Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
Keyword Clustering: Algorithms and Approaches of Popular SEO Tools

Let’s dive deeper inside the milestones of clustering, not only from the SEO point of view, but also from machine learning theory.
Clustering algorithms in machine learning
- General mathematical approaches
- Approaches based on artificial intelligence systems
- Logical approach
- Graph-theoretic approach
Clustering algorithms of popular SEO tools
- Serpstat
- Cluster army
- Spy fu
- Contadu
- Umbrellum
- Simple SEO tool
- SEO Scout
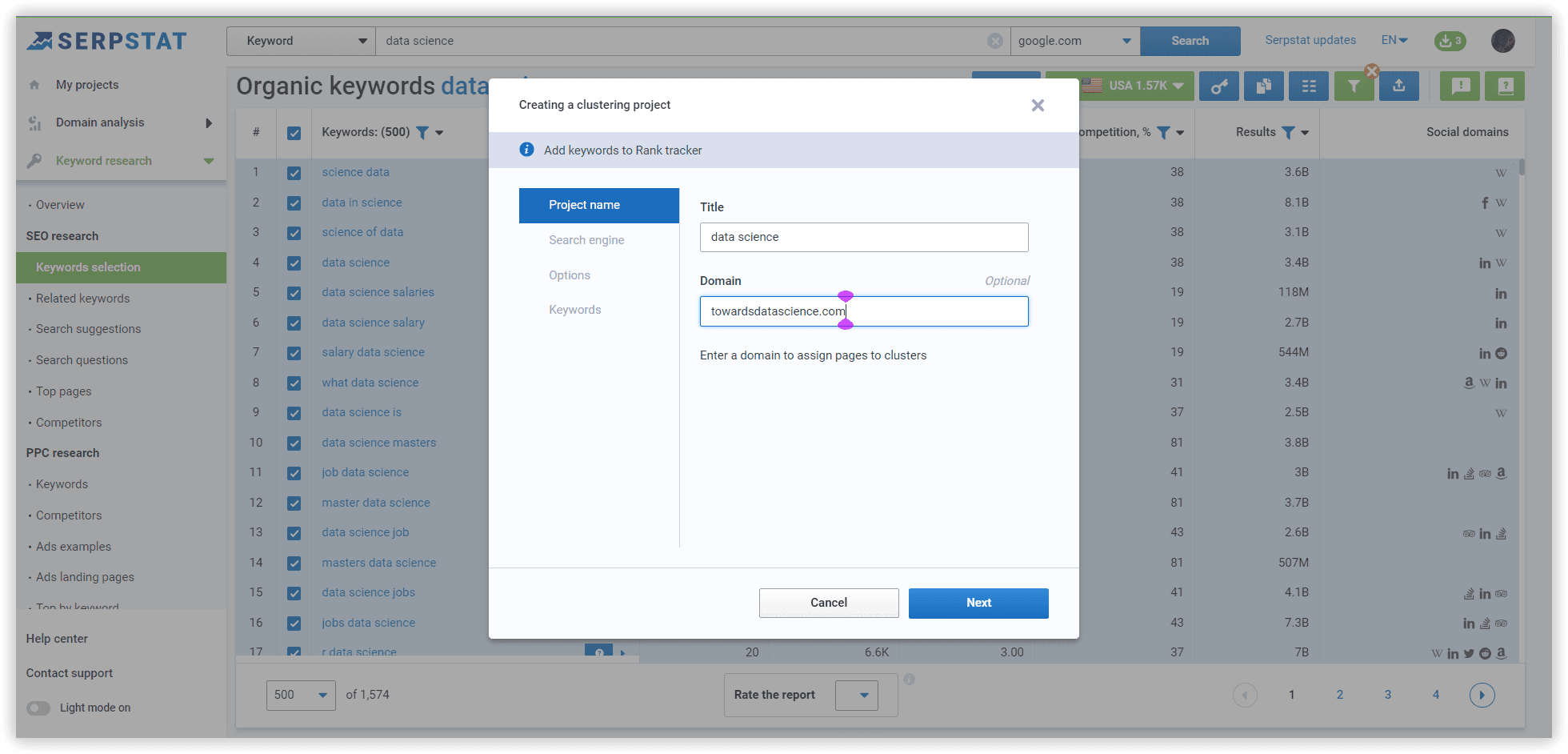
- How to collect data for your project in Clustering using Serpstat?
- The basics of clustering setup explained
Features of Serpstat Clustering
Use-case from author’s practice
Conclusions
What is keyword clustering, and what is it for in SEO?
Your SEO content strategy can be elevated by using keyword clusters, which make your site more Google-friendly. Clustering is the process of dividing a set of objects into tight groups called clusters. The similar objects should fall into the same group, at the same time, the objects in different groups should be as different as possible. Clustering helps you to prioritize collected keywords and filter the irrelevant for better ranking.
In 2013 Google rolled out its Hummingbird update and the algorithm started focusing on phrases instead of single keywords, it helped to bring meaning to the words that people were using in their queries. Further, in 2015 the RankBrain update was presented that was able to define themes of search queries and find multiple similar keywords.
Building your clusters also gives more opportunities to add internal links to your website, increasing users' engagement on your website. Internal links help Google understand which website pages are the most important.
If your business has multiple products or areas of expertise, you will be able to build out more clusters on your website.
If you only sell one core product or service, the number of keyword clusters you identify will be fewer. Still, exploring your primary topic areas with lots of helpful content can help you outrank your rivals in less time.
One of the key tenets to doing impactful digital analysis is understanding what your visitors are trying to accomplish. One of the easiest methods to do this is by analyzing the words your visitors use to arrive on site (search keywords) and what words they are using while on the site (on-site search).
There are two major types of keyword clustering in SEO:
Why should you use automated keyword clustering?
- Clustering makes it possible to combine phrases by meaning and conduct a deeper analysis of your keyword pool.
- By using keyword clustering, you can create a content plan that organizes over a series of pages the most relevant phrases to promote different parts of your site.
- Clustering helps better understand user intent. Topic-focused SEO offers a more thorough response to users: putting similar phrases together, you target user intent instead of a single keyword coverage.
- Clusters you received, as a result, will help you determine how the potential segments of your content should be connected. These enable you to assess semantic relationships between your pages in the general site architecture.
- Keyword clustering can allow you to create more effective landing pages to have a positive impact on generating traffic, leads, and CTR in your campaigns.
- You can organize the structure of your website from scratch using a clustering hierarchy. Clustering helps to improve your overall website structure and UX, making it more navigable for your visitors.
- Keywords from the same cluster can be placed on the appropriate page without risks of traffic cannibalization or mixed content on your website.
- Non-clustered keywords can be used for other purposes.
- Thanks to keyword grouping, you can boost your site’s visibility and authority, both for users and search engines.
- Automated keyword clustering gives you all the above benefits quickly and efficiently.
There are different approaches to clustering methodology. For example, using "soft" clustering, some tools pick the keyword with the most significant search volume and compare the TOP search results shown for the keyword with the top results shown for the other keywords based on the number of corresponding URLs within the search engine.
When the number of common URLs is equal to the level of keyword grouping accuracy, the key phrases will be grouped. With such approaches, clusters of keywords are linked but not necessarily related.
There is also the “hard clustering” method, which requires the connection between all elements within the cluster. The downside of this algorithm is that it creates an excessive number of clusters that could be merged into larger ones. High-accuracy hard clustering might ignore the similarities between several groups. So semantically close keywords you got as separate clusters might be united as one more significant cluster. The intelligent hierarchical clustering combines clusters into a supercluster.
In case of "wide" keywords, binding to some group will occur randomly in the event of a collision. And in theory, it may turn out that the same set of keywords will be divided into different clusters with each new start of clustering.
Manual clustering will require you to break each keyword into terms, define their intent, and make lists of keywords based on the parameters you need. The problem is still in phrases with different intents - this is especially true for homonyms or words with a broad meaning.
There are also a lot of words that have changed their intent. The good examples of such keywords, changes depending on personified results or country-specific SERPs are:
- “Tesla”;
- “Corona” (as a virus, lager beer, or software);
- “Kafka” (as a writer and event streaming platform);
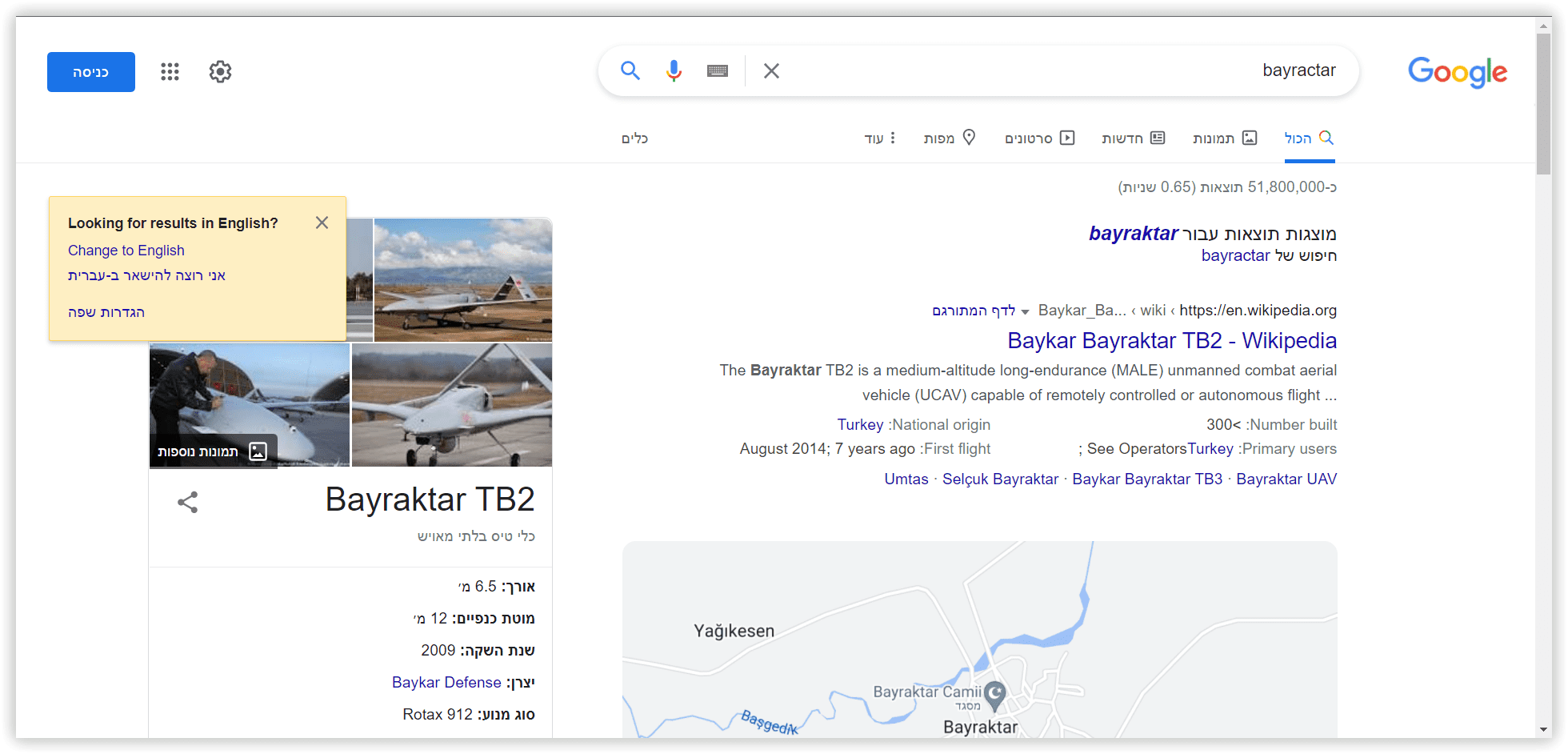
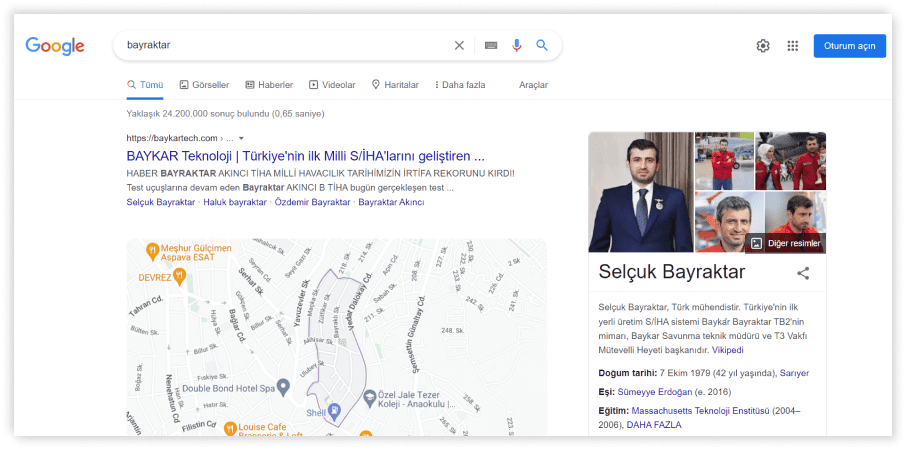
- “Bayraktar” (as the famous tactical drones and Turkish surname, which means “Standard-bearer”).
The features in interactions between computers and human language are studied in the science field called Natural language processing (NLP). At the same time, AI (Artificial Intelligence) — is concerned with giving computers the ability to understand the text and spoken words in much the same way human beings can. This knowledge helps to assess the way programs and computers can process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. Google made a historical shift in understanding the intent of users' search in this unit with BERT (which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, an algorithm that includes a method of pre-training language expressions).
NLP combines computational linguistics with statistical, machine learning, and deep learning models. With Apple's introduction of Siri as part of the iOS operating system, this technology was fully represented. Other examples of NLP at work are: Alexa, and Google Home devices, Autocomplete in Google Search and Gmail, Language translation software, Spell and grammar check, Spam filters, Search, Chatbots.
Clustering algorithms in machine learning
In solving classification problems, for example, to sort spam into a separate email folder, these algorithms are used to accurately categorize test data. Linear classifiers, support vector machines, decision trees, and random forest are all common classification algorithms. Regression data models help you predict numbers based on point data, such as future sales revenue.
In the context of machine learning, clustering belongs to unsupervised learning, which infers a rule to describe hidden patterns in unlabeled data.
In unsupervised learning, machine learning algorithms are used to analyze and group raw datasets. These algorithms identify patterns in the data without human intervention. Unsupervised learning models are built to detect anomalies, improve recommendation services, predict customer behavior, etc.
Unsupervised learning models are used to perform three main tasks - clustering, association, and dimensionality reduction. Clustering is a data mining technique to group unlabeled data based on their similarities and differences. This method is suitable for market segmentation, image compression, etc. Association is an unsupervised learning method that uses certain rules to identify relationships between variables and a given set of data. These methods are often used to analyze shopping behavior, create recommendation services and select products in the "To buy with" categories. Dimensionality reduction is a technique that is used when there are too many features (or dimensions) in a certain data set. This technique is frequently used in the data preprocessing phase, to remove noise from visual data to improve image quality.
The goal of unsupervised learning is to get useful information from a huge amount of new data without corrections. In supervised learning, the algorithm "learns" by making predictions based on the training dataset and adjusting them until it gets the correct answer. Although supervised learning models are usually more accurate than unsupervised, they require direct human intervention and accurate data labeling. For example, a supervised learning model can predict how long it will take to get to work depending on the time of day, weather conditions, and so on.
Unsupervised learning requires powerful tools to deal with large amounts of unclassified data. These models independently learn the internal structure of unlabeled data. However, they still require little human intervention to validate the output variables. For example, an unsupervised learning model might reveal that online shoppers often buy groups of products at the same time, but a data scientist would need to check whether it makes sense for a recommendation service to group all of these products into one group.
There is no generally accepted classification of clustering methods, but several groups of approaches can be distinguished (some ways can be attributed to several conditional groups at once, there are many methods, and methodologically, they are significantly different):
General mathematical approaches
Using this algorithm, please note that you have to set the approximate quantity of needed clusters. You can try to convert your keywords data to vectors to research how this approach works with Google ranking.
K-means with Serpstat dataset (Strength and Homogeneity, 10 clusters):
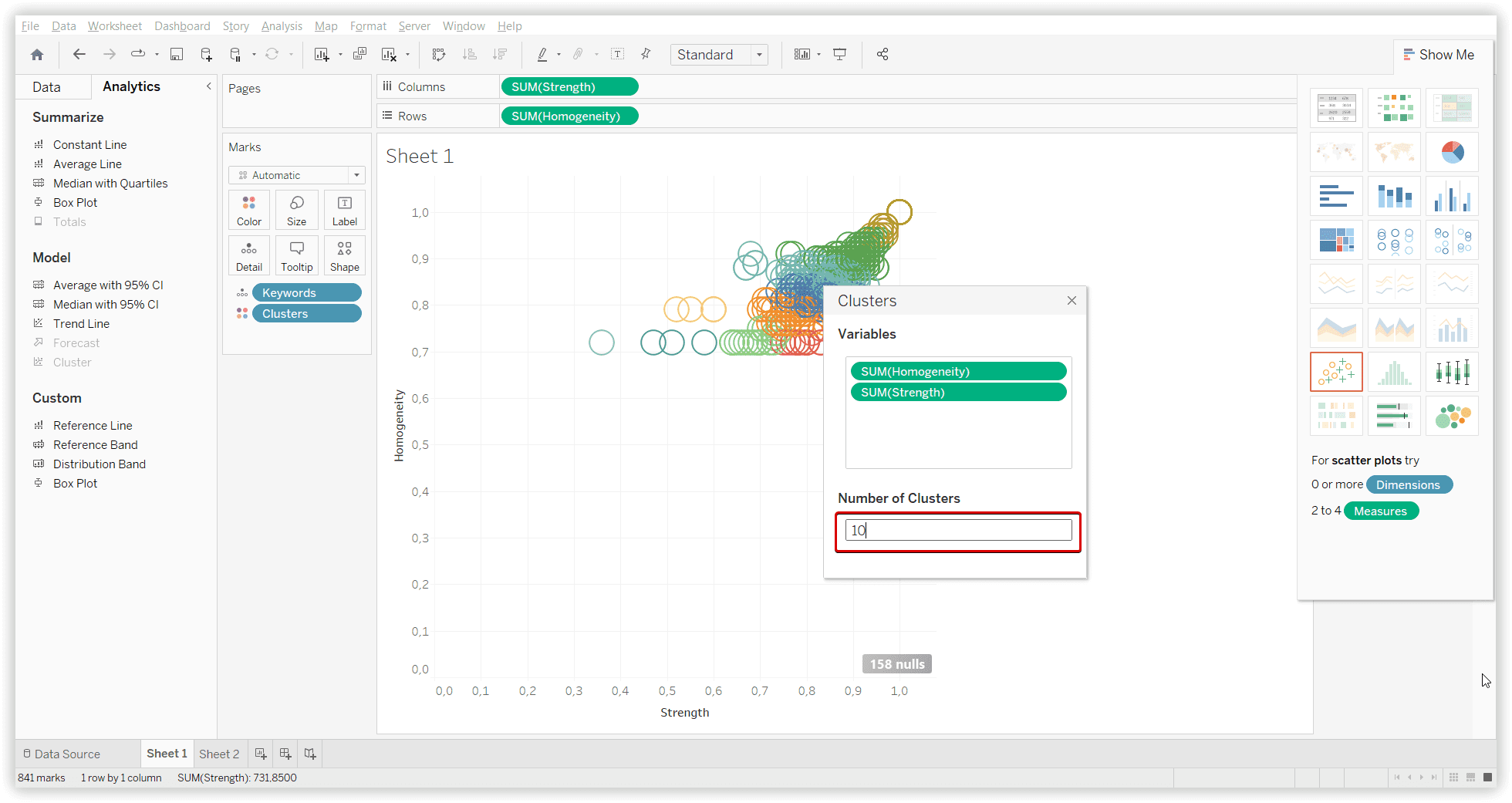
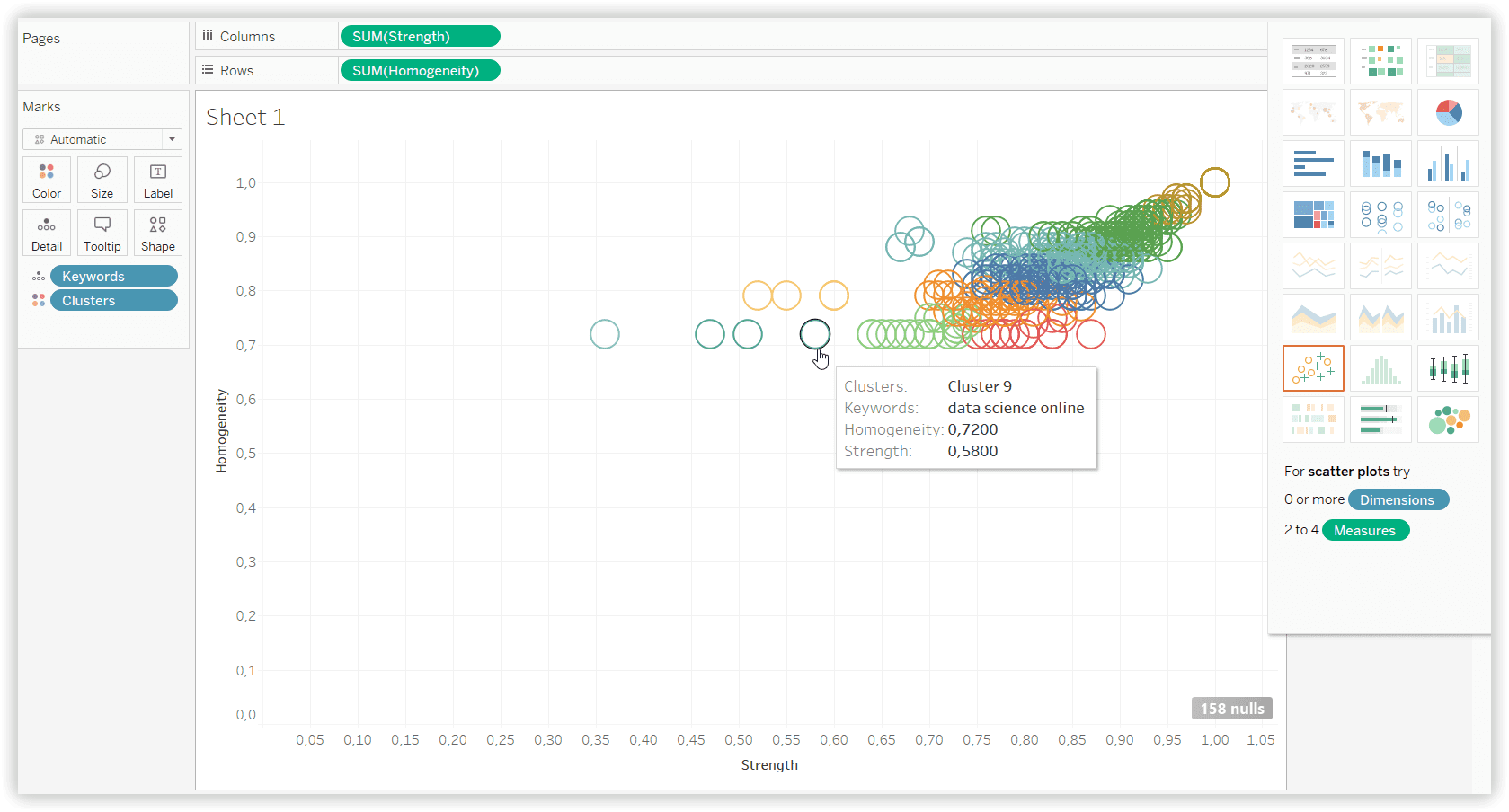
The median is most often used to measure average income because it represents the middle point.
Approaches based on artificial intelligence systems
- Fuzzy clustering method (C-means) Fuzzy C-means create k numbers of clusters and then assign each data to each cluster, but there is a factor that defines how strongly the data belong to that cluster.
- Kohonen networks. Kohonen's networks are one of the most basic self-organizing neural networks. Such self-organizing systems offer new possibilities — adaptation to previously unknown input data. It seems the most natural way of learning in our brains when no patterns are defined. Instead, the patterns emerge during the learning process, combined with regular practice.
- Genetic algorithm (GA-clustering) A Genetic Algorithm (GA) is a search-based optimization technique based on Genetics and Natural Selection principles. It is frequently used to find optimal or near-optimal solutions to complex problems that otherwise would take a lifetime.
Logical approach
In this case, the dendrogram shows which keywords are most similar by their own clusters, which began with two general groups and broke down into smaller clusters with the most similar keywords.
The visualization of such an approach you can find in Keyword Cupid.
