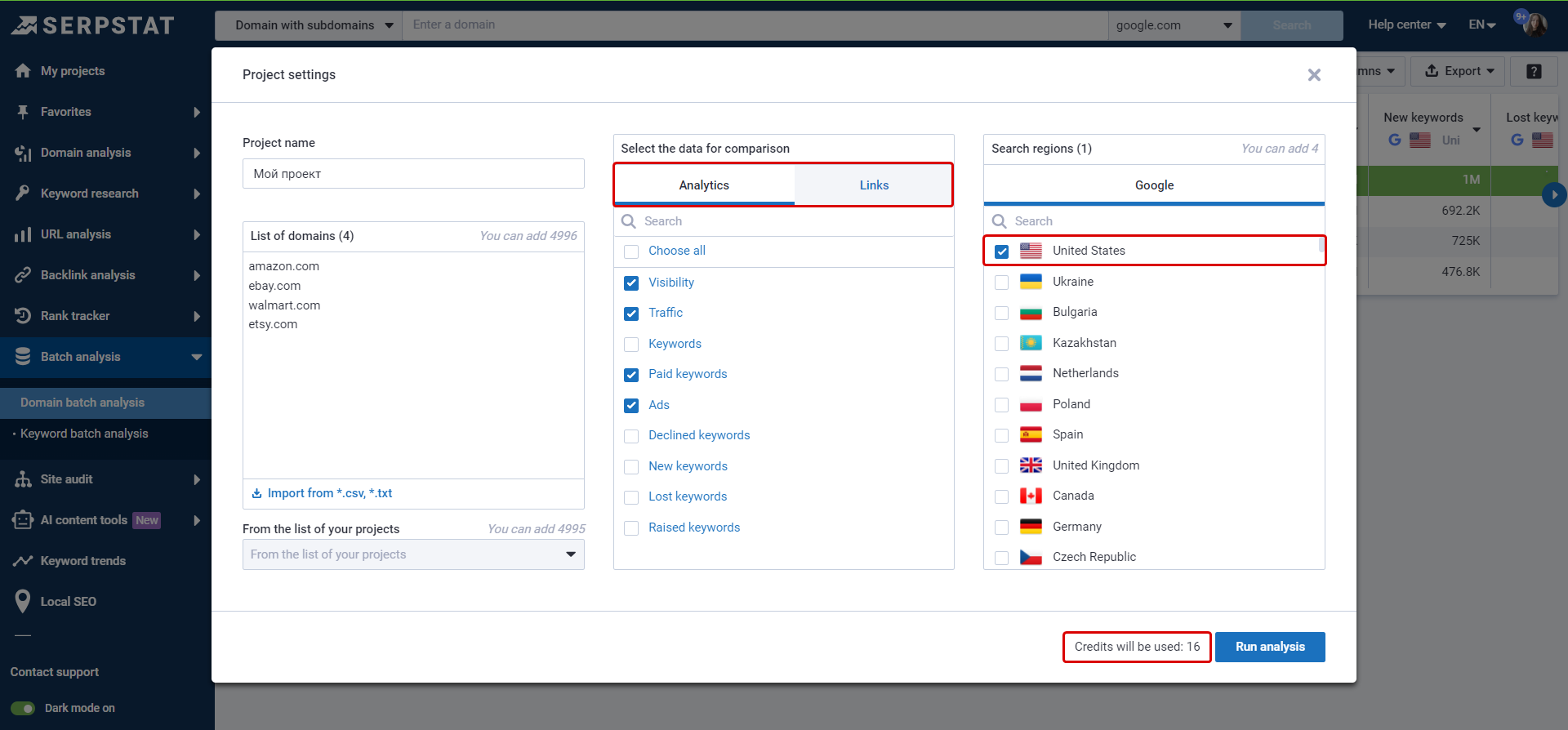
Check the credits for Domain batch analysis in your account.
Please note: credits for Keywords batch analysis, Domains batch analysis, Clustering, Text analysis, and AI content tools are shared.
Features launch stages
Export
Free trial
When you start the free trial, you enter credit cards for verification purposes. Verification charges $1 and returns it to your account in 5–30 minutes.