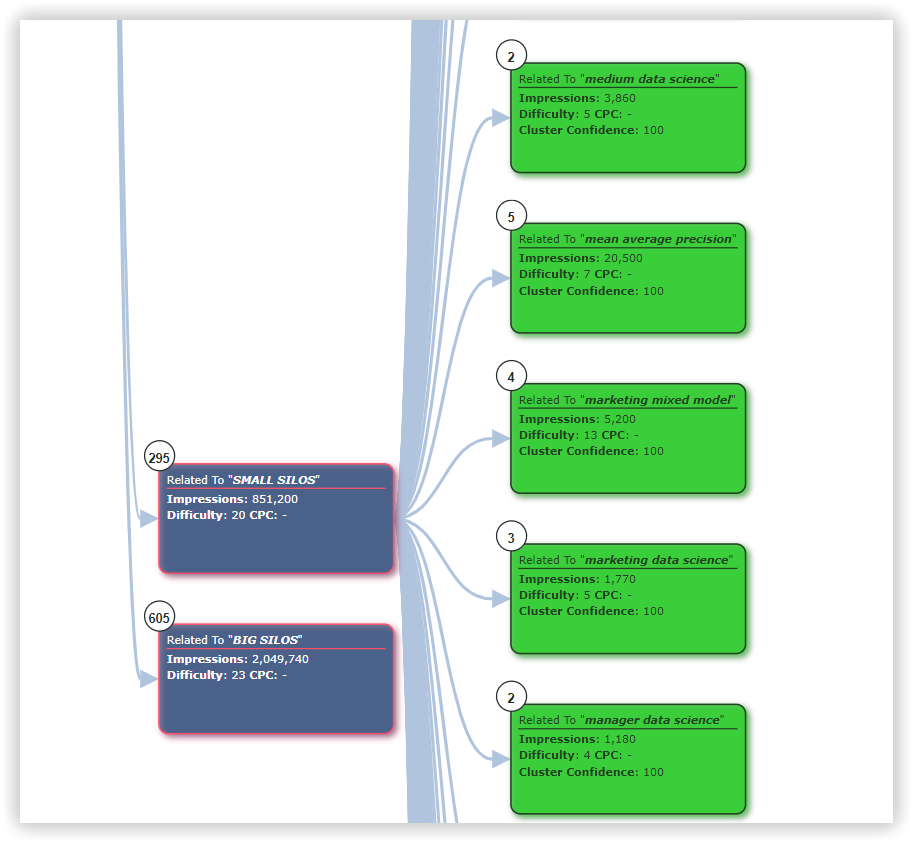
Graph-theoretic approach
Hierarchical clustering (also graph clustering algorithms and hierarchical cluster analysis) is a set of data ordering algorithms to create a hierarchy of nested clusters. The hierarchical approach assumes the presence of nested groups (clusters of different draw orders). Heuristic clustering involves separating data into groups based on some measure of similarity, determining how they're alike and different, and further narrowing them down.The second method, on the opposite, goes from unique objects and consecutively combines this data into larger groups.
Clustering algorithms of popular SEO tools
Serpstat
We build an Adjacency matrix, according to the quantity of common URLs. Let’s say, keyword “nettop” will have the same quantity of common URLs as misspelled “netope”, it might be 12, but two keywords “nettop” and “Mac Mini” will have only 5 common URLs from the analyzed top 30 SERP results.
As a next step, we transform the matrix so that relative numerical values are close together. If we assign each numerical value a color, we have the classic Czekanowski diagram.
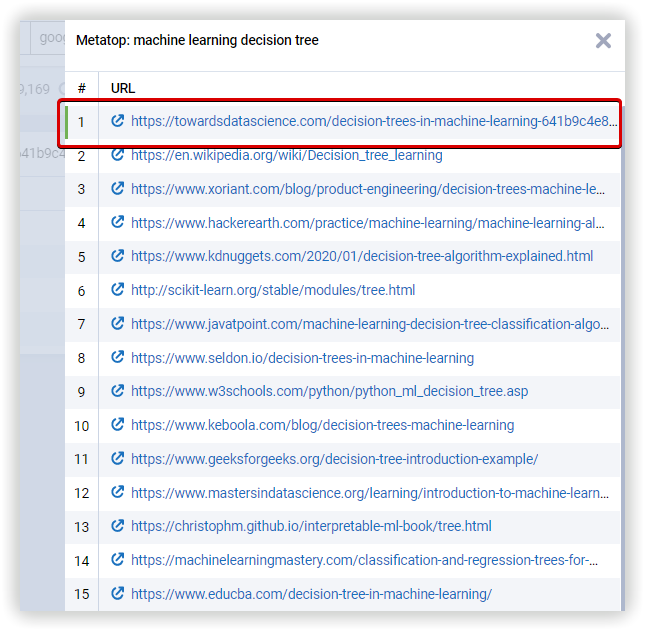
An example
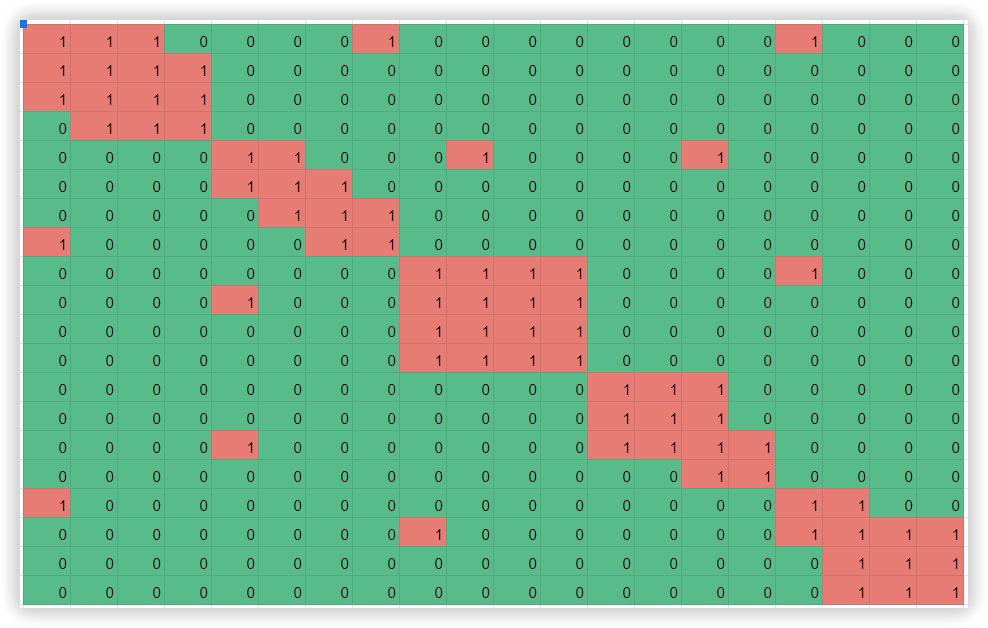
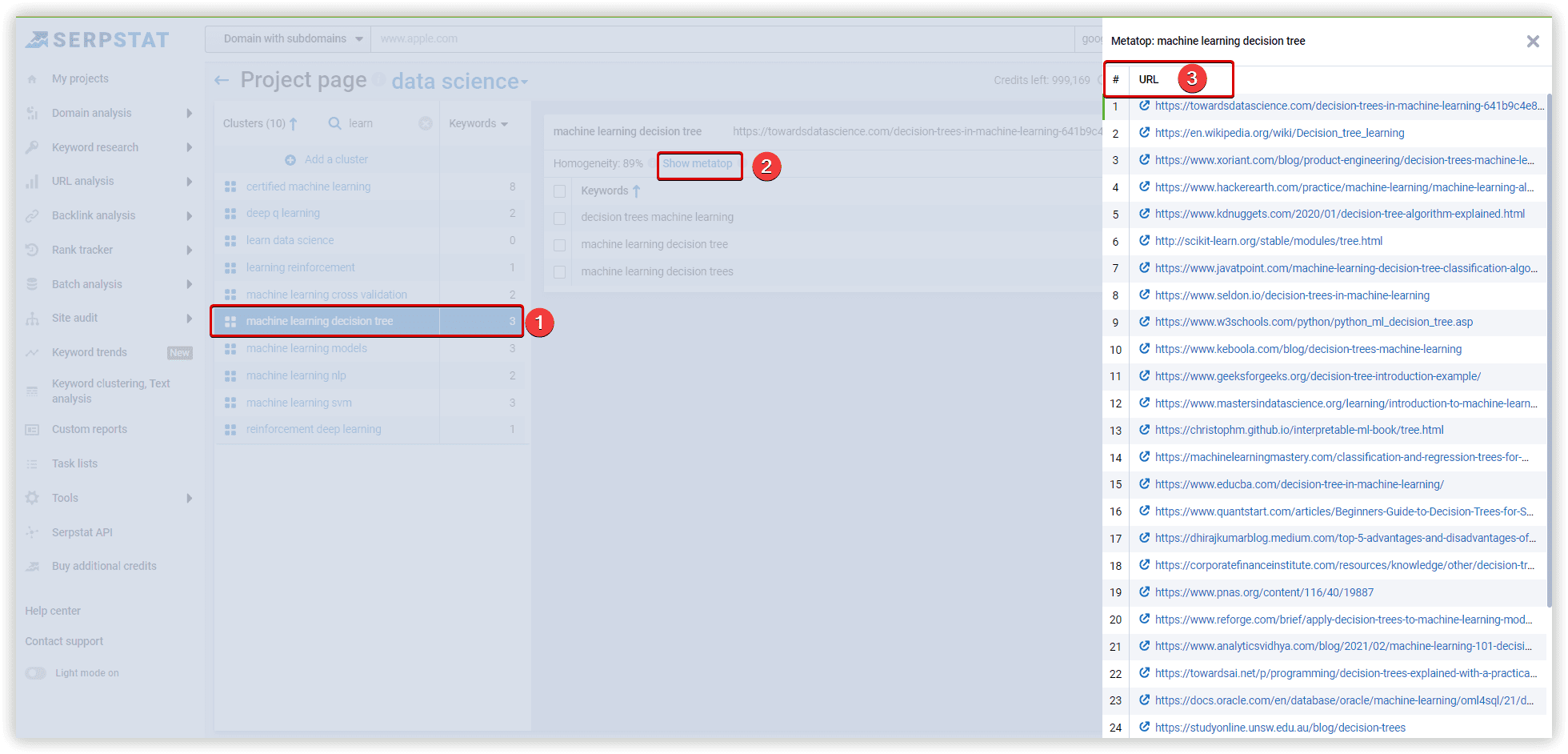
With the Czekanowski method, it is more likely that a metatop would function as a centroid - i.e., a set of URLs representing the cluster. In this case, the proximity of the keyword to the cluster is calculated with the similarity of the SERP of the keyword and the analyzed metatop.We have developed a unique iterative algorithm that allows you to find and correct inaccuracies in clustering.
Serpstat also has special metrics to describe final clusters. There are: Homogeneity, and Connection Strength.
Cluster homogeneity indicates how the keyword in this cluster is related between each other (%). This metric estimates SERPs for each keyword.
Connection Strength is the similarity between a metatop and a specific keyword’s SERP. Based on a scale of 0 to 100, it shows how close the keyword from the cluster is to the cluster's main topic.
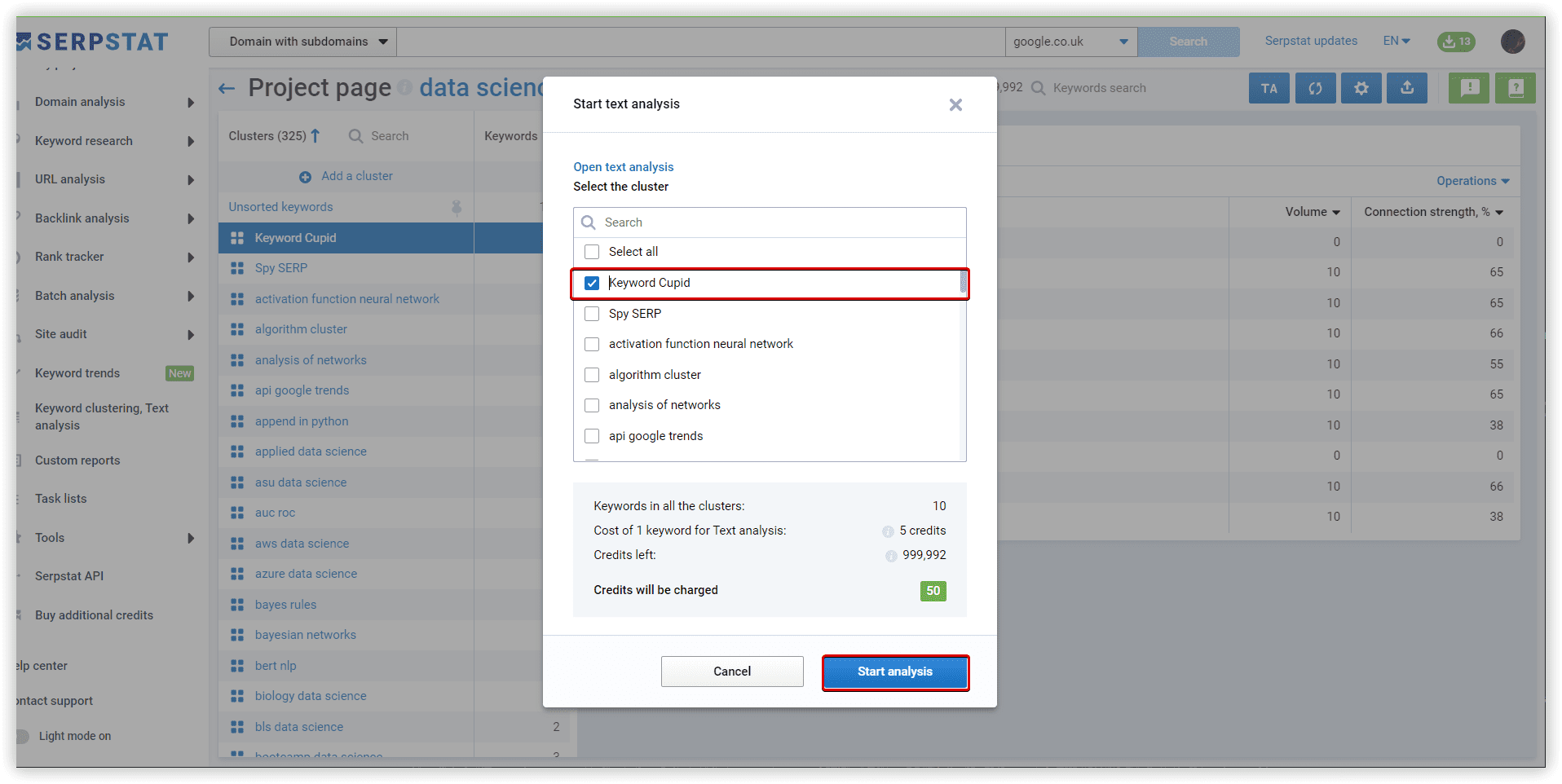
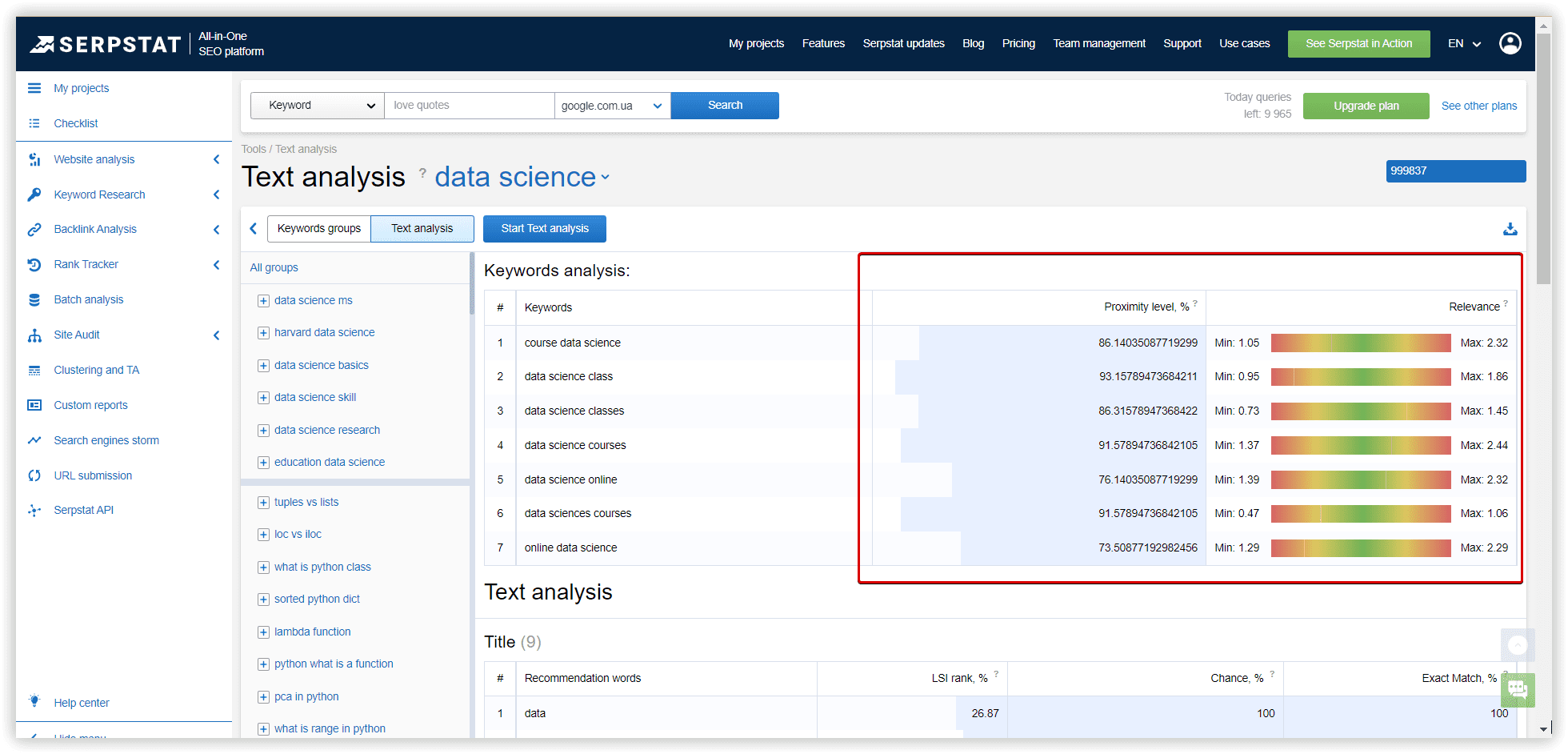
To check how different clustering approaches work, we will perform Text analysis in Serpstat on clusters we created using several SEO platforms with the same clustering algorithm - SERP analysis.
Text analytics in Serpstat is a tool that helps you to improve the relevance of your content based on the TOP 15 of your competitors via SERP analysis. This tool will show the occurrence of particular keywords in your text and allow you to understand if the text is overstuffed with specific phrases. Alternatively, if you didn't include some relevant keywords in your content, you will see them as recommended words in the Text analytics results. In addition, if you attached target URLs, it's also possible to check some technical issues on the page.
For Text analysis, and also to understand the intent better, Serpstat operates an algorithm TF-IDF-CDF (TF - term frequency, IDF - inverse document frequency and our own CDF - cluster’s document frequency). We use this approach to rank the keywords that define the topic for the entire cluster:
TF - takes into account the number of occurrences of the keyword in the text;
IDF - controls uninformative keywords found in a large percentage of text, stop-words;
СDF - finds the most powerful keywords for each cluster.
With Text analytics by cluster, you will get the most valuable keywords for your website's structure. Then, you can use these keywords to start a project in the Rank Tracker and observe your website's performance.
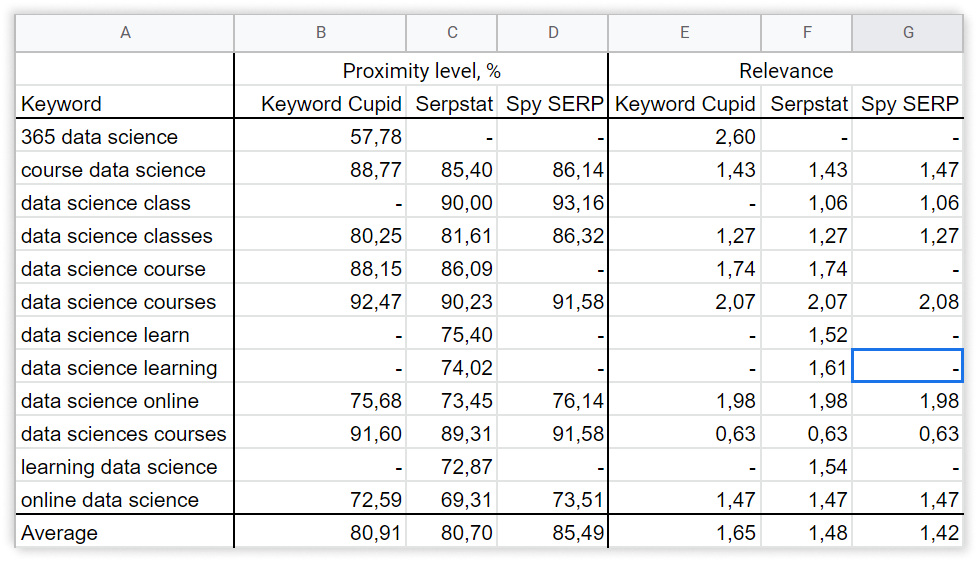
To monitor the quality of clusters done by different SEO tools, we will also compare metrics from the Text analytics, not only clustering. The same dataset and settings for clustering will be used in this experiment for three different platforms.
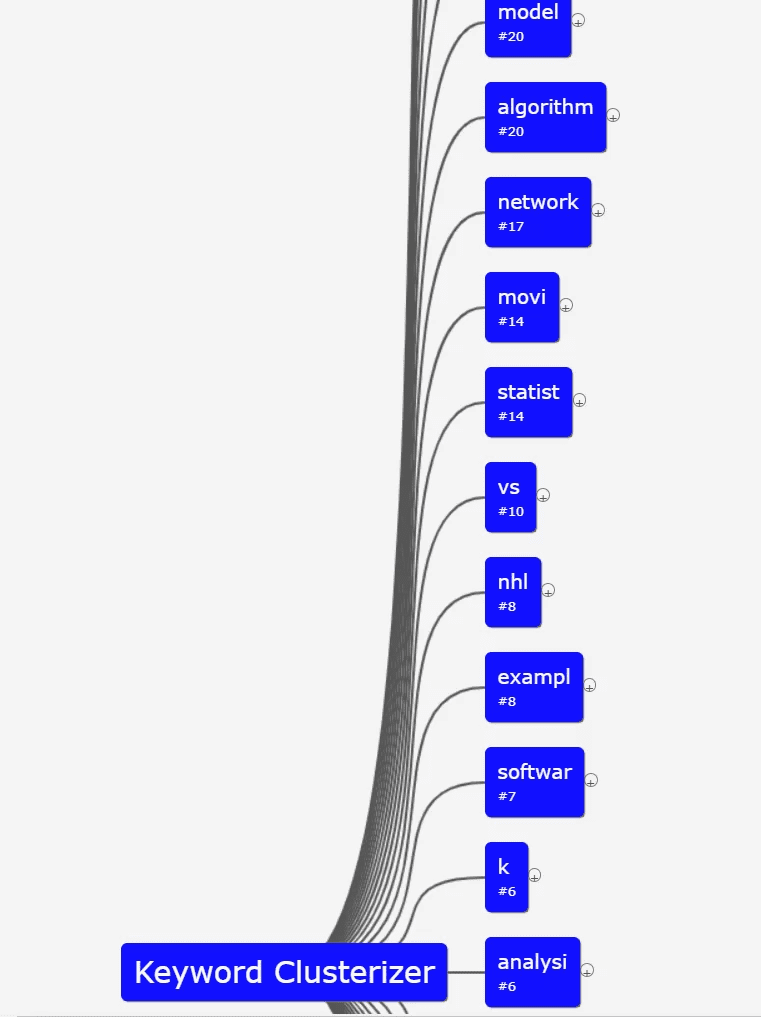
Cluster army
- wait (infinitive)
- wait (imperative)
- waits (present, 3rd person, singular)
- wait (present, other persons, or plural)
- waited (simple past)
- waited (past participle)
- waiting (progressive)
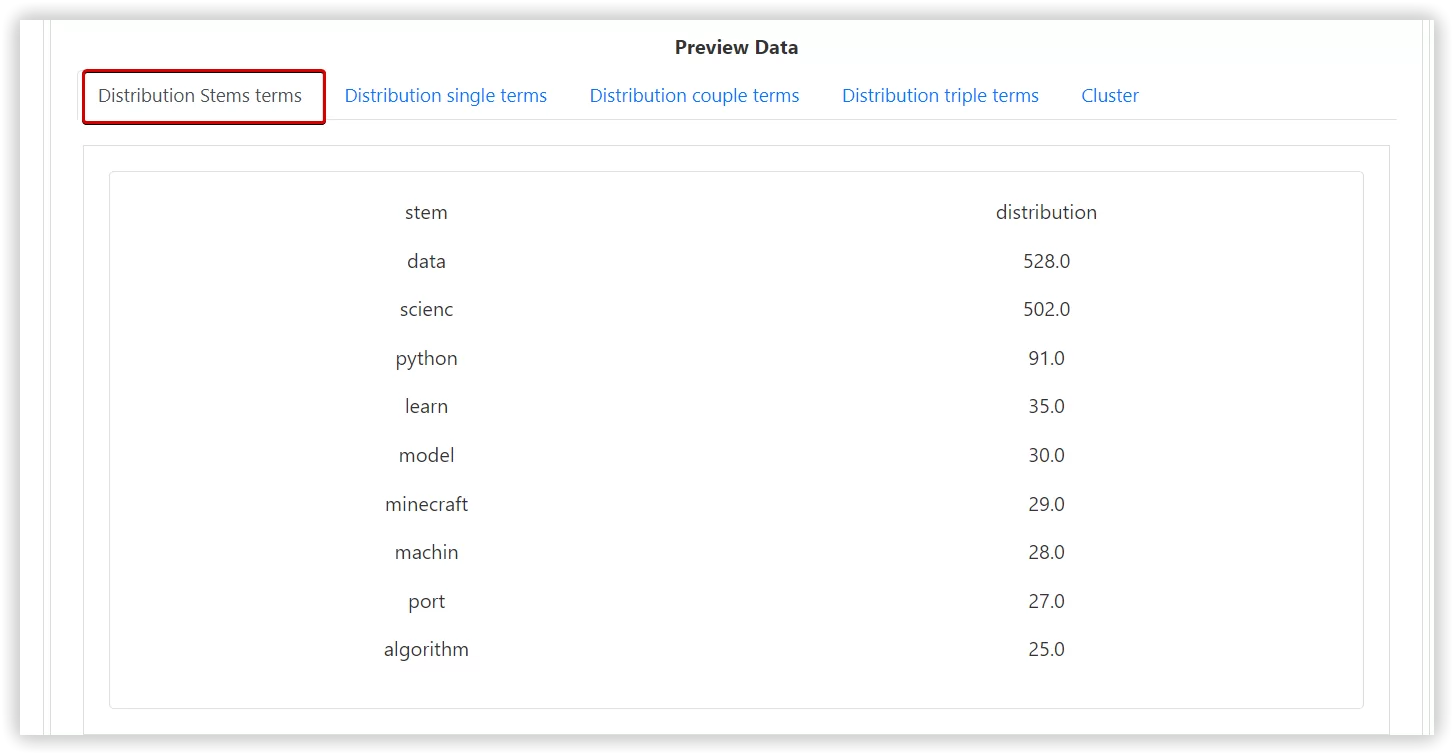
A stem is a form to which affixes can be attached in one usage. Thus, in this usage, the English word friendships contain the stem friend, to which the derivational suffix -ship is attached to form a new stem friendship, to which the inflectional suffix -s is attached. In a variant of this usage, the word's root (in the example, friend) is not counted as a stem.
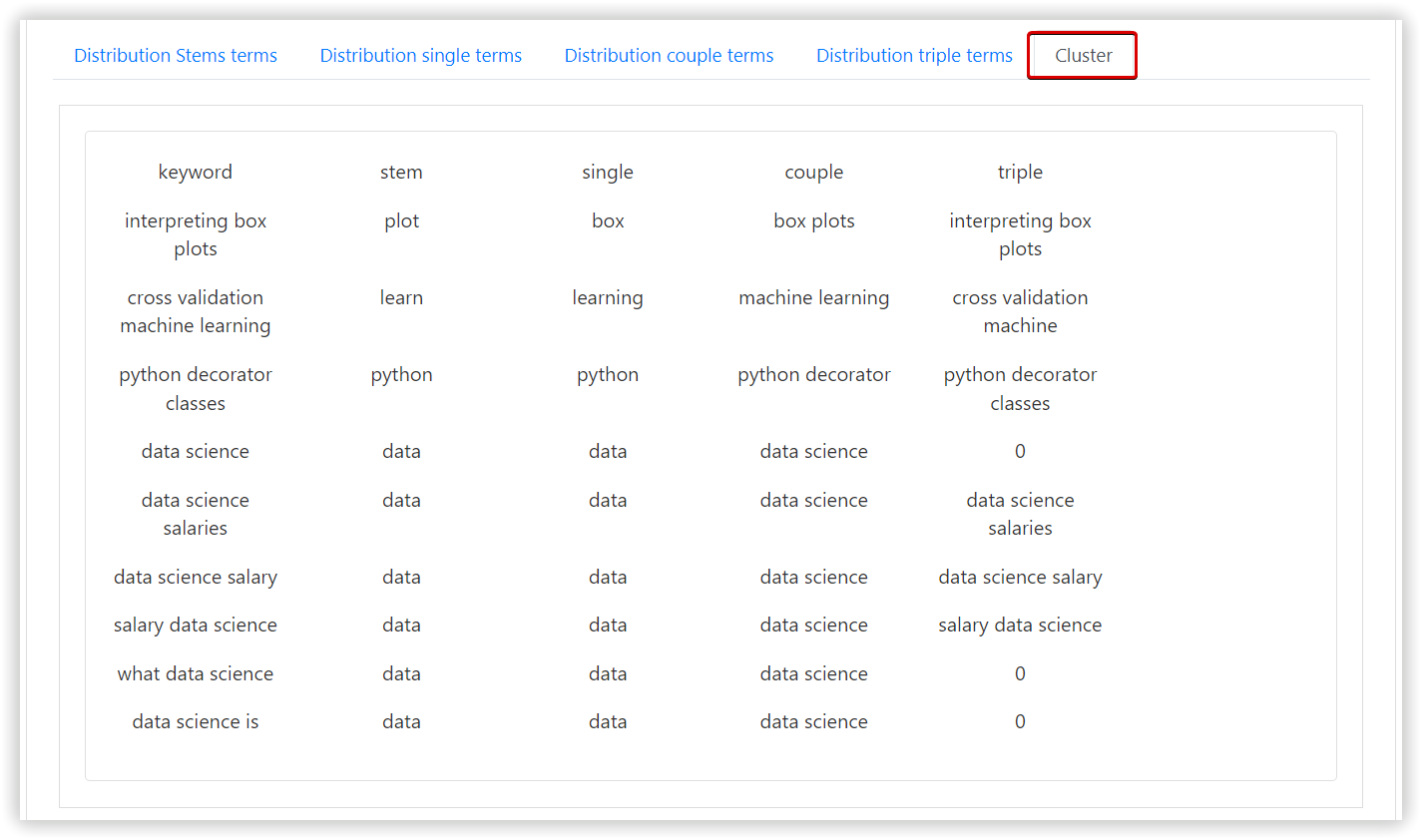
Cluster Army performs a 7-step process:
- To explore the imported list.
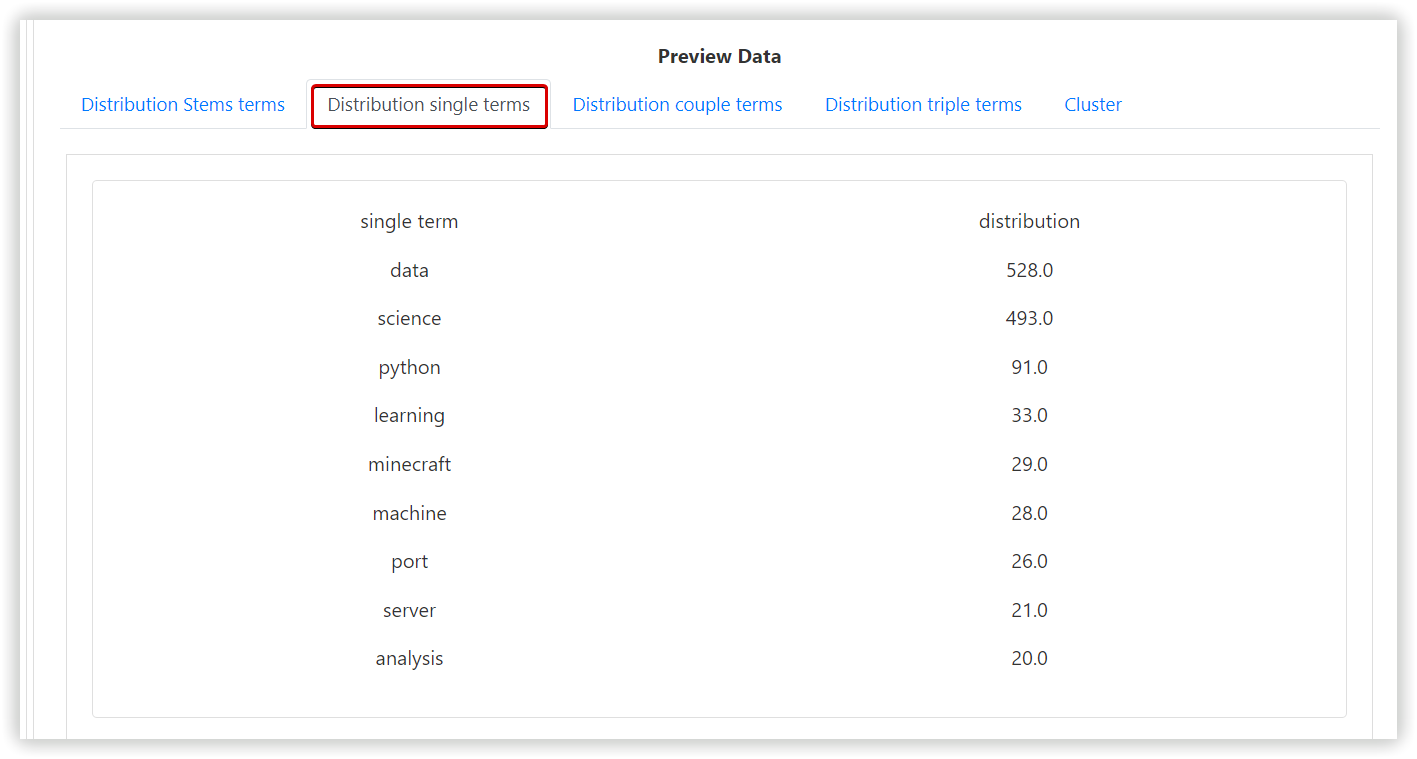
- To find the distribution (search volume) of each single stem, if the option is selected the stop-words will be removed.
- To find the distribution of each single term, if the option is selected the stop-words will be removed.
- To find the distribution of all term pairs, stop-words are not excluded.
- To find the distribution of all triples, stop-words are not excluded.
- To create the table with the first keyword associated with the high-volume stem, single, double and triple terms.
- Finally, the tool generates a chart for each distribution that you can use in your project.
Spy fu
SpyFu clustering tool works in this way:
- You can paste your branded and long-tail keywords. Spy Fu will add data to them to get the complete picture of your research.
- Then, sort your keywords to see how new data affect your priorities or filter them down, relying on automatic groups.
- Finally, export your new keyword list to other platforms or conveniently add them to the built-in tool inside Spy fu.
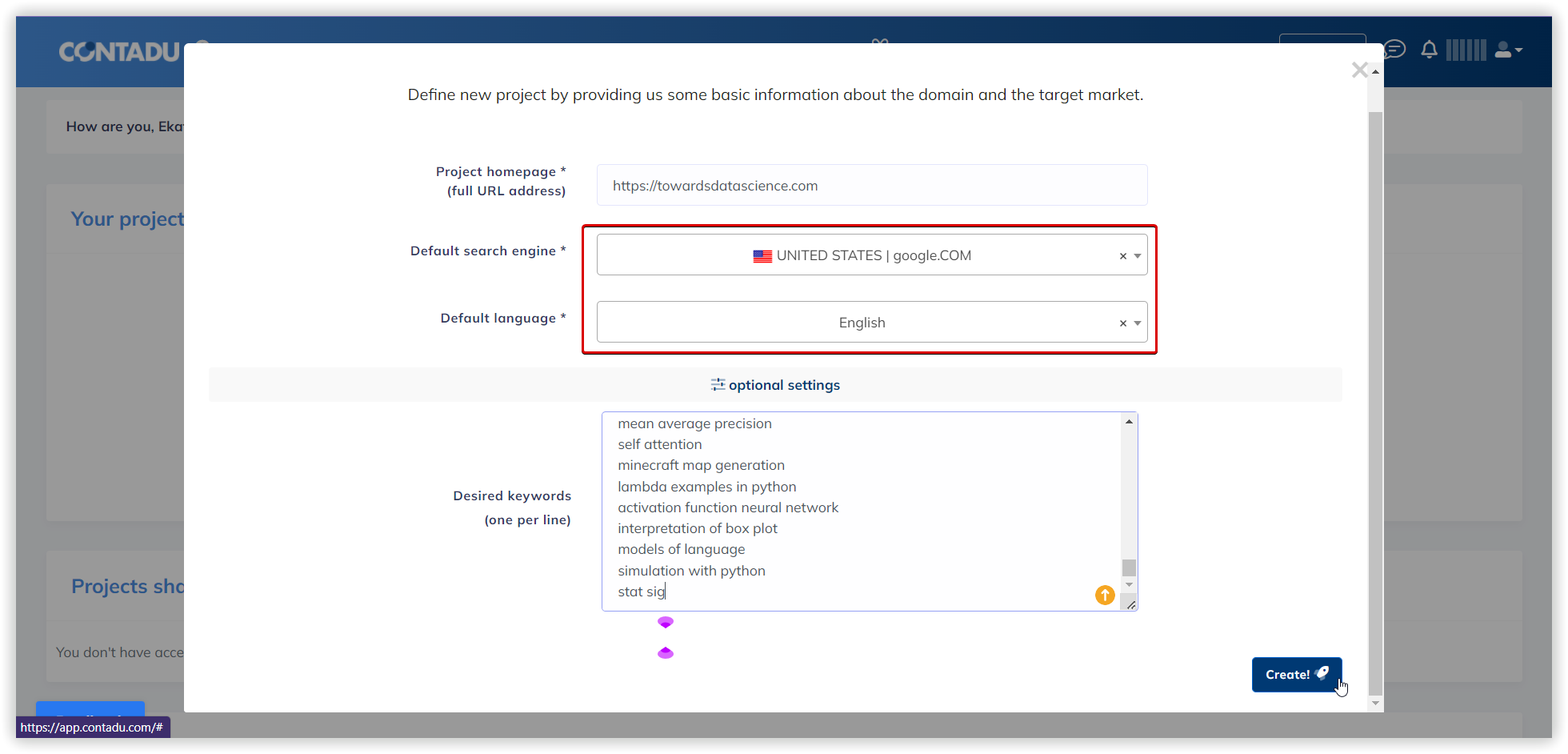
Contadu
The topic analysis process in Contadu holds a few steps :
- To collect keywords ideas based on your input.
- To check search volume, trends, CPC, and competition values.
- To search results for all keyword ideas.
- To build the similarity matrix between the keywords.
- To start clustering based on similarity levels.
An unsupervised clustering mechanism is required to generate a self-organizing hierarchical structure for classification. Hence, Umbrella’s algorithm is based on spectral clustering, which identifies the structure of the data set and clusters them according to the degree of affinity.
To do so, Umbrellum uses clustering with Levenshtein distance — a string metric for measuring the difference between two sequences. The Levenshtein distance between two words is the minimum number of single-character edits required to change one word into the other.
Technically, it is a number that tells you how different two strings are. The higher the number, the more diverse the two strings are.
The typical illustration of the Levenshtein distance is the distinction between “kitten” and “sitting.” The answer is 3 since, at a minimum, 3 edits are required to change one into the other.
kitten → sitten (substitution of “s” for “k”)
sitten → sittin (substitution of “i” for “e”)
sittin → sitting (insertion of “g” at the end).
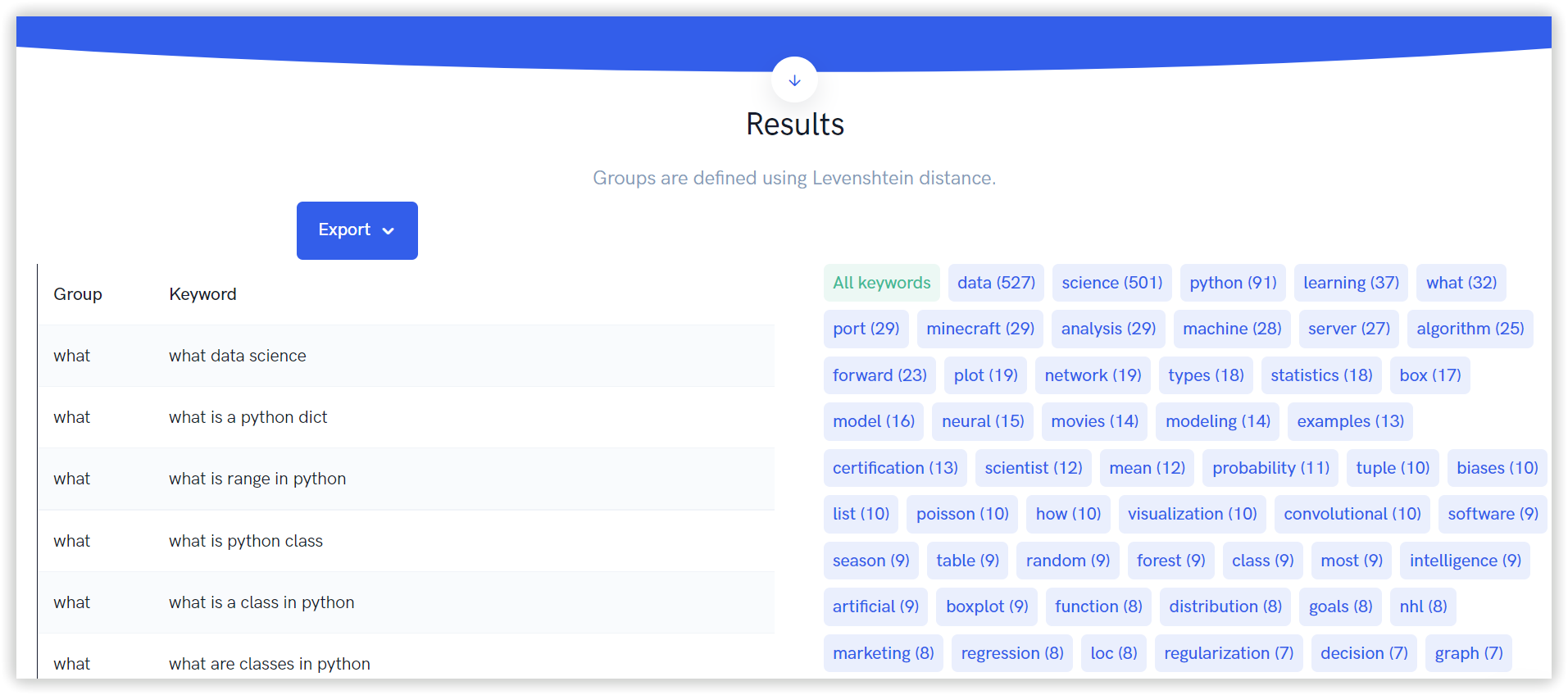
You can see the range of long-tail keywords each group represents and the total potential search volume for the queries you might rank for.
Each group can be sent to a content planner, where you can start to build an outline of the articles you plan to write, build up a cluster of relevant articles, boosting your topical authority.
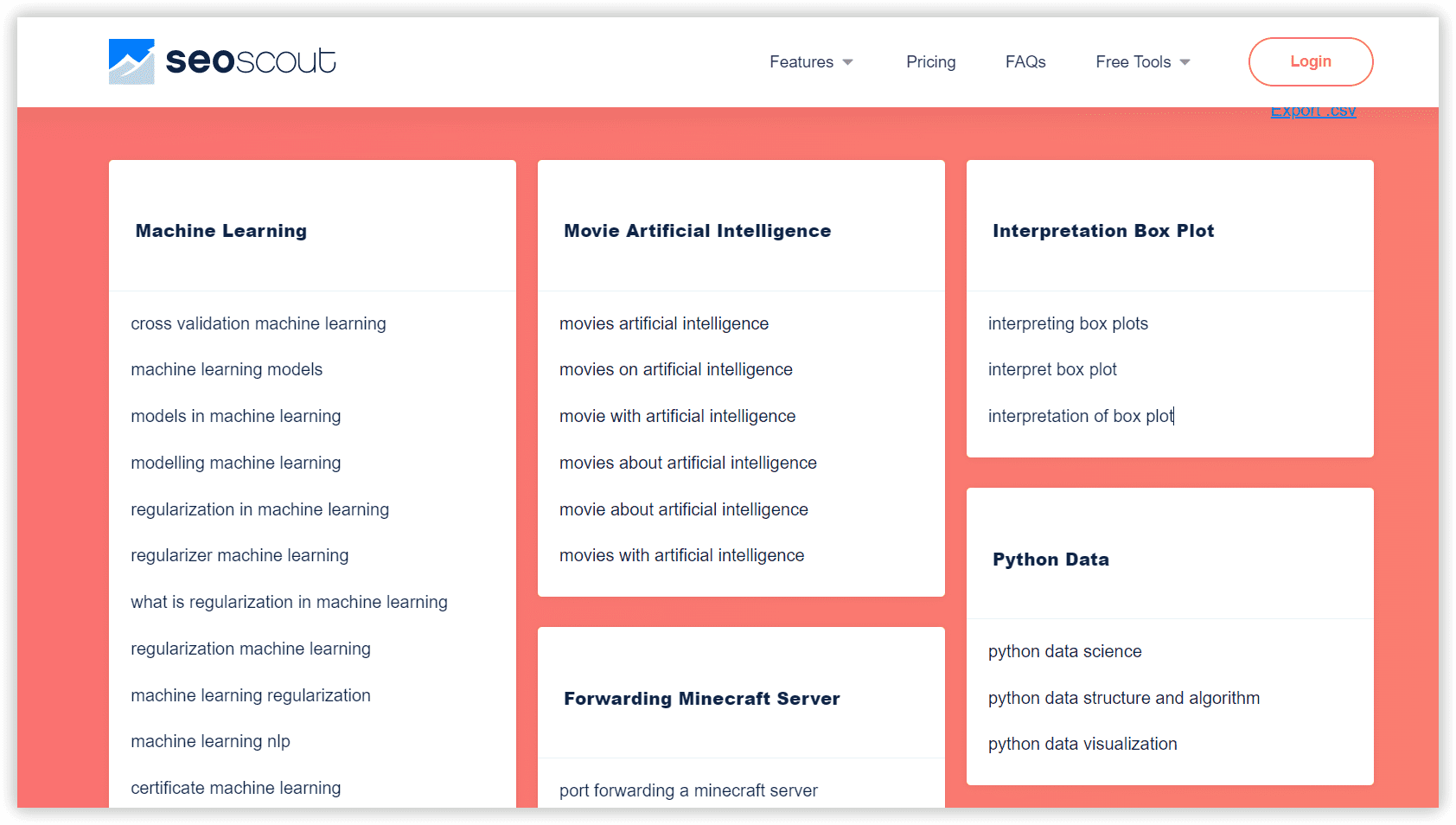
You only want to include keywords that will bring the right kinds of searchers to your website, those who are interested in the products or services you offer and are likely to convert.
Here are the criteria you should use to group these keywords into clusters:
- Semantic Relevance. The keywords in your clusters must share similar search intent.
- Search Volume and CPC. The core keywords in your clusters should have a reasonable search volume (otherwise, you optimize for nobody). This keyword pool should also have conversion potential (CPC).
- Organic Difficulty (KD). Include only keywords your site has a realistic chance of ranking for.
In contrast to lemma-based keyword grouping, SERP-based keyword clustering produces groups of keywords that yield no morphological matches but conform to the search results. Using it, SEOs can create keyword structures that match what search engines require.
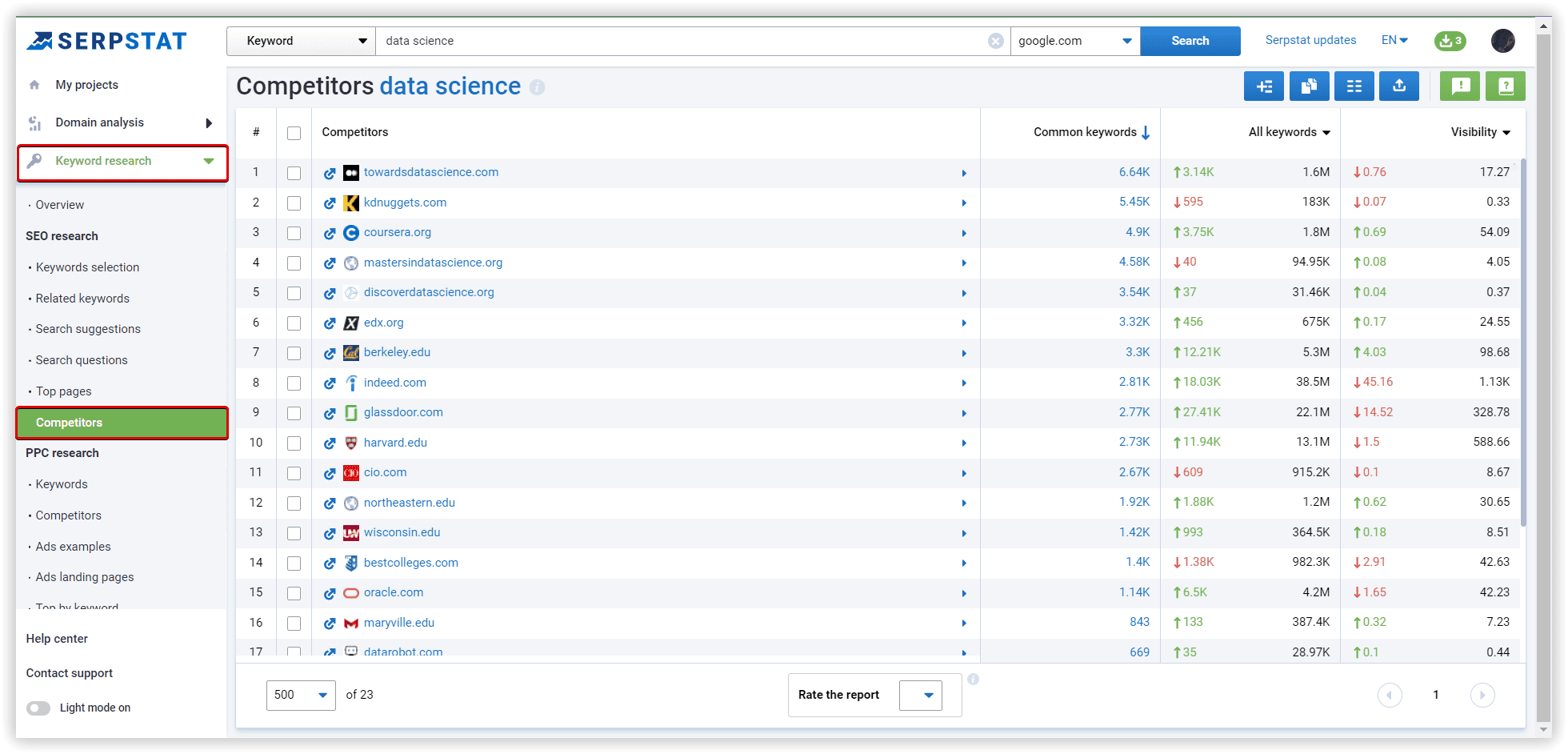
The primary research will mainly concentrate on the SERP-based algorithms of Serpstat, Keyword Cupid, and Spy SERP.
Try Serpstat wіth a 7-day trial, use comprehensive training articles, webinar recordings, and advices from a our specialist.
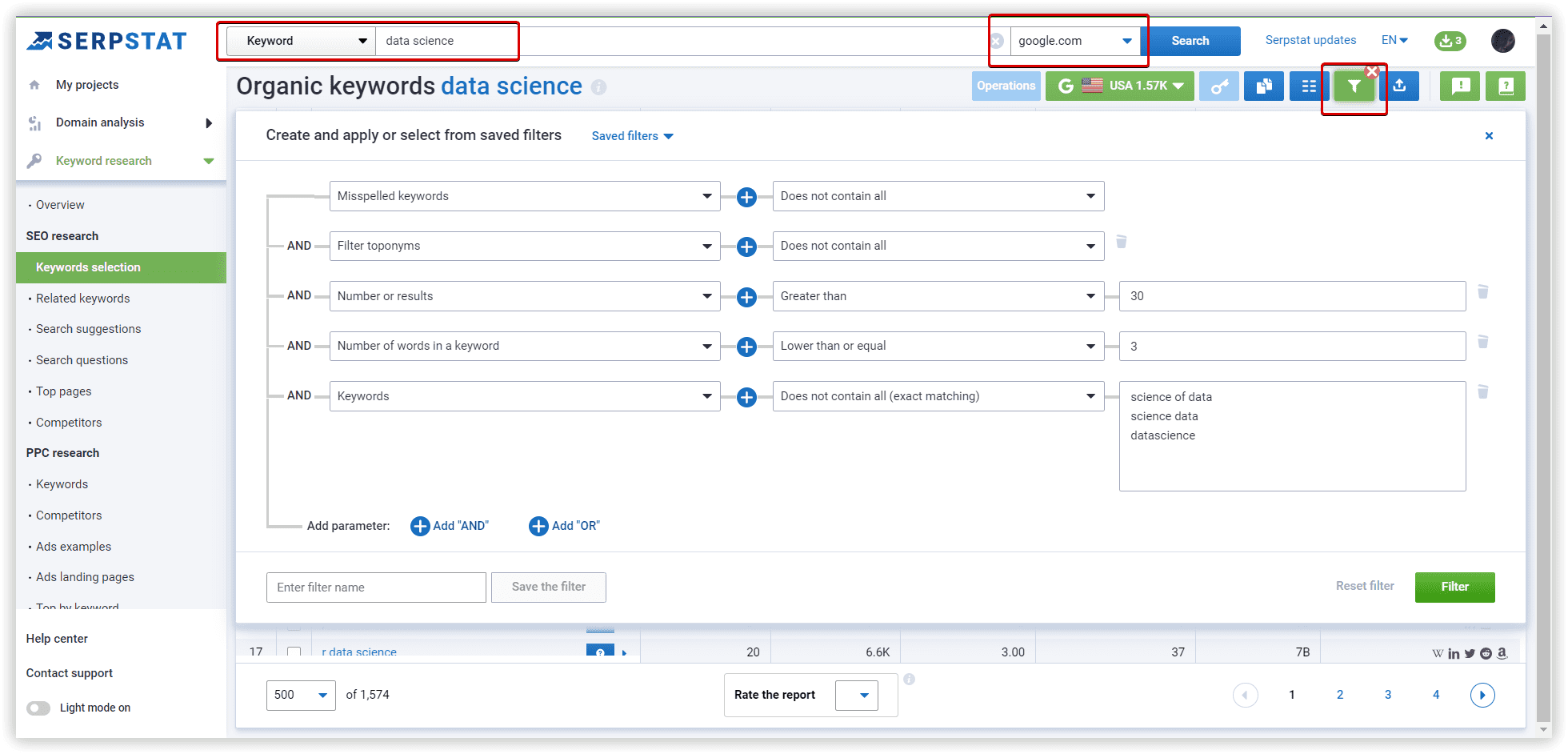
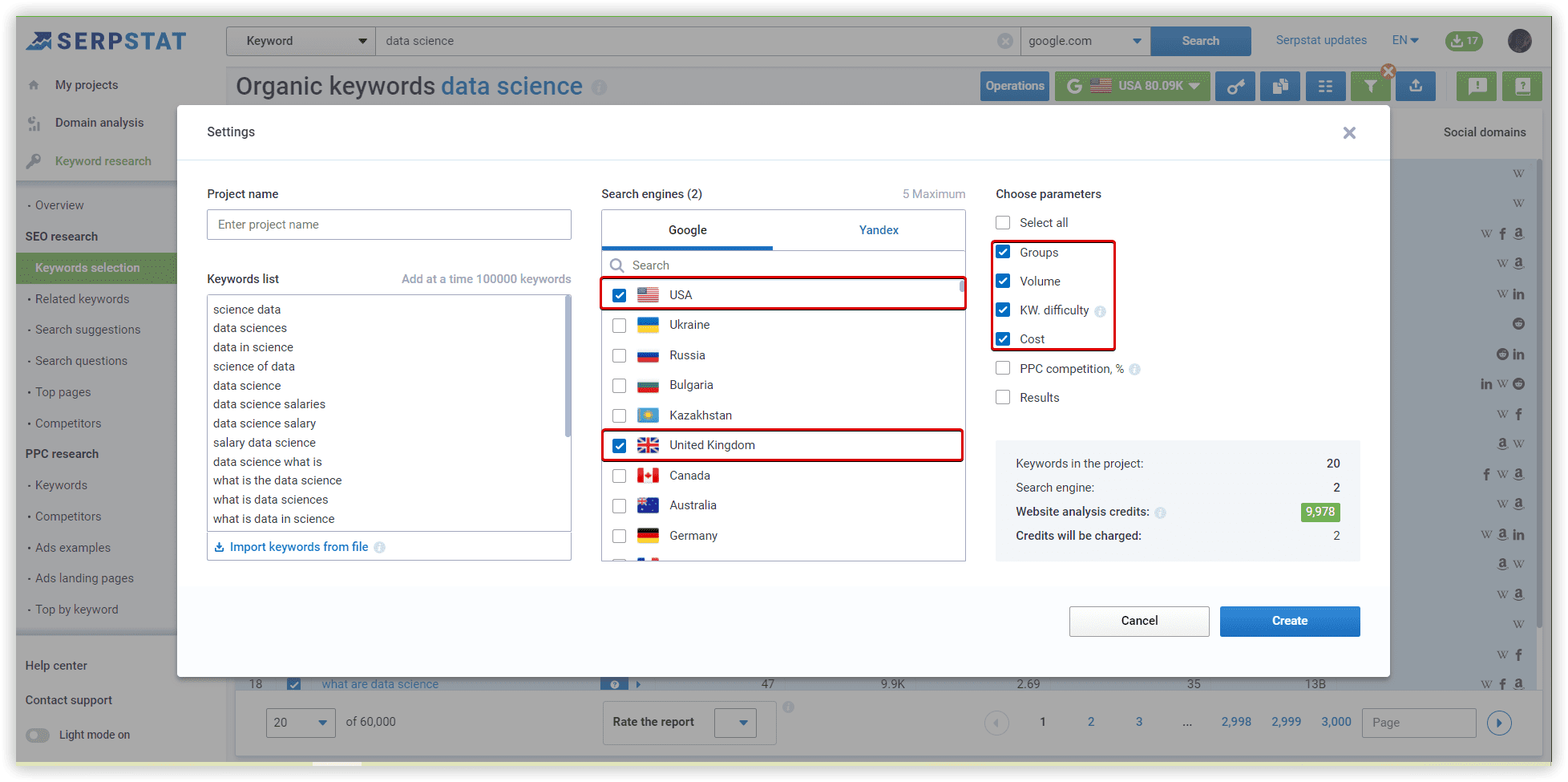
How to collect data for your project in Clustering using Serpstat?
There’s an array of free and paid tools that will help you find keywords for your website. Use Keyword Trends to track the top search queries and current tendencies in search results. While doing your research, note that there are different types of search queries: you can distinguish them by length and specificity (use long-tail keywords) and by user intent (navigational, informational, transactional). These differences will give you an idea of how intense the competition is for particular keywords.
The most credible reports you can use to expand your keywords list:
- Keywords selection ( organic keywords associated with the searched keyword),
- Related keywords ( all search queries that are semantically related to the searched keyword);
- Search suggestions and Search questions ( queries offered to users under the search bar, which complement and facilitate the wording of an original query; questions that include a selected keyword that users are looking for an answer to).
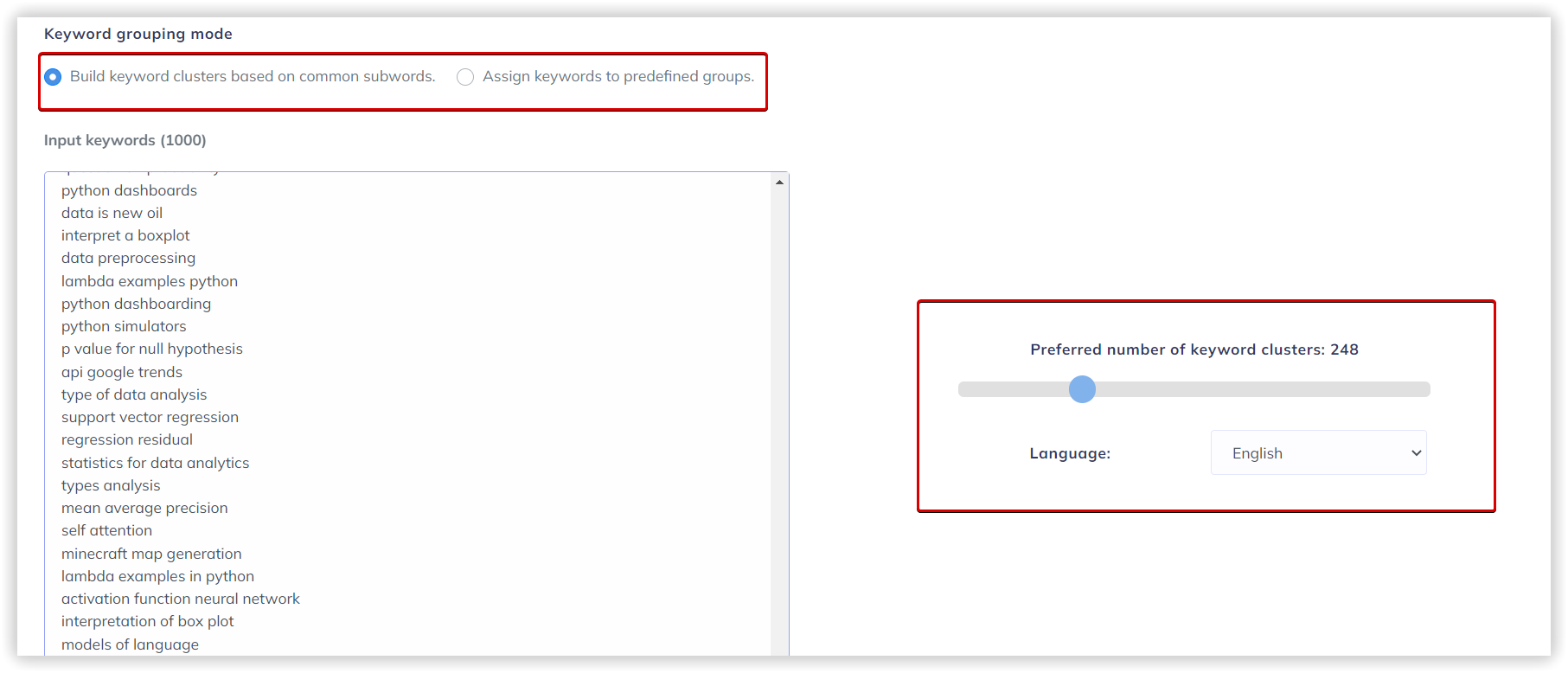
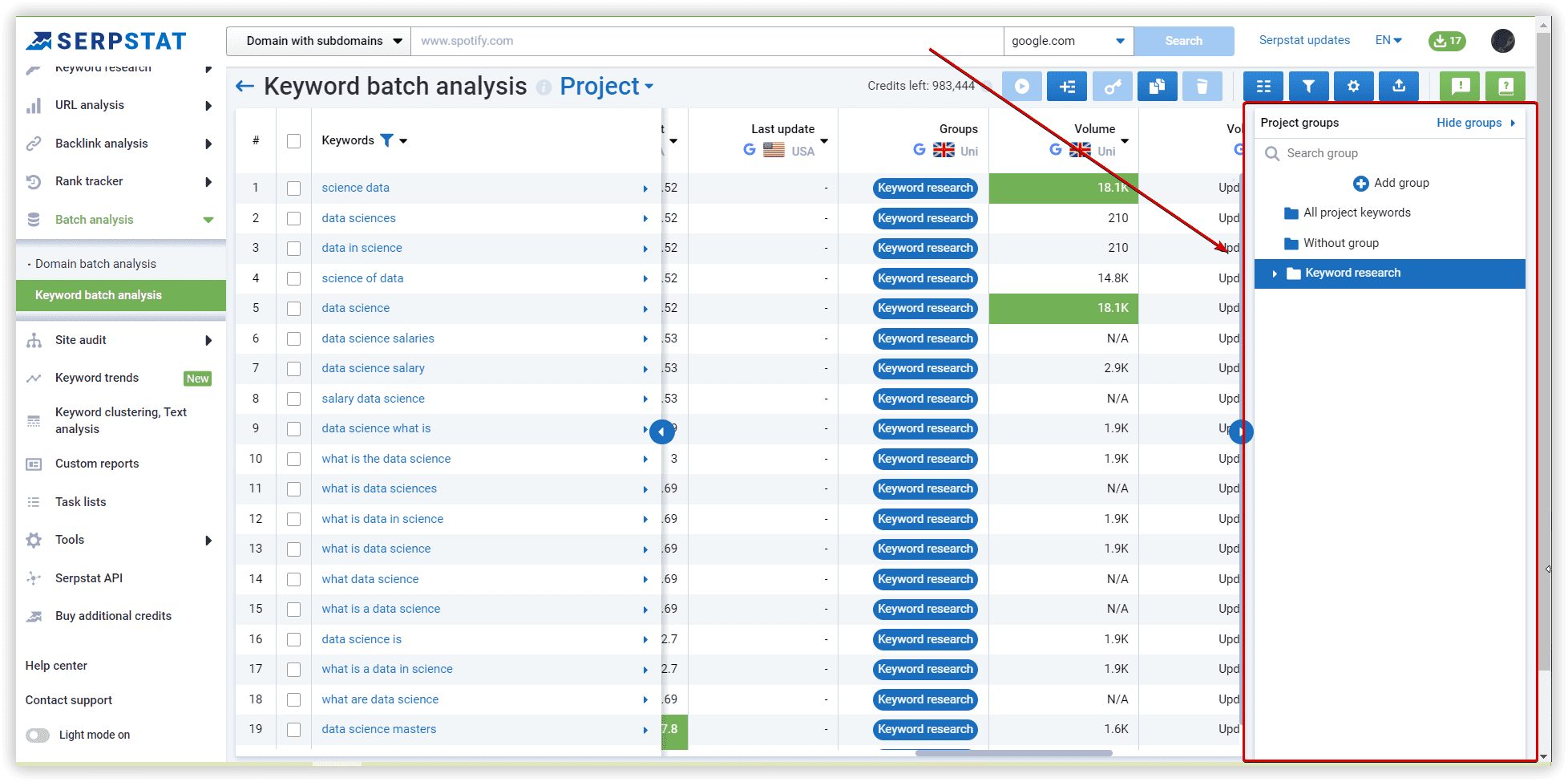
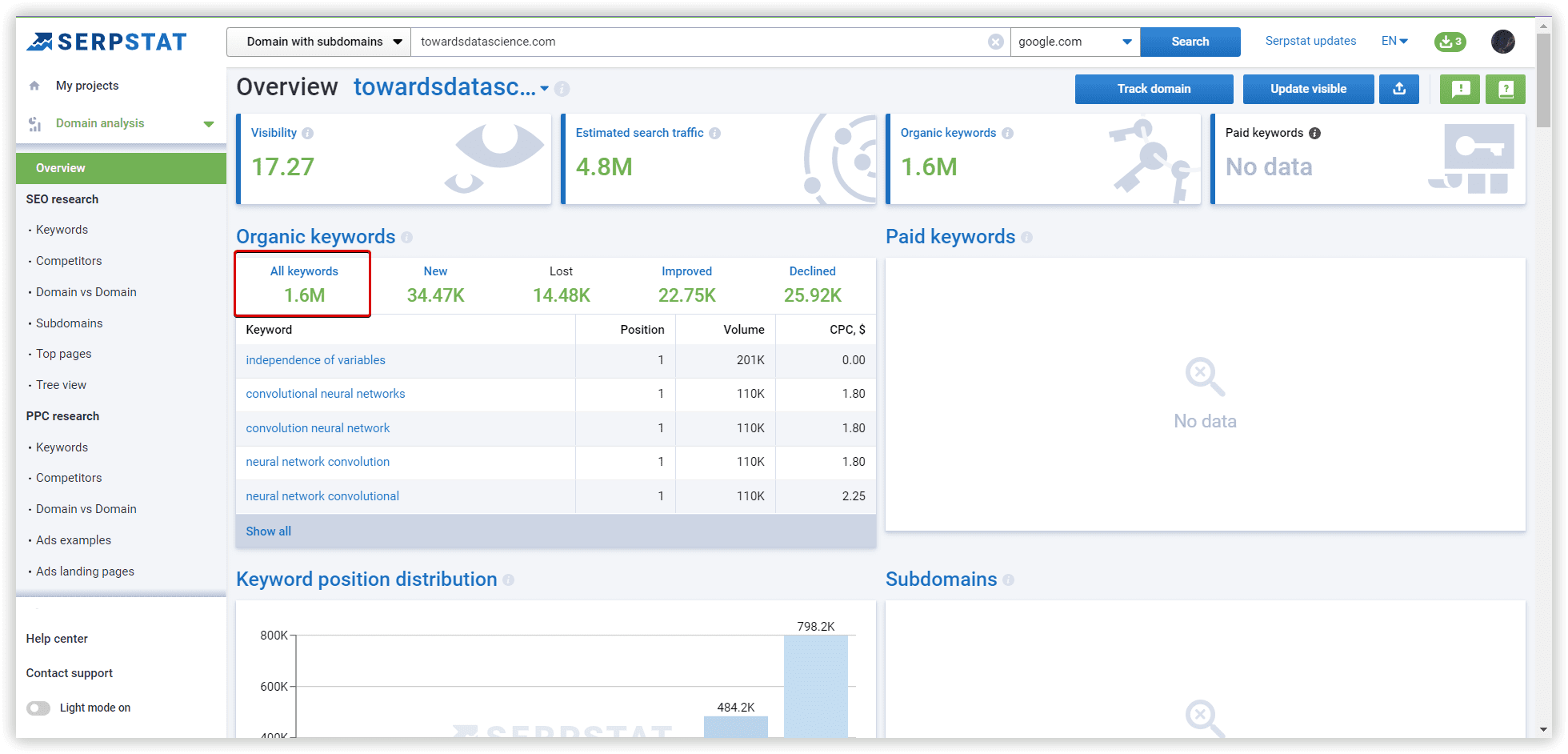
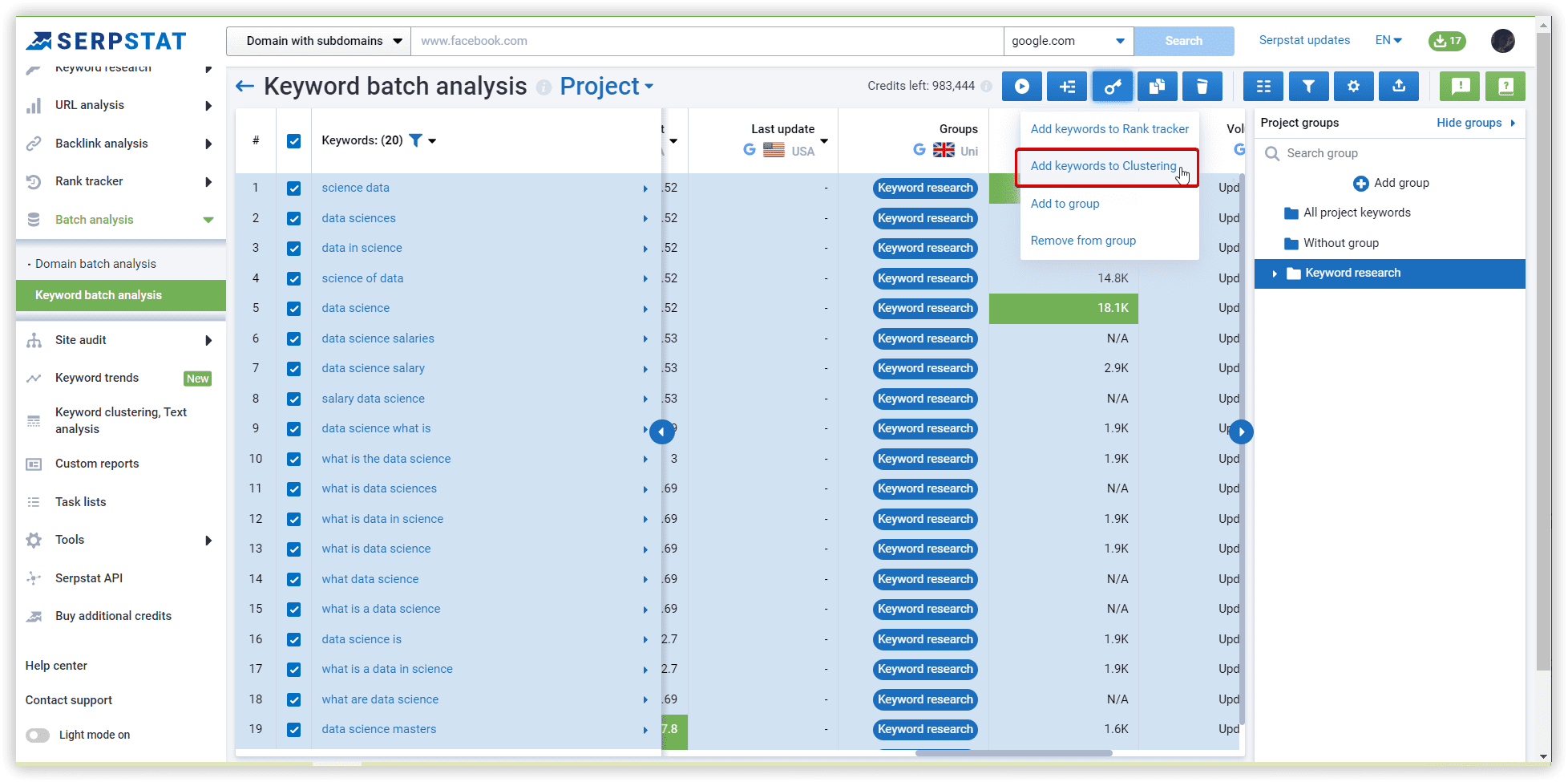
Using Serpstat, we have started our project with our data set. The following are step-by-step instructions.
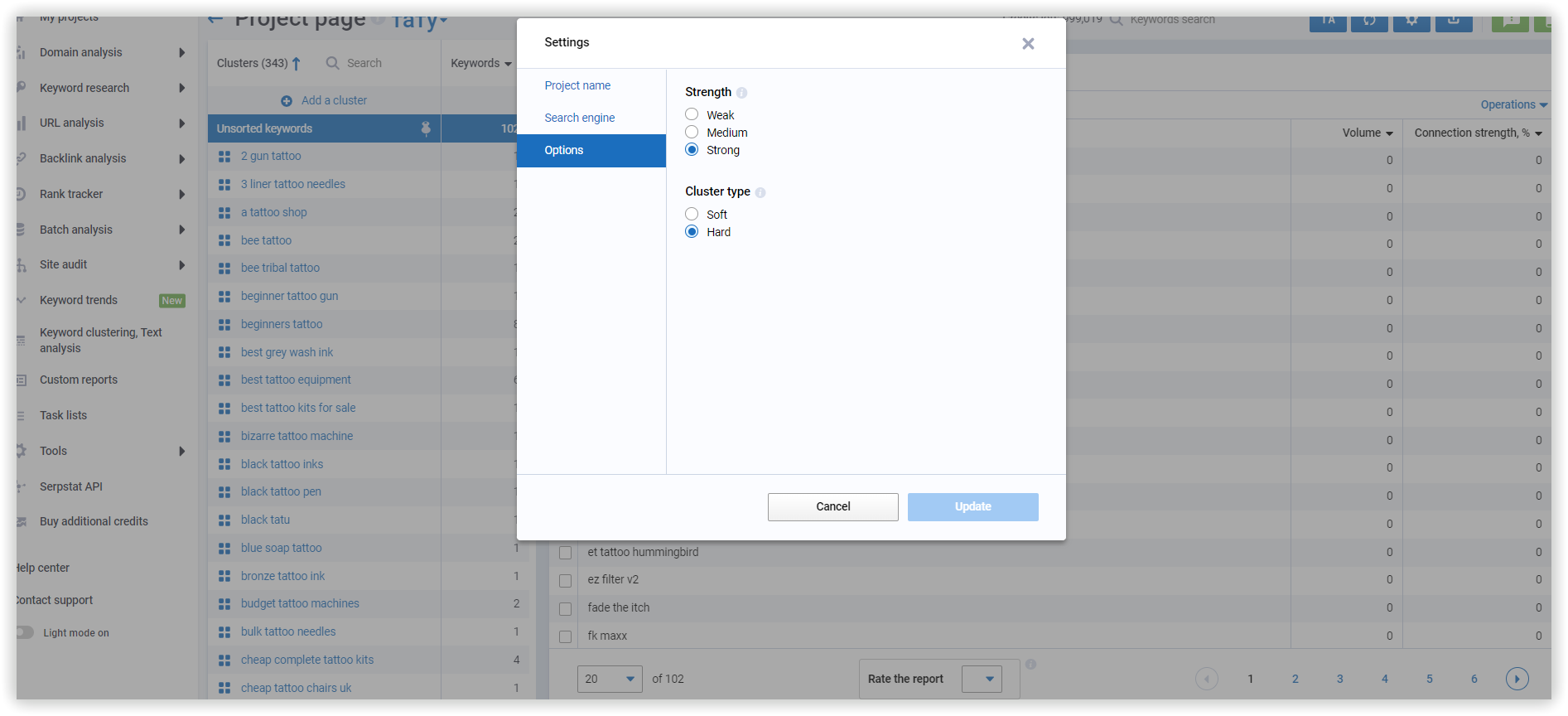
The basics of clustering setup explained
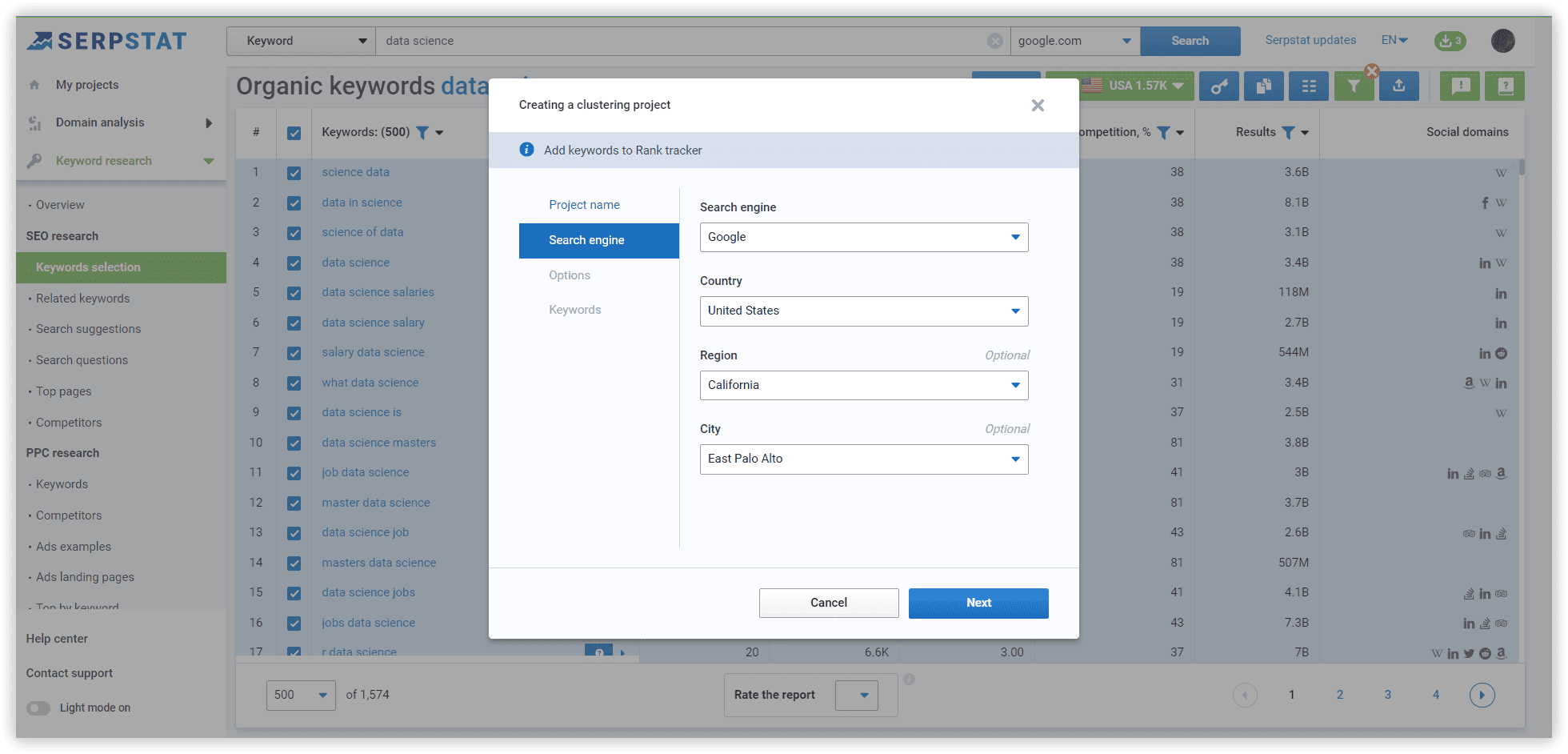
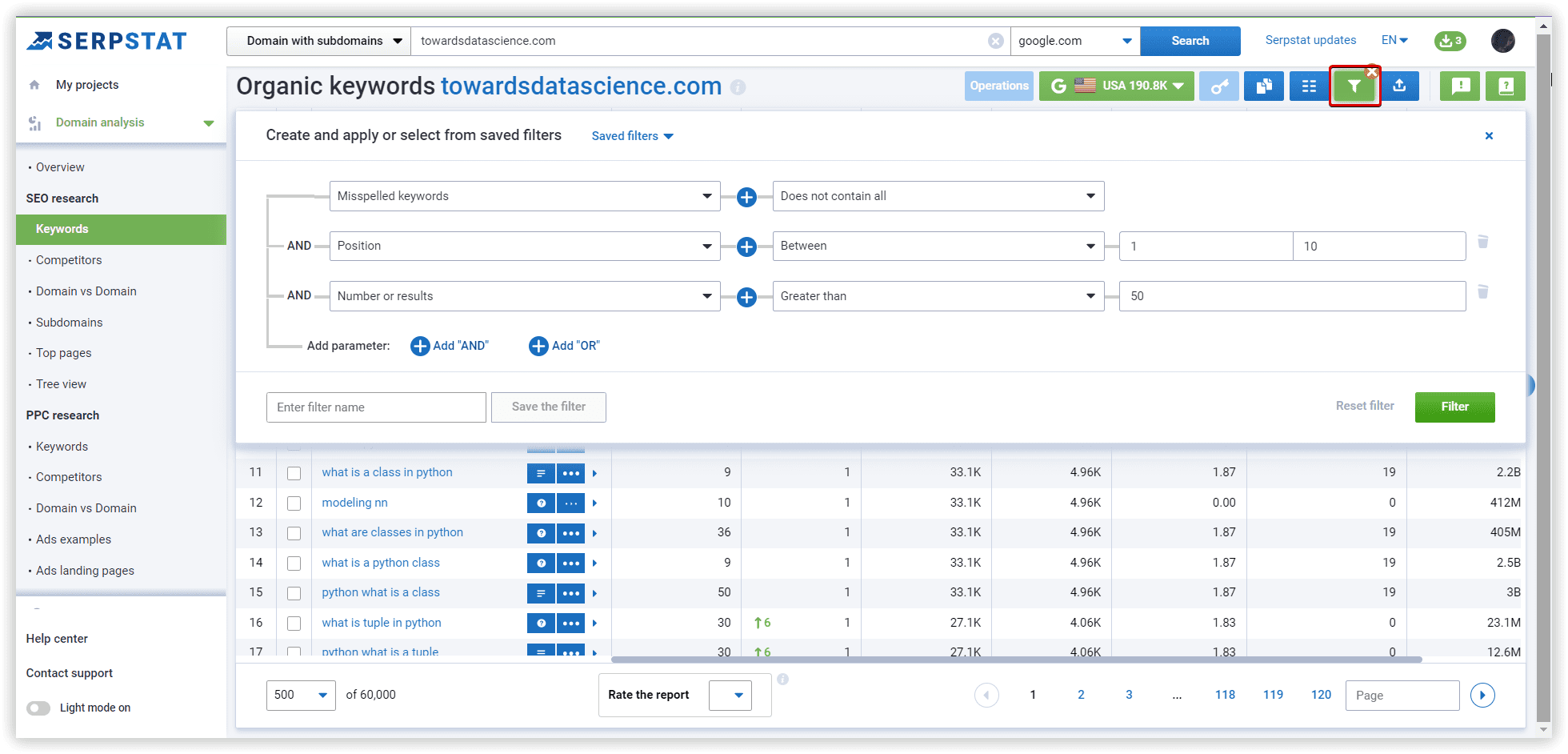
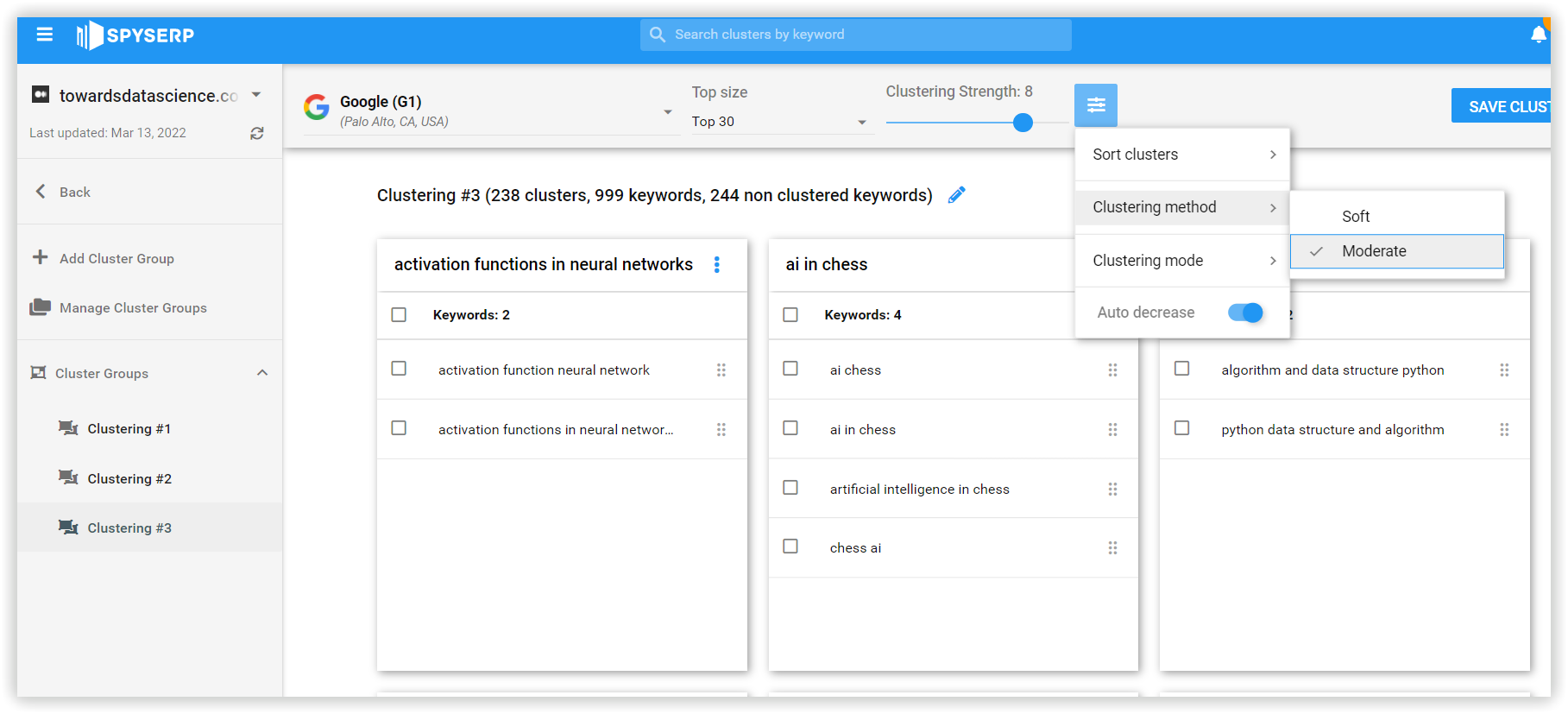
Options for “Medium” - at least 8 common URLs in SERP between two keywords. In case we apply “Weak,” there will be a lot of clusters containing keywords related by intent with at least 3 common urls. In the case of “Strong” strength — we will need 12 common urls, which leads to many unsorted keywords because of increased requirements to group these phrases.
Cluster type: Soft - we do not need common urls between ALL keywords to create a cluster.
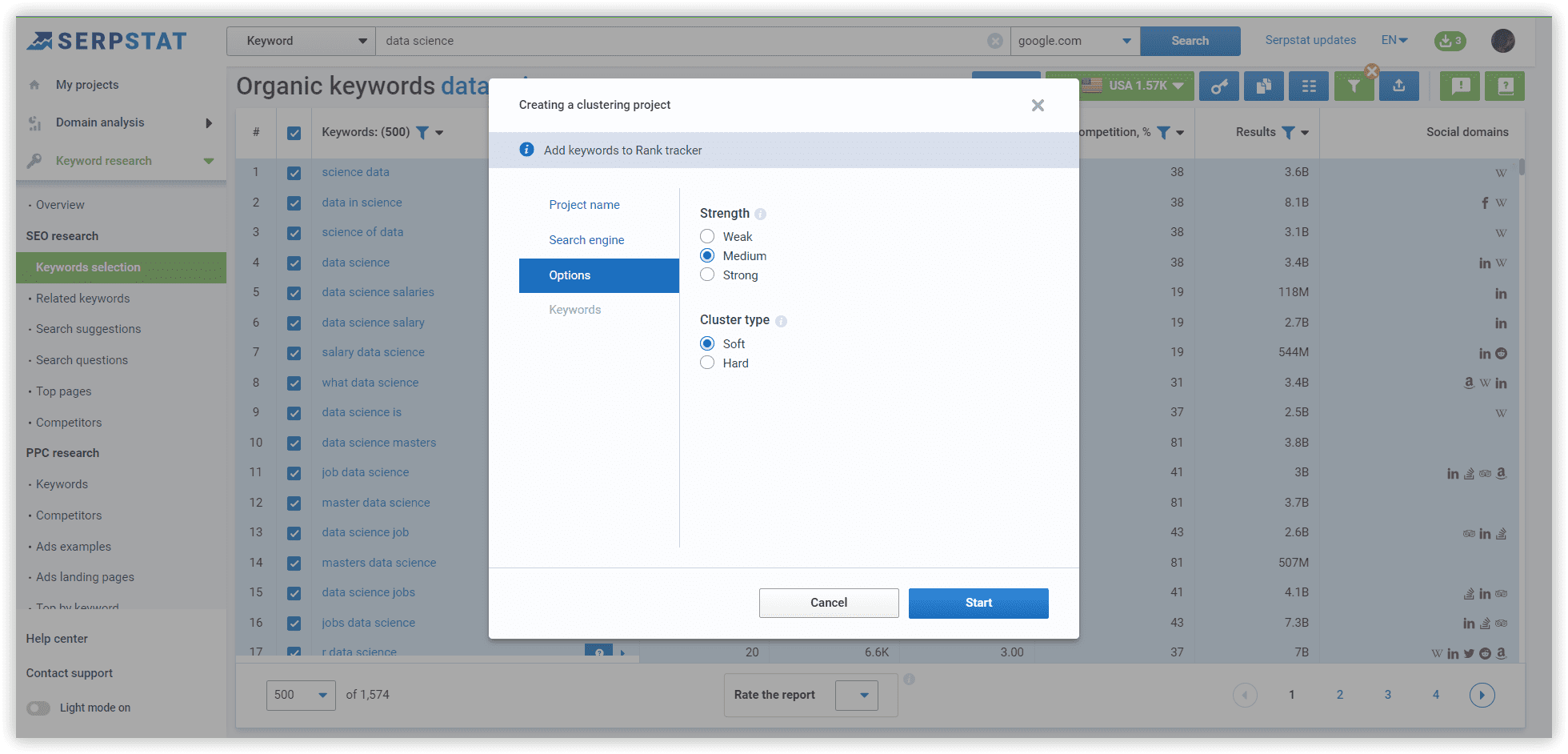
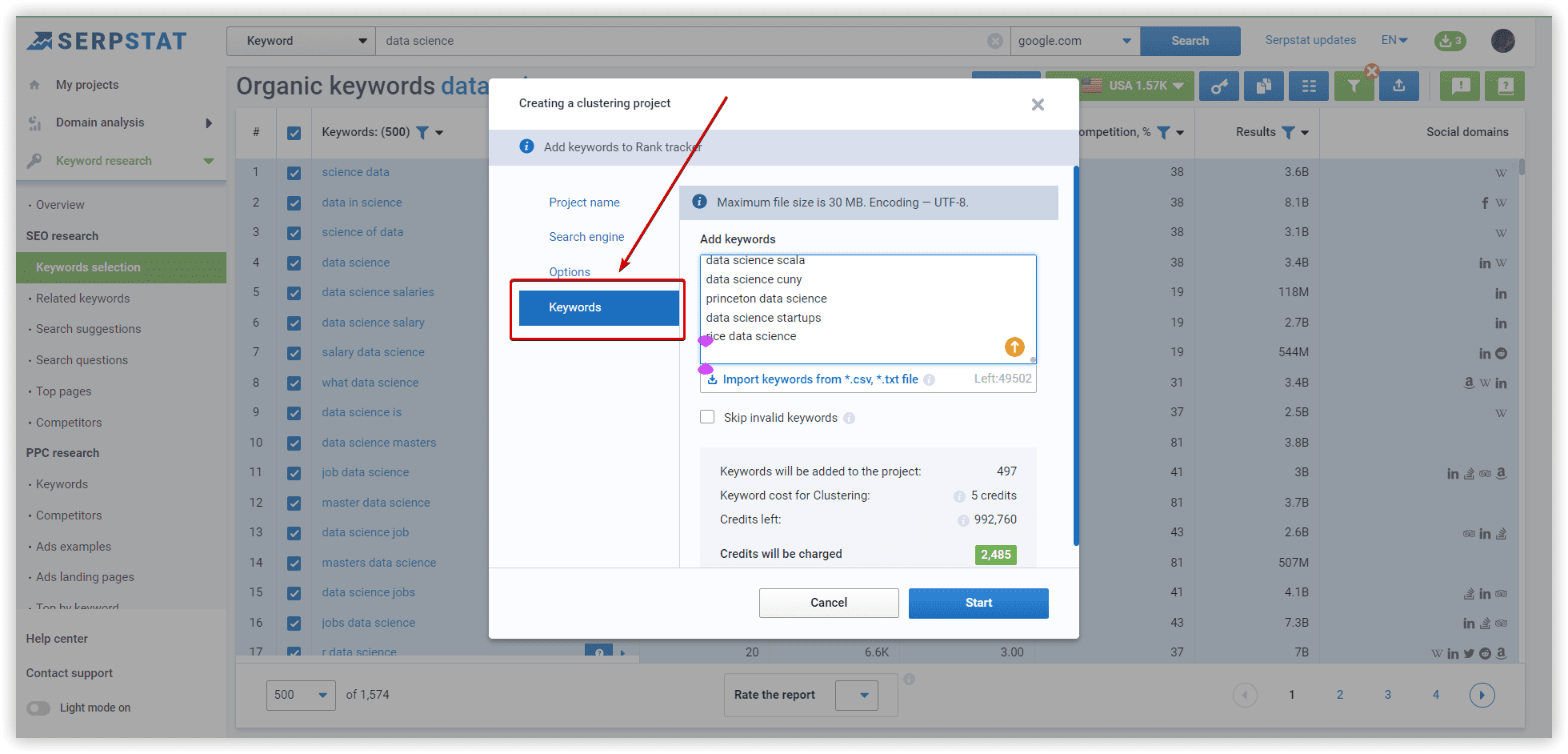
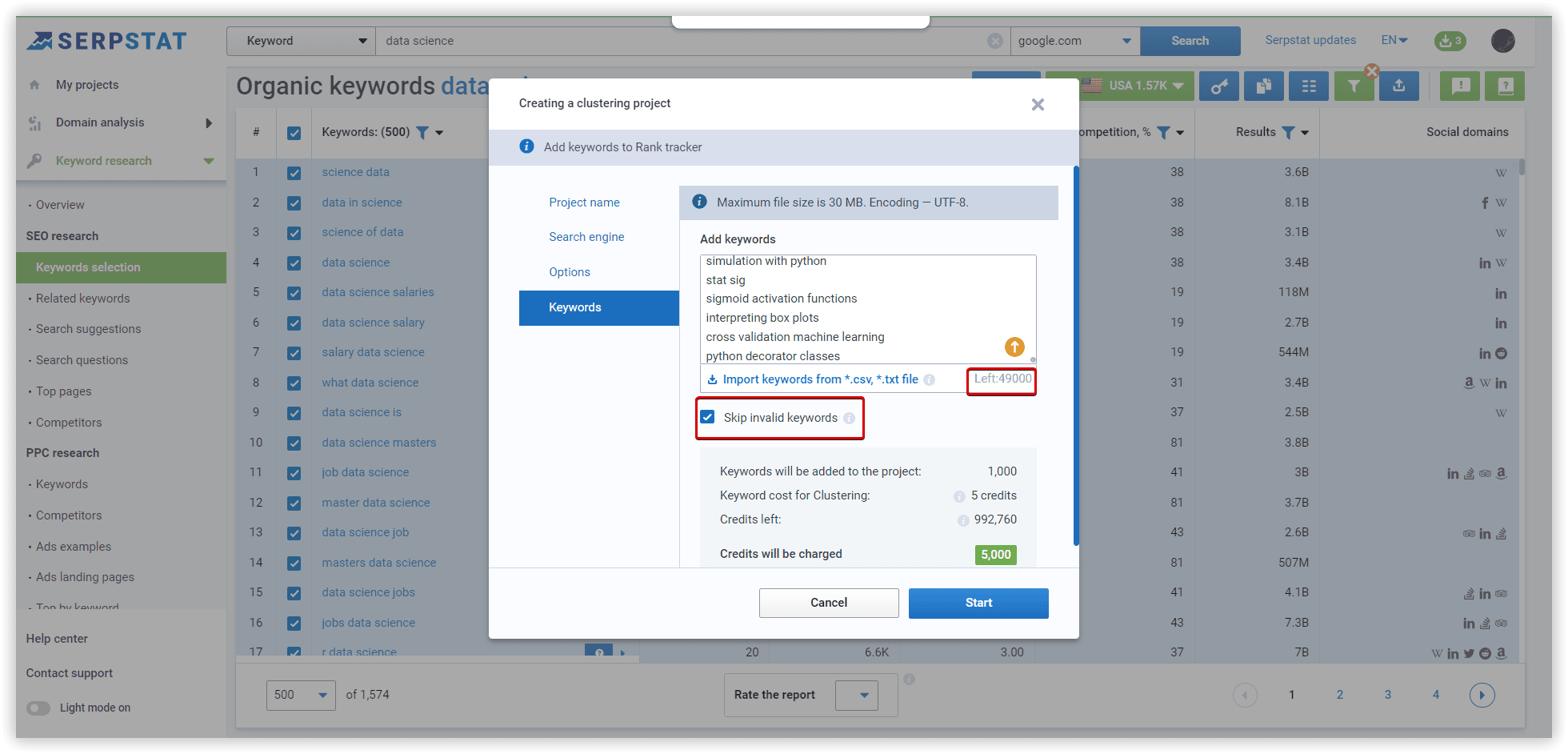
The duration of the clustering procedure in Serpstat is from a few minutes to a few hours, depending on the number of keywords in your project.
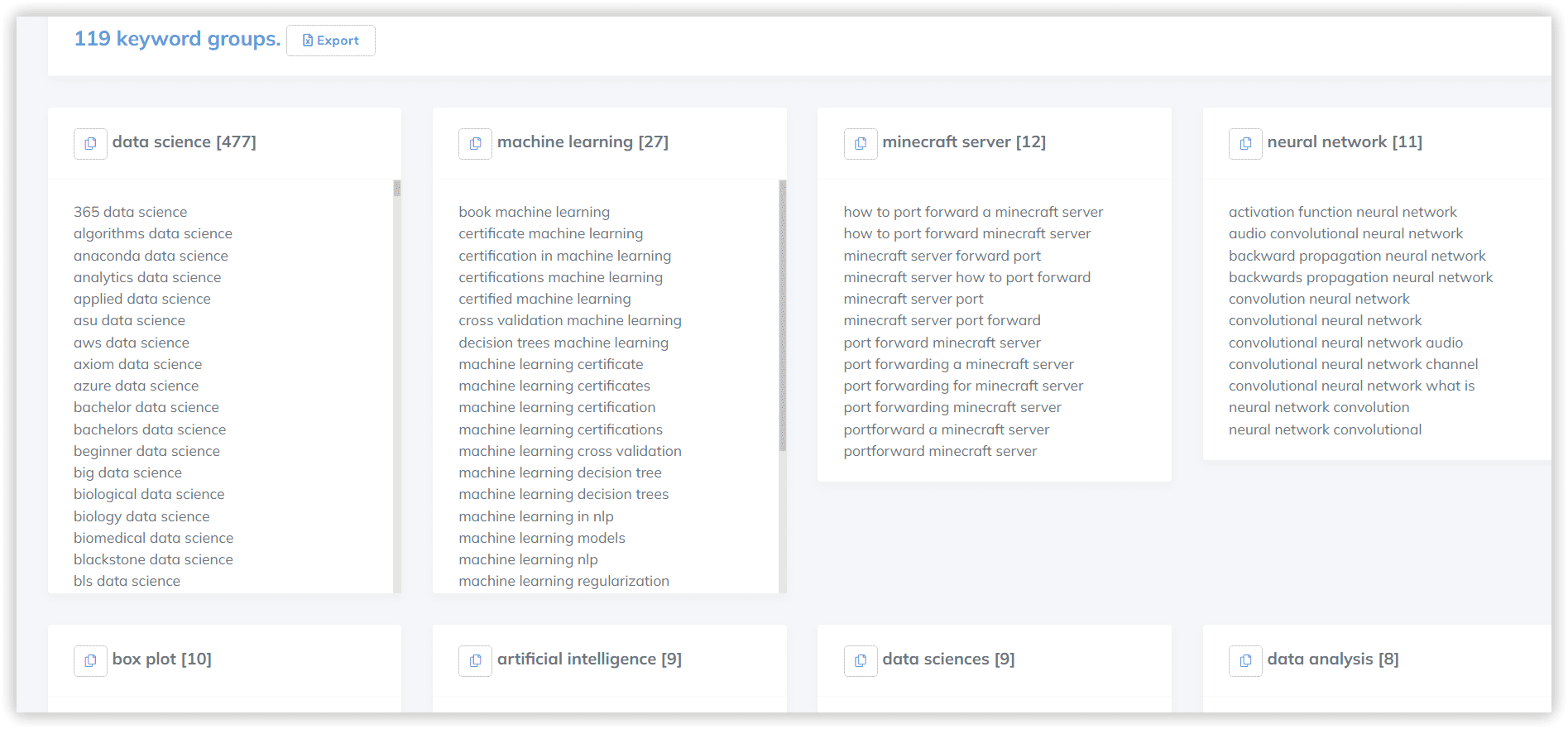
The visualization of Clustering we got using Serpstat by Homogeneity, Group size and Group names can be depicted in this way:
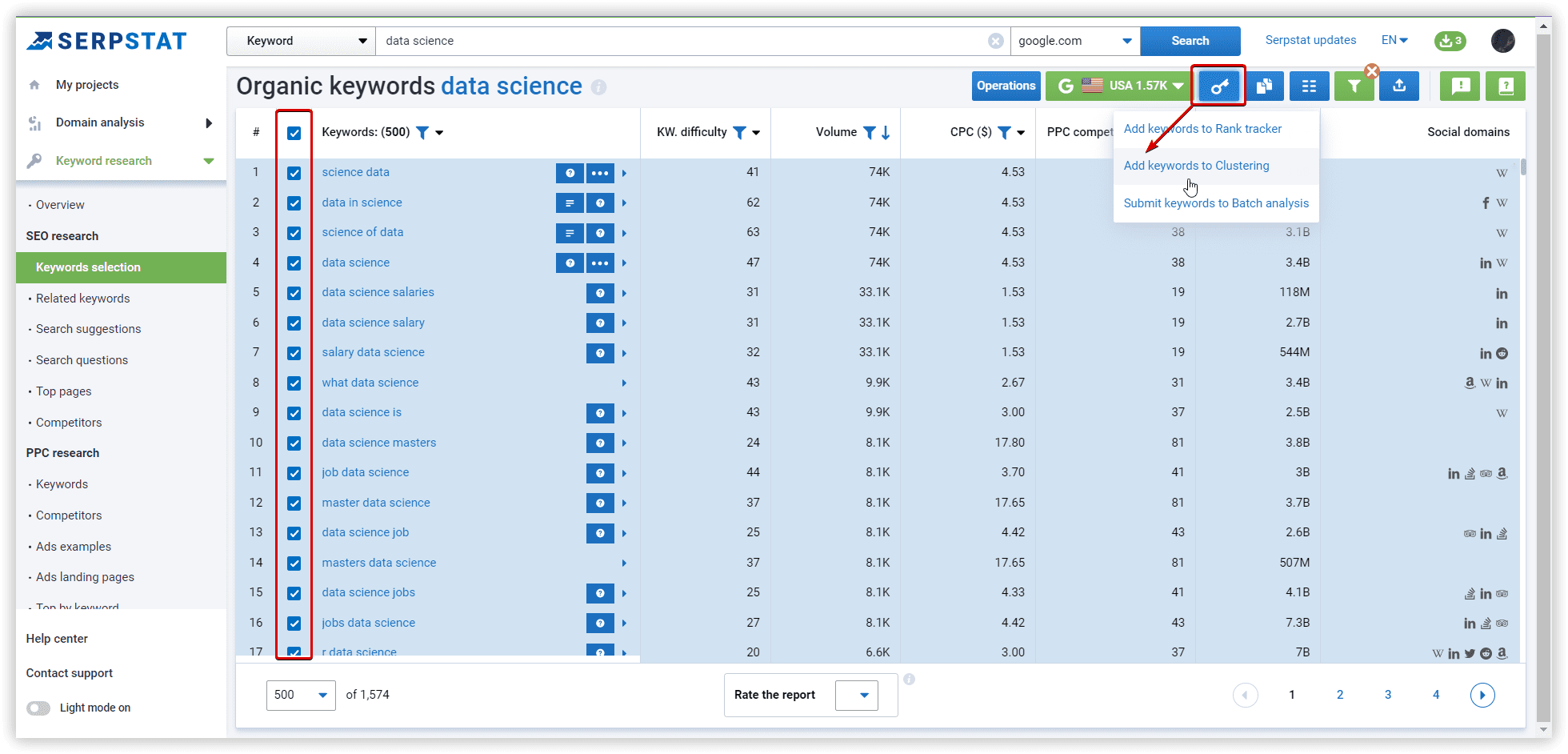
- You have to start a project from scratch in the Rank Tracker to get SERP data. According to your settings, the tool collects data, and matches the web pages from SERPs to every keyword (from top 3 to top 100).
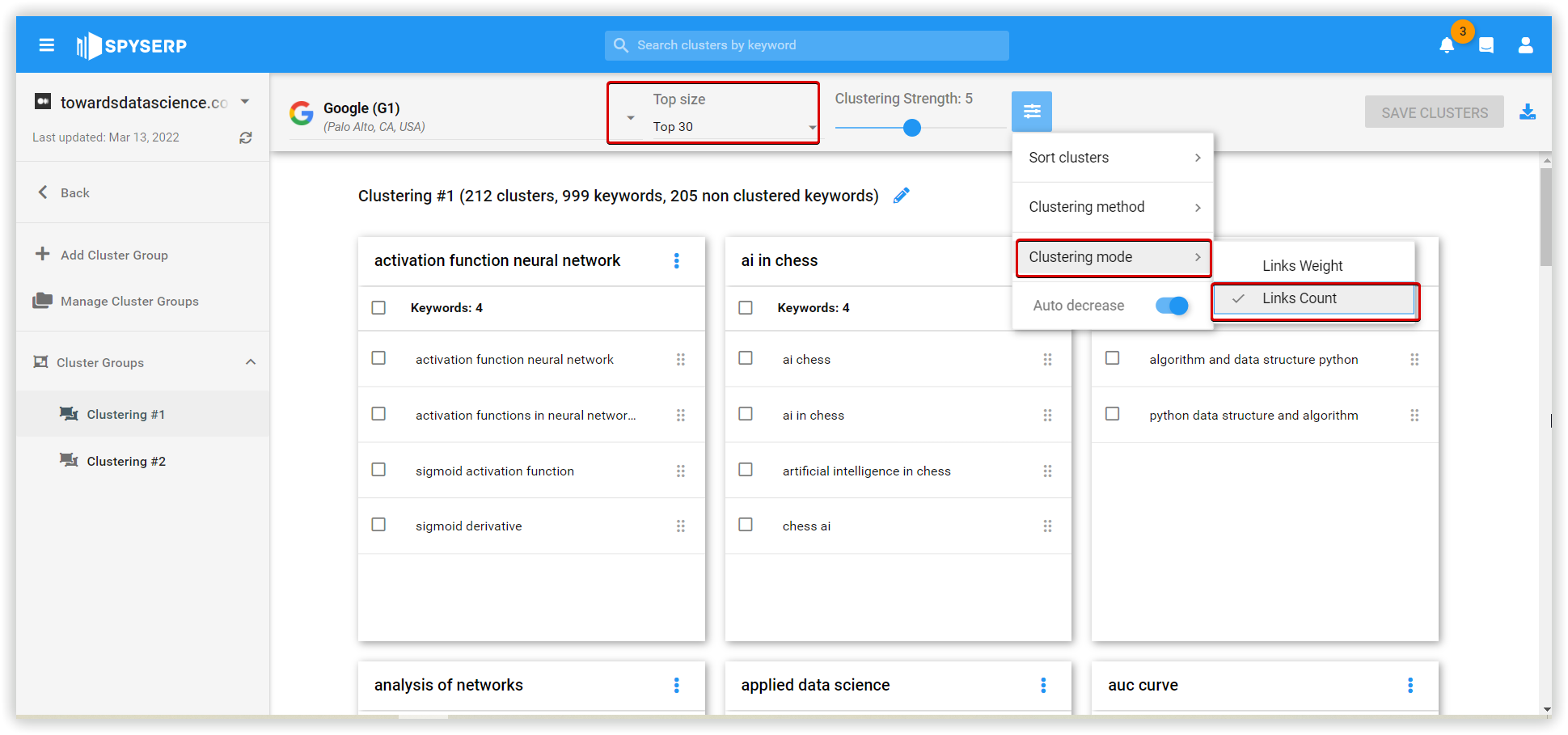
- If the same pages are assigned to various keywords with several matches, a bot will group such keywords. You can also set a clustering power (a minimum number of matches). The lower this metric is - the more significant quantity of clusters will be created. If there are no matches for the keywords in SERPs, they are grouped apart.
There are different types of keyword clustering out there. Soft keyword clustering is a method of grouping keywords around multiple clusters, taking into account the popularity of keywords. In another method - the SERPs are compared with each other, moderating keyword clustering. This method of grouping keywords around multiple groups is based on the relevance of keywords.
The approach is unique because of using two kinds of neural networks. The first neural network focuses on grouping together the keywords you uploaded in very tightly themed clusters to ensure that at least the first level clusters will be correct. Since this action, even if it neglects some keyword relationships that would otherwise make sense.
The second neural network focuses on grouping the clusters created and uses a set of simple rules in its neurons to allow for more "flexible relationships".
Keyword Cupid doesn't use the NLP algorithm, TF-IDF, or other relevancy scores to group keywords together. Also, it doesn't provide the number of SERPs indicating a solid relationship in the cluster. If Google comes up with the next version of its language model and becomes more competent, results will improve.
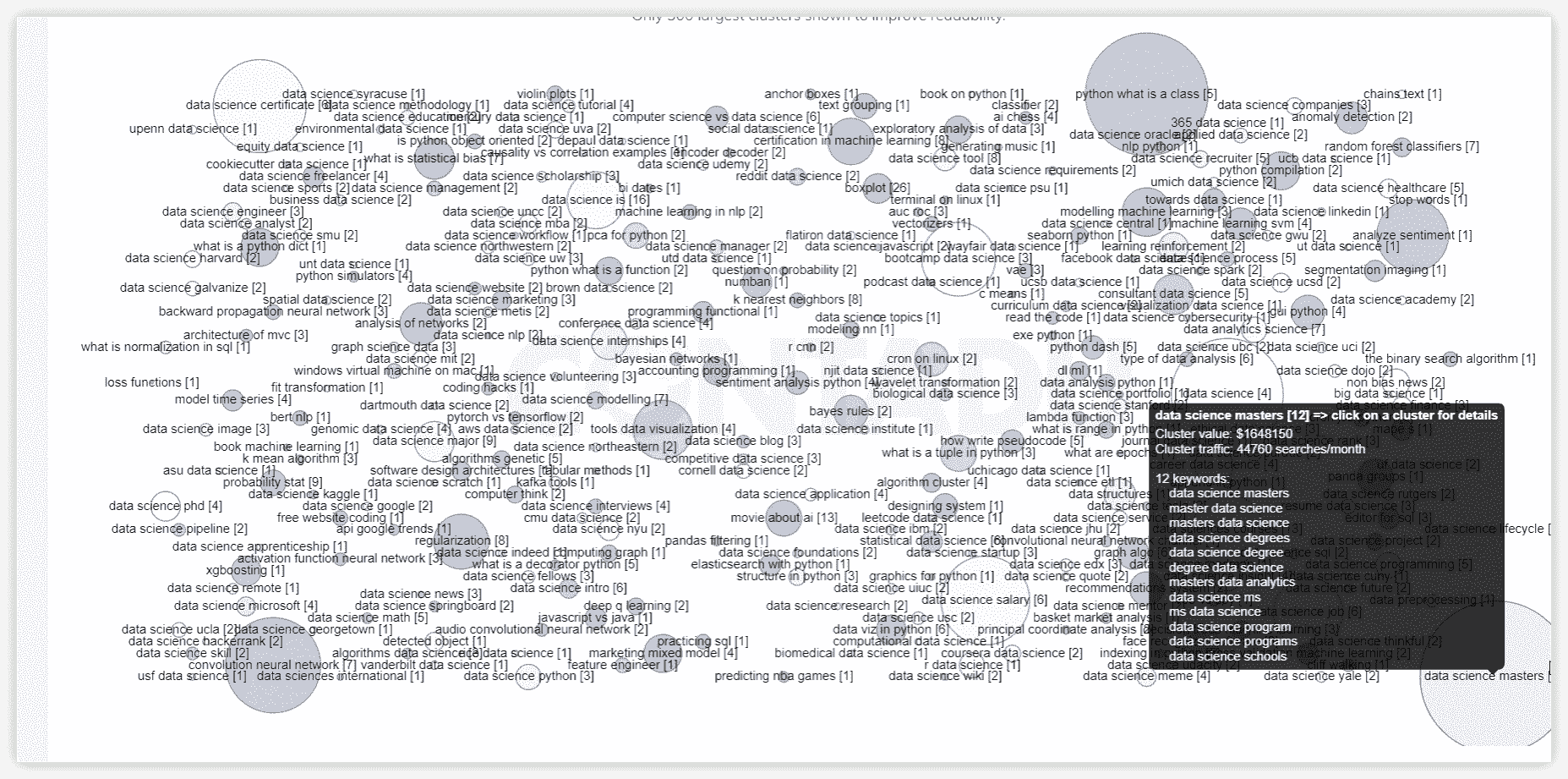
The cluster name serves as the label of the resulting group. In other words, it is used as a model of the themes inside the node (the unit or topic).
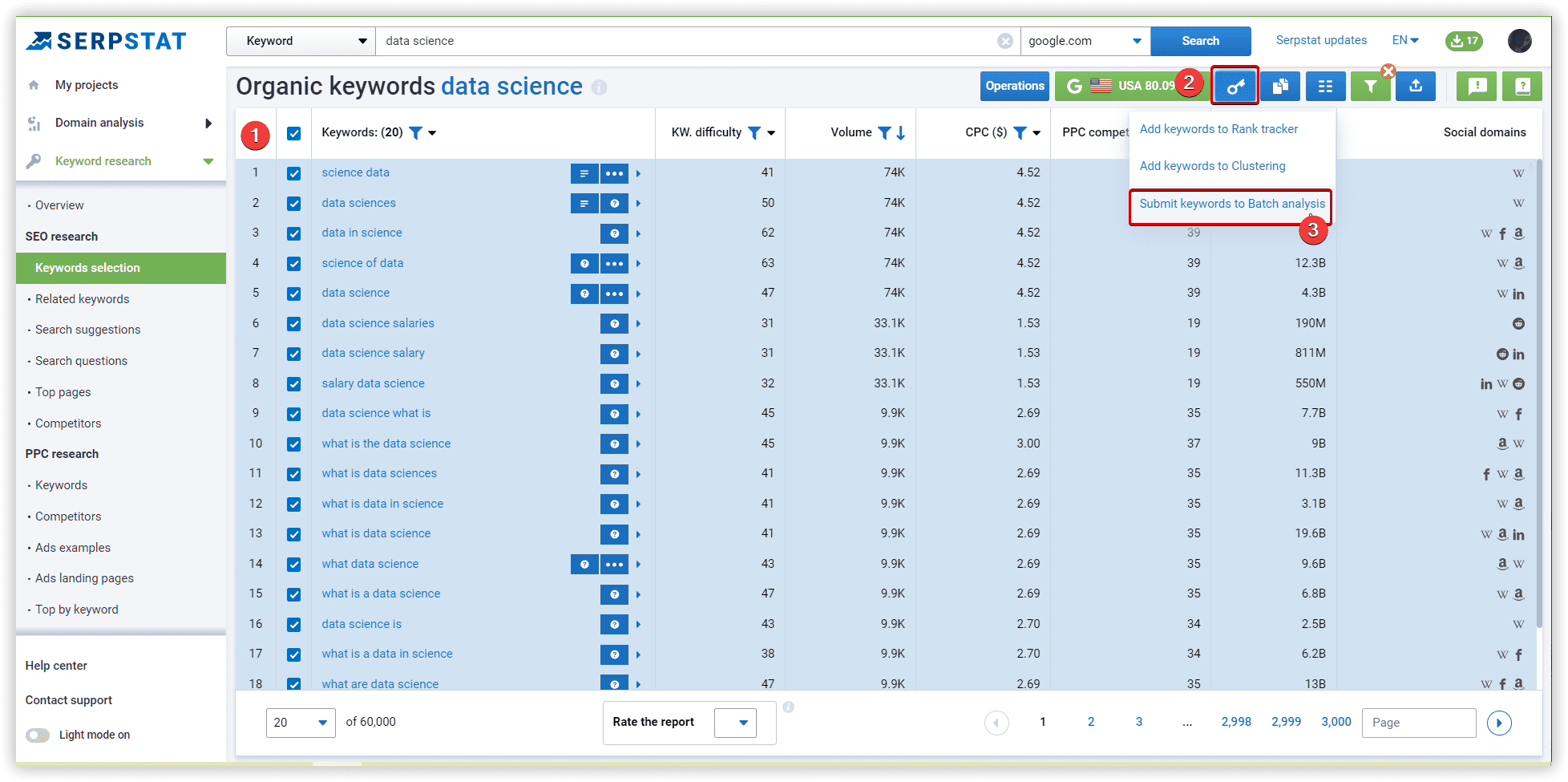
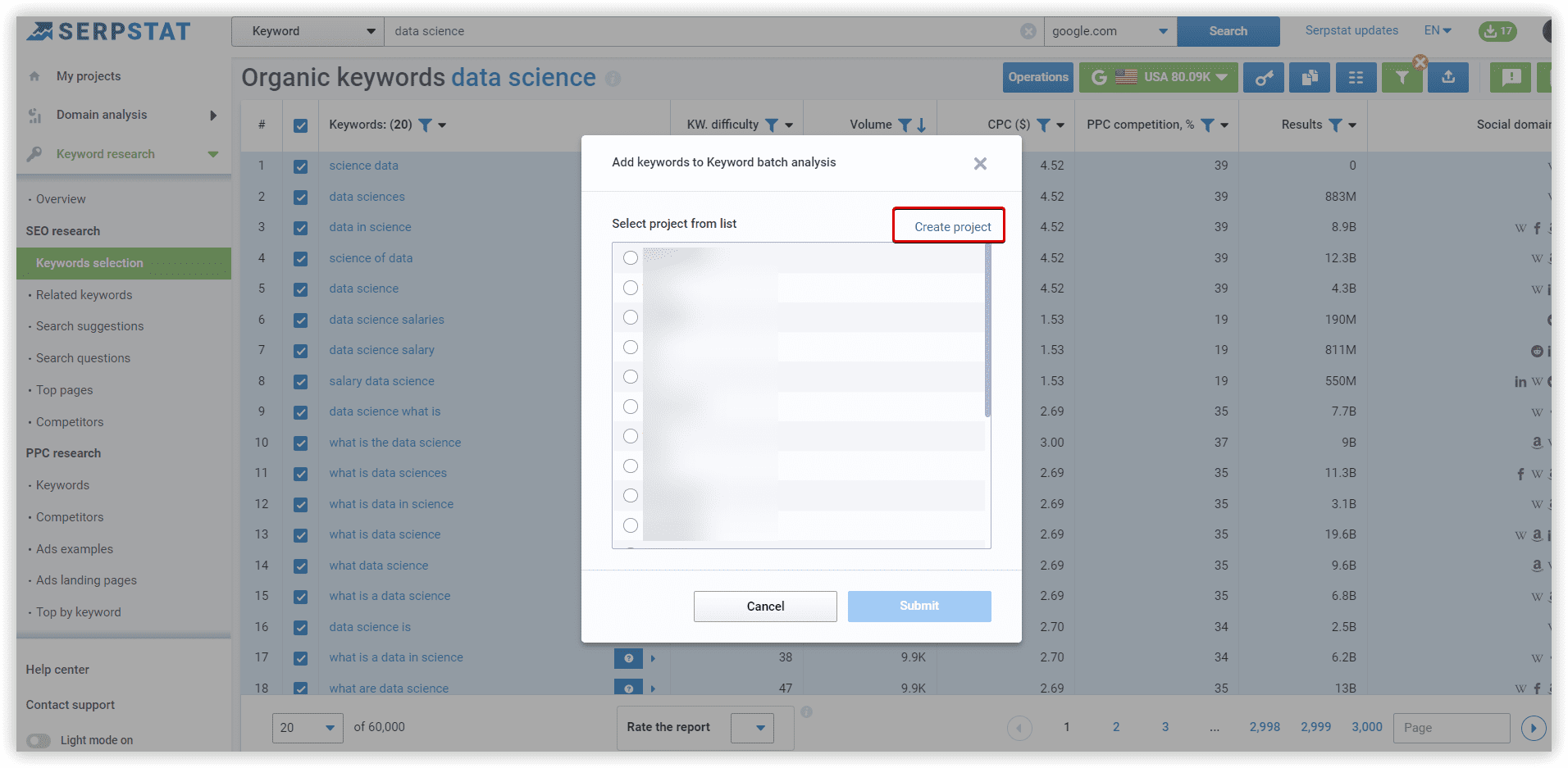
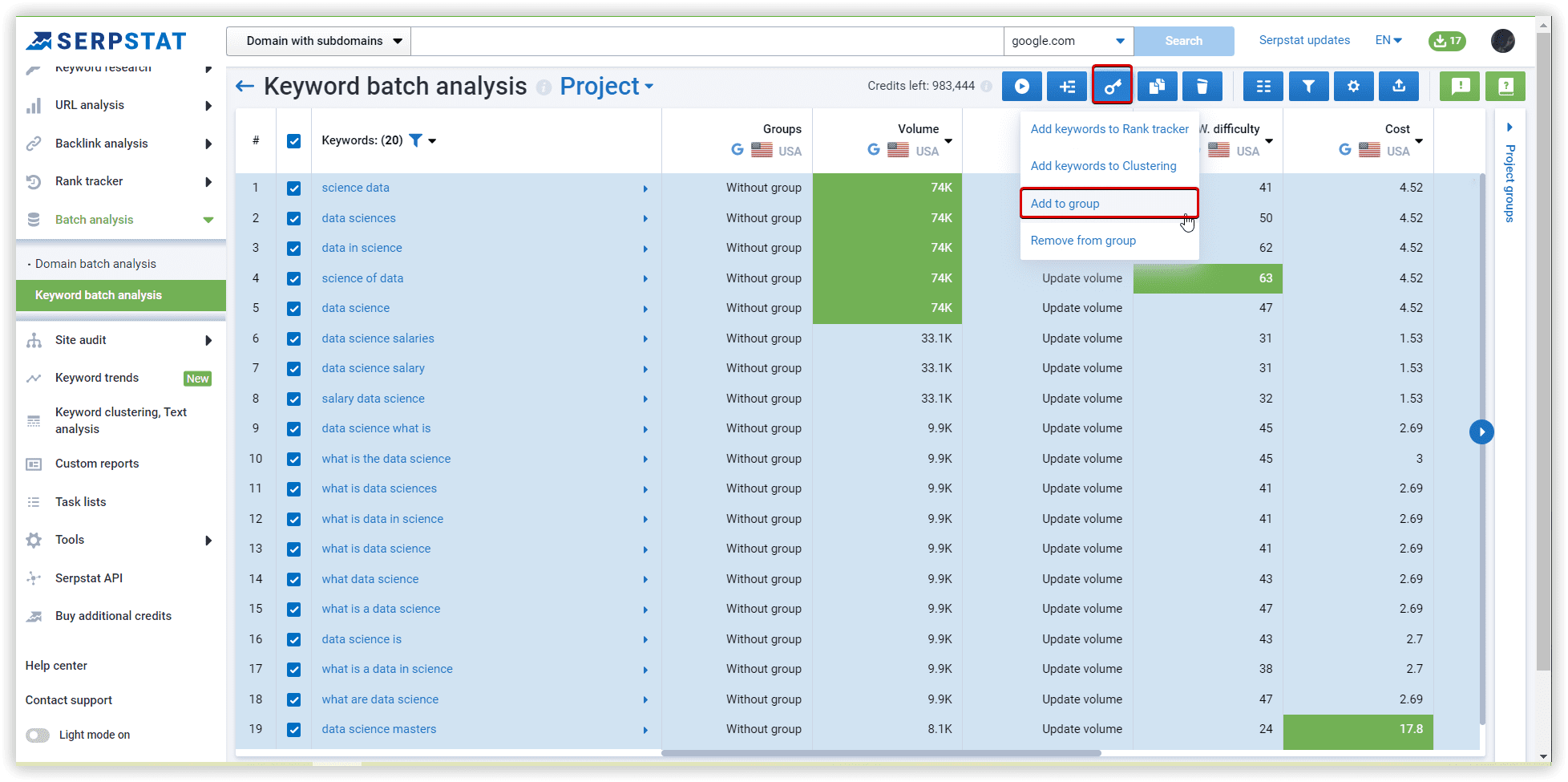
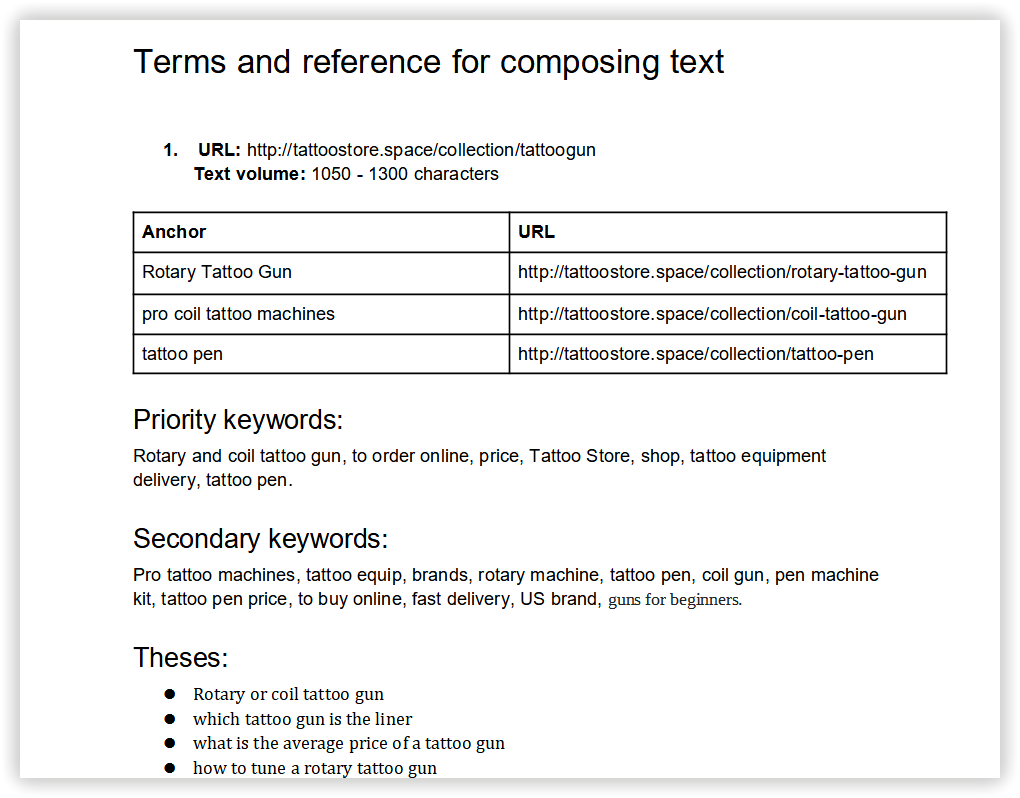
To start the analysis of your dataset, you have to prepare a file with KD, CPC, and search volume. I did it via Serpstat Batch Analysis.
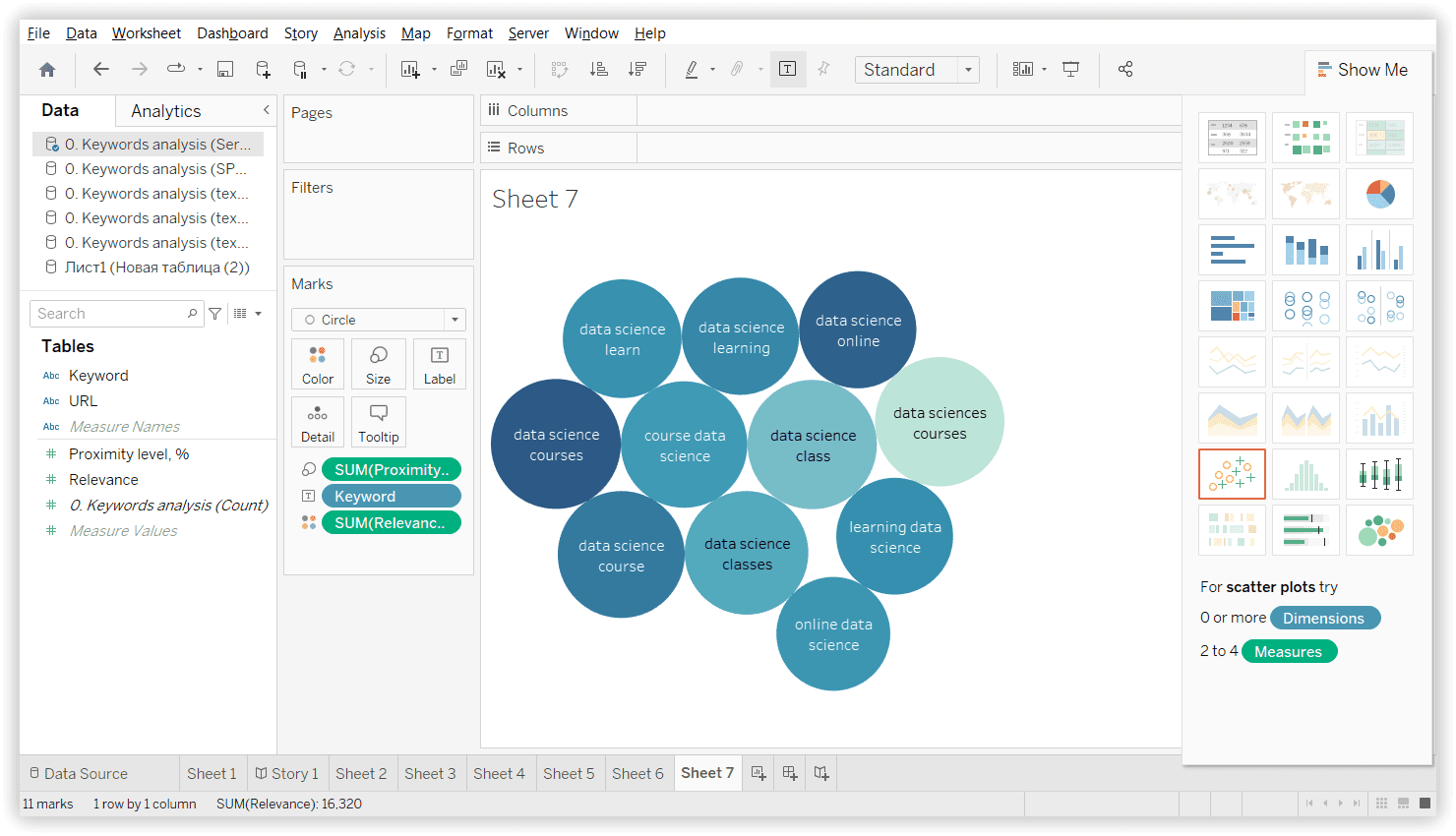
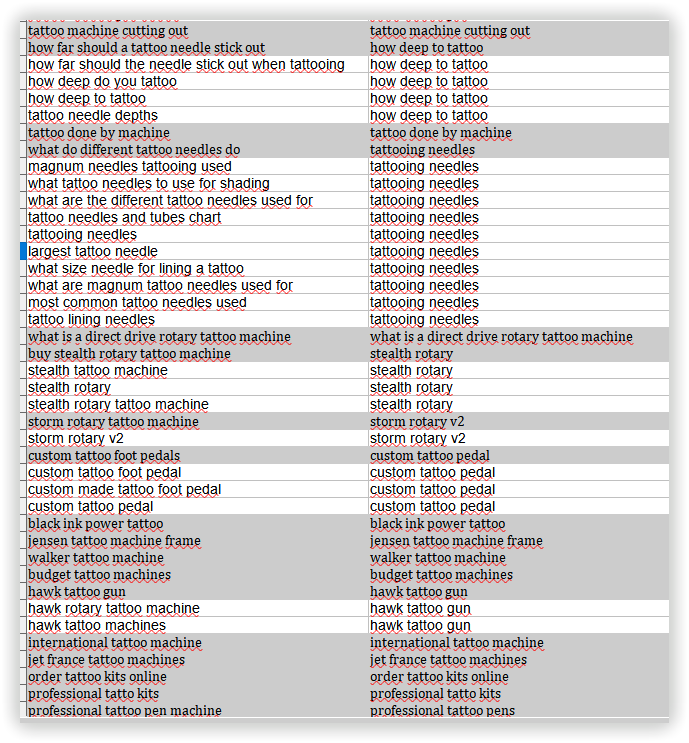
To check the quality of created clusters, we chose one random and common for different tools to compare them in Text analysis.
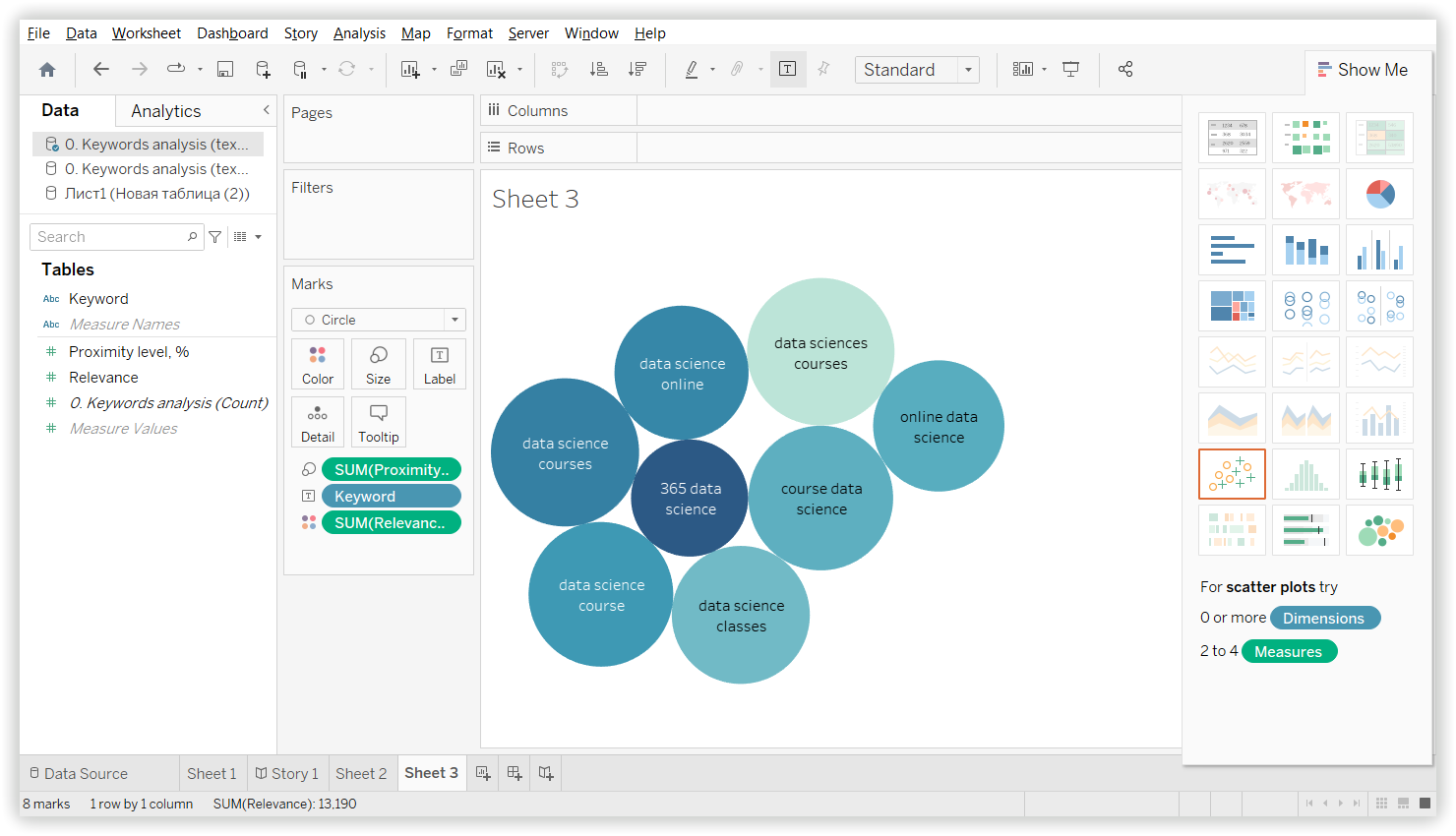
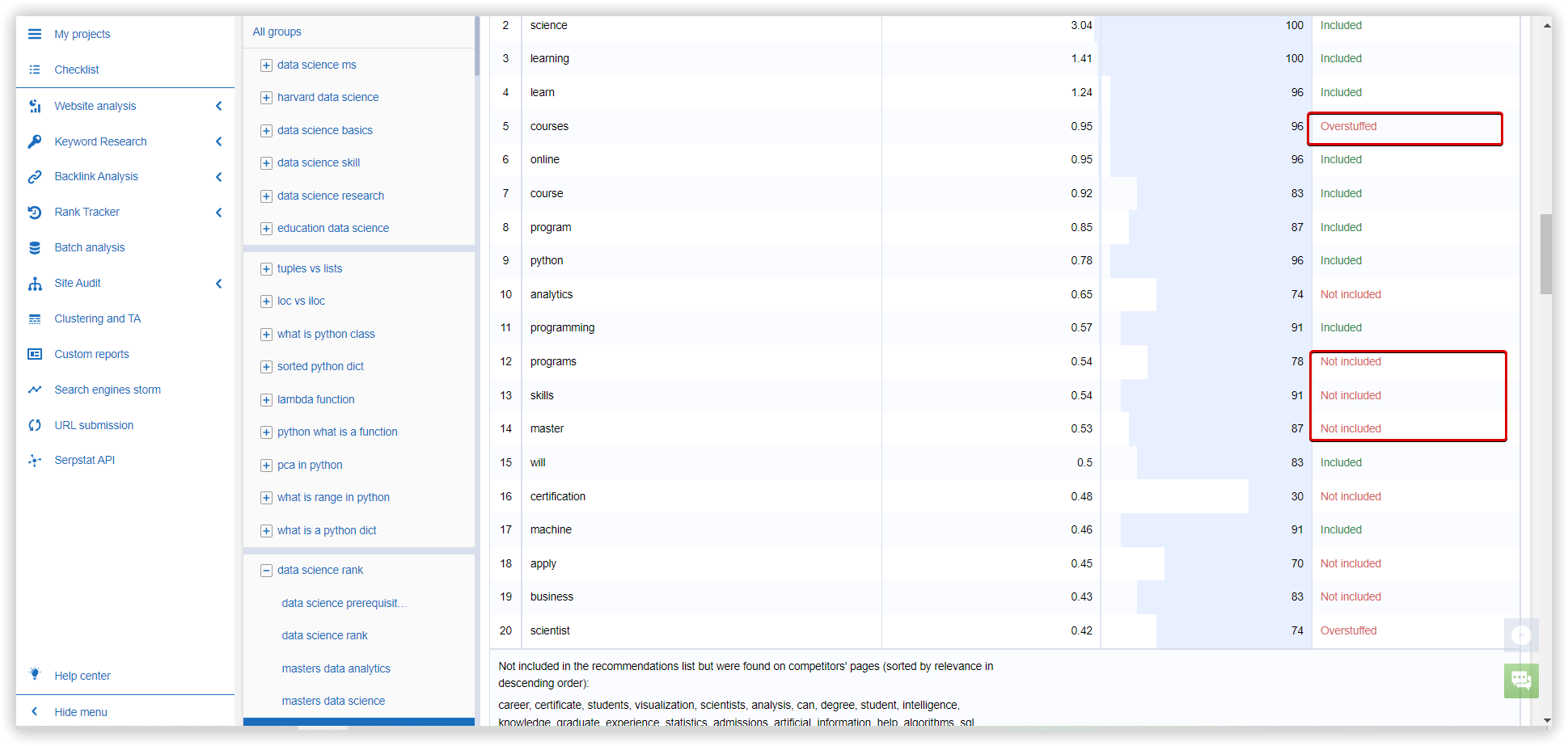
In Serpstat it was “Data science learning” - 13 keywords:
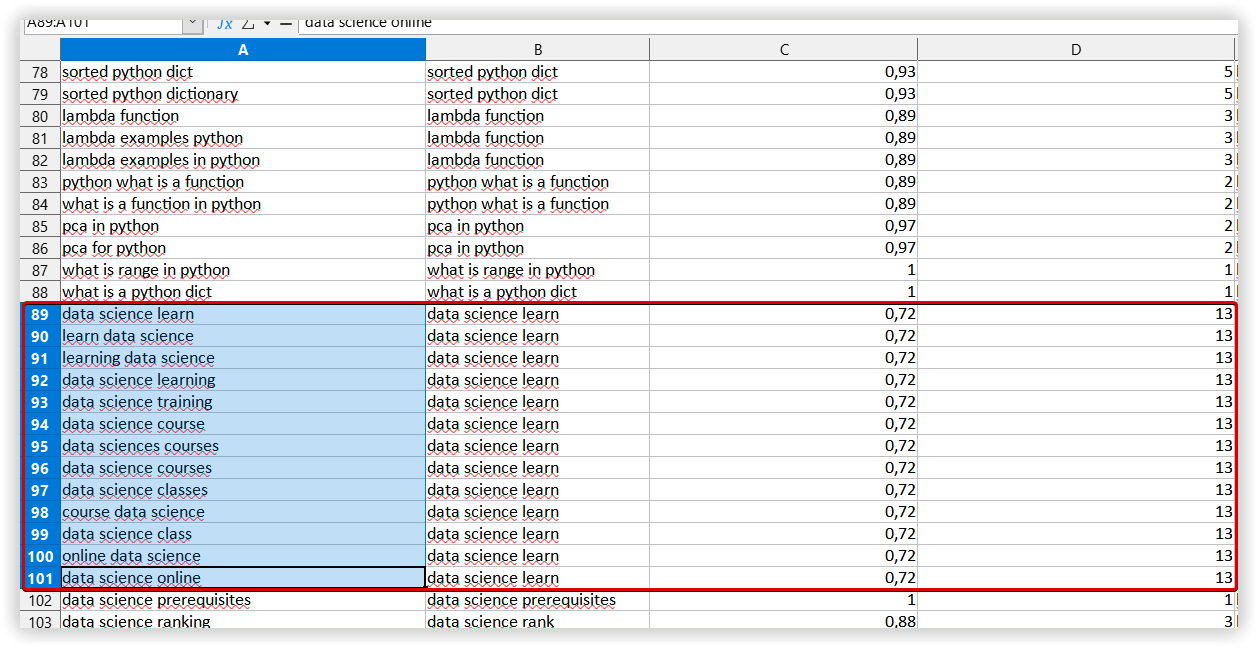
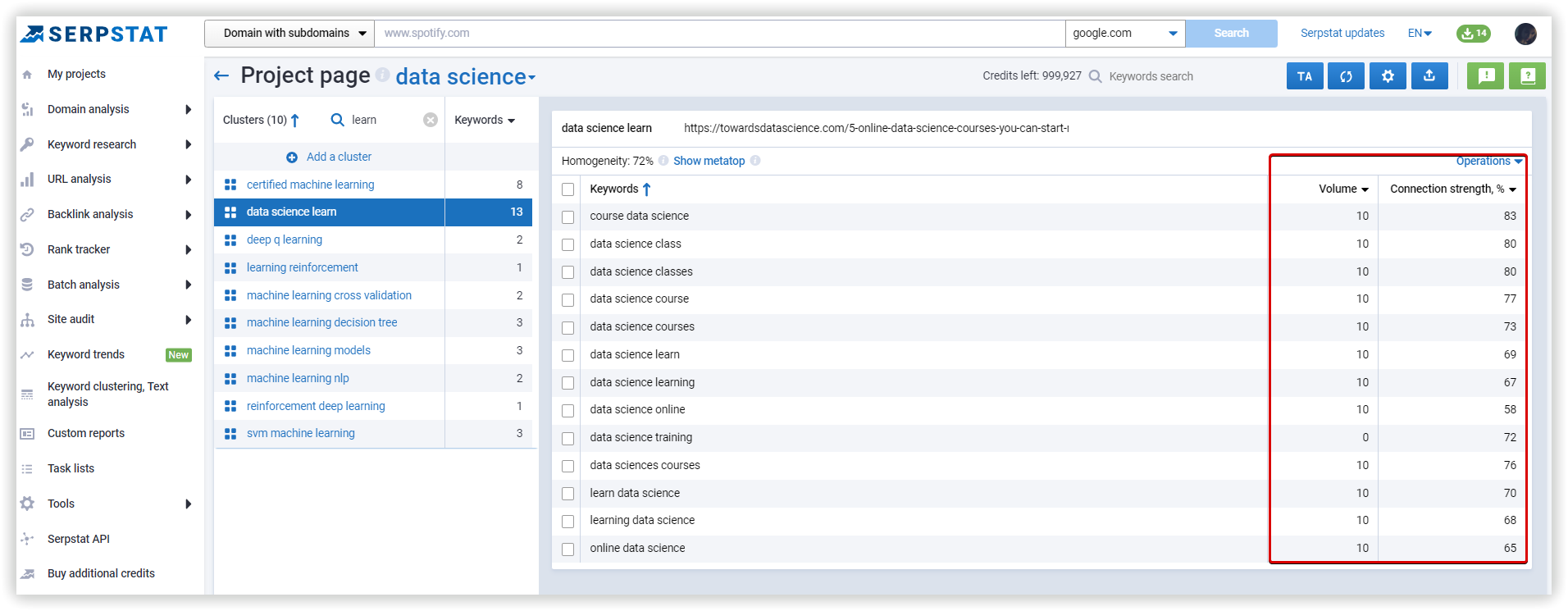
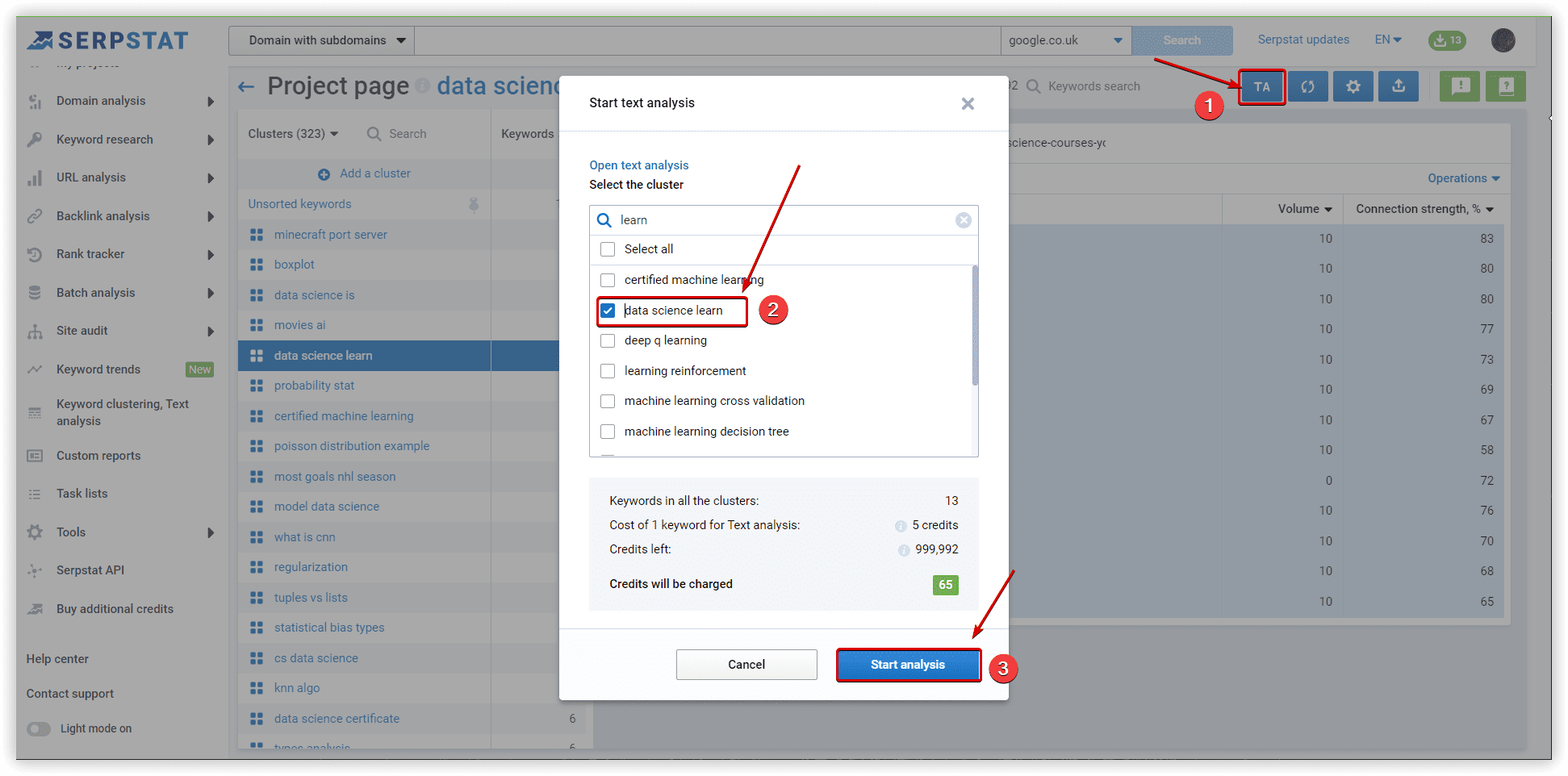
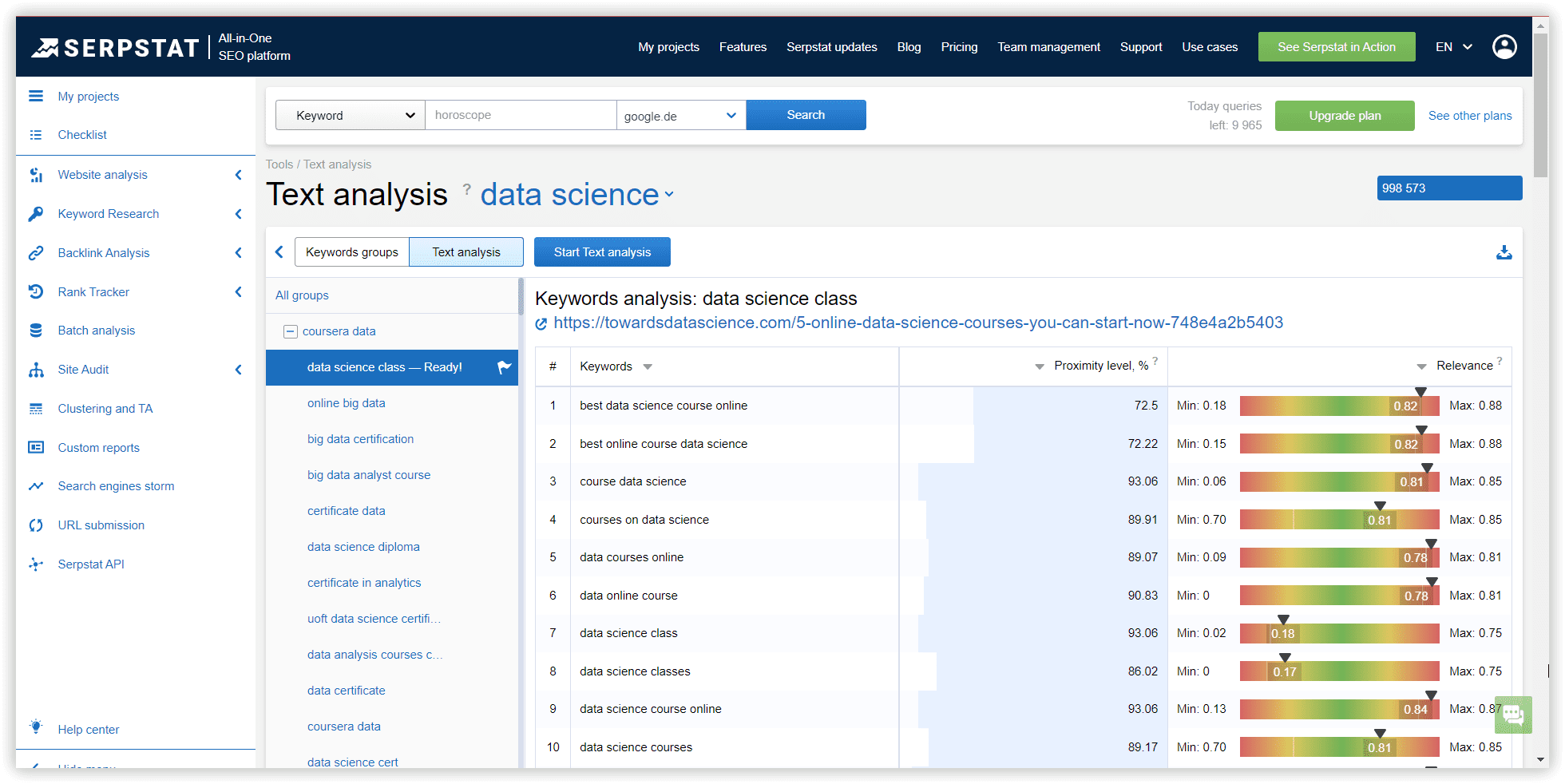
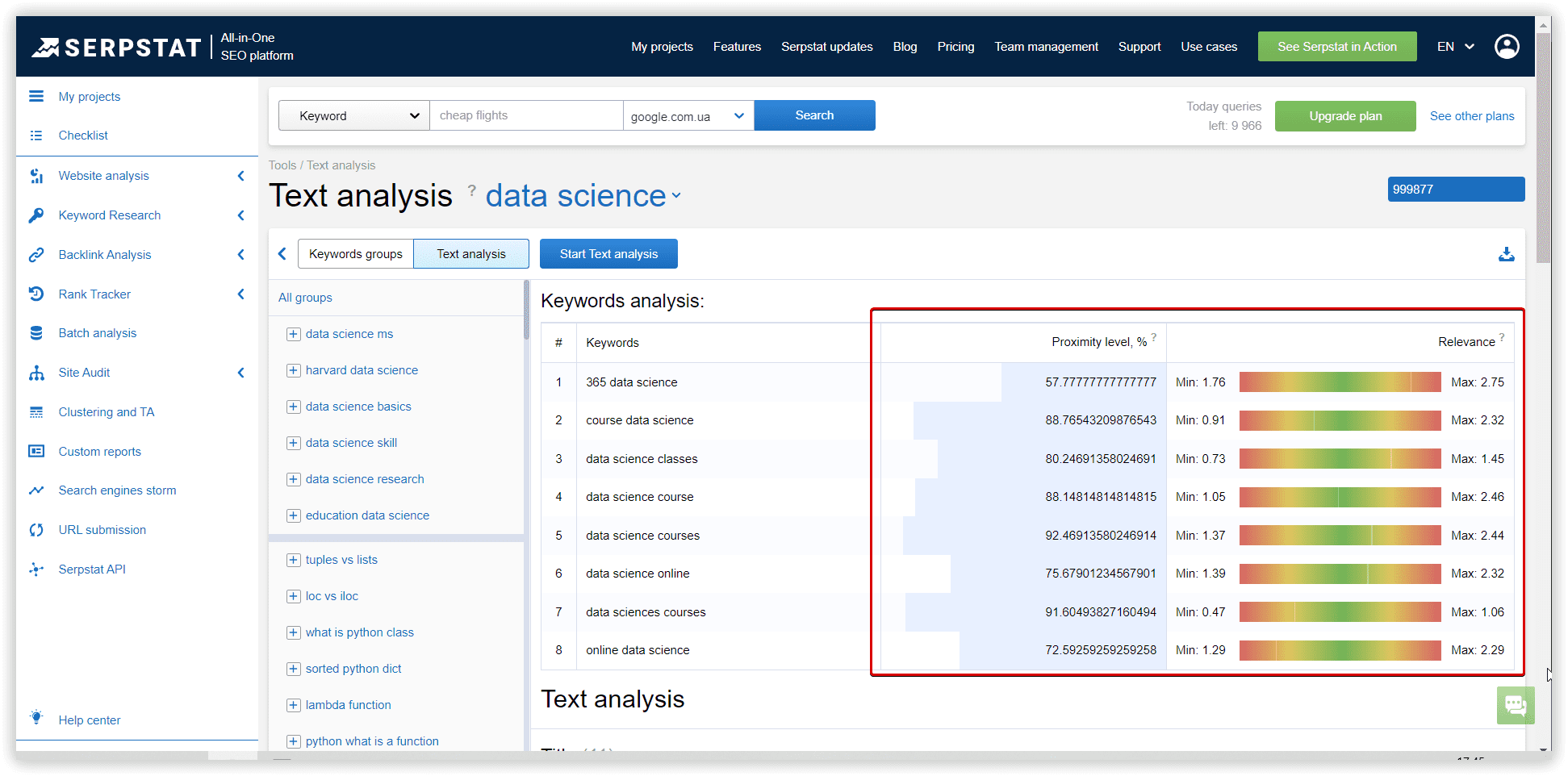
Proximity level indicates the strength of a keyword’s relation to other keywords in the group based on their topics.
Relevance is the keyword and target page subject match. According to the TF-IDF formula, we consider the importance of each keyword in competitors' titles in the metatop. After that, we display the average value for each keyword.
LSI Rank, % - the importance of the keyword for Title/H1/Body in the context of the analyzed subject. This metric is calculated as the ratio of a keyword to a set of keywords used in the text of competitors.
Chance, % - shows how many competitors use this keyword, popularity. The score shows how important it is to use the keyword. The higher the score, the more necessary it is.
The exact match metric (%) shows how often competitors use the exactly matching keyword.
Text analysis result example, Serpstat:
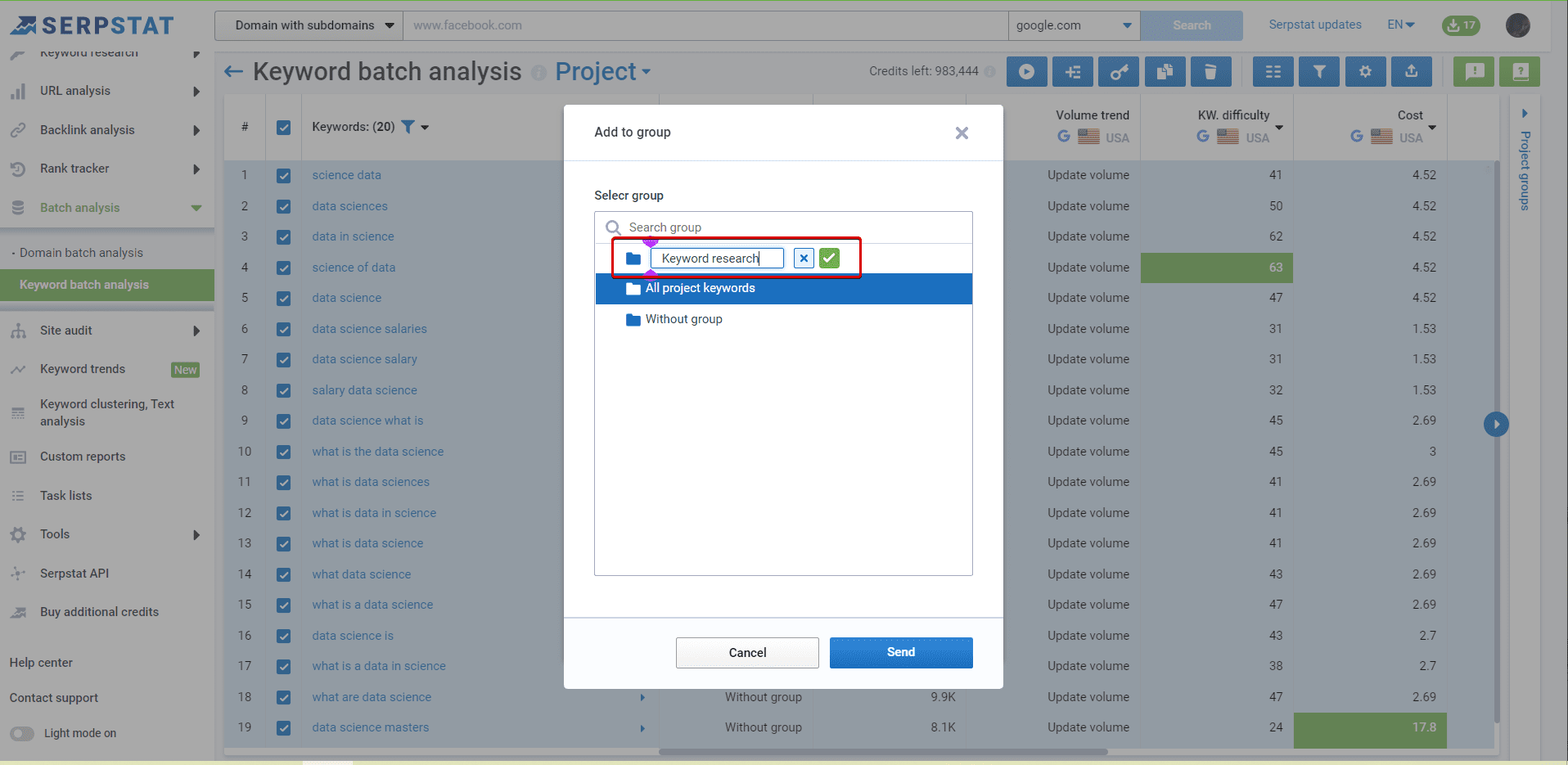
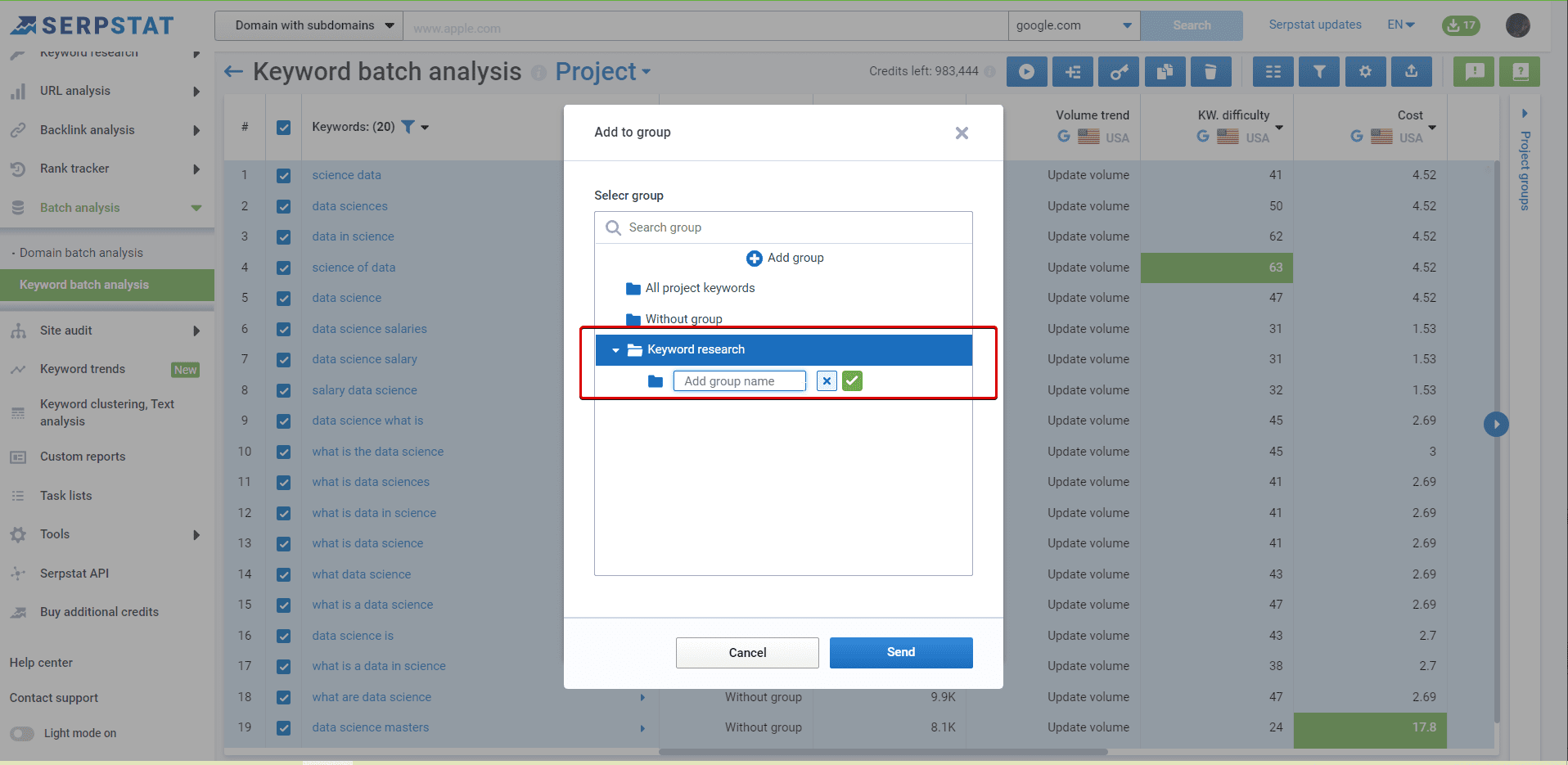
To add a new cluster, use the button :
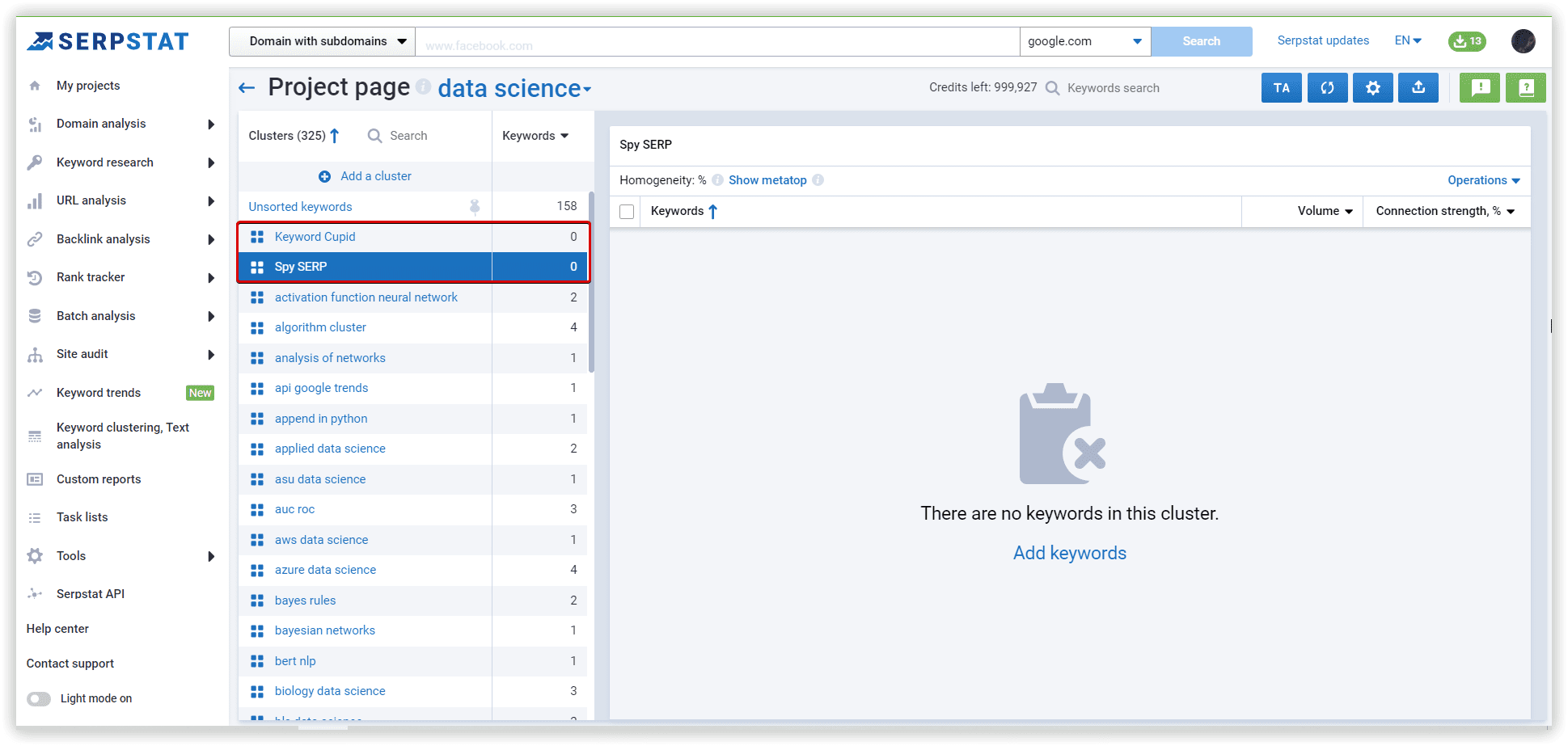
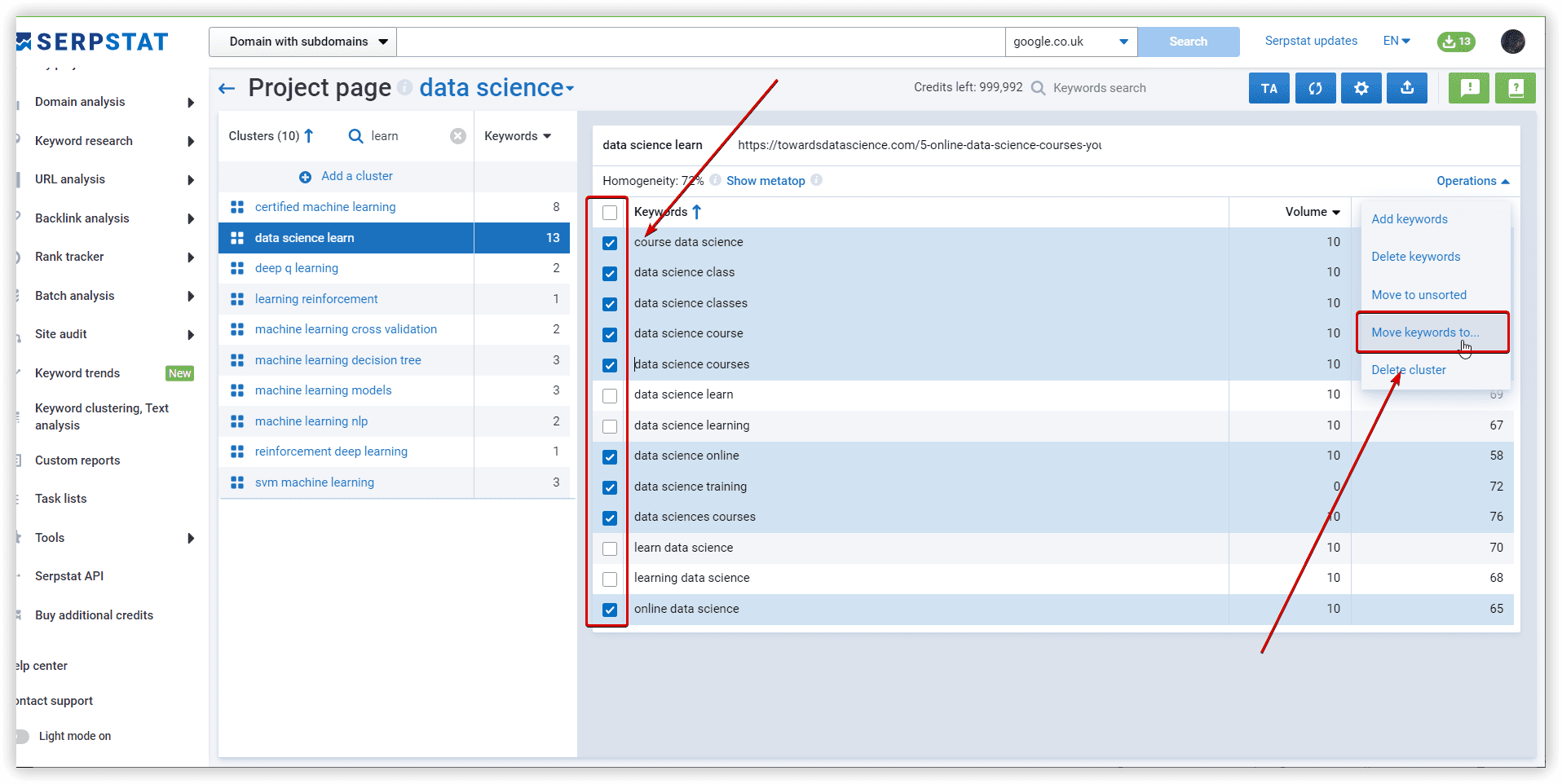
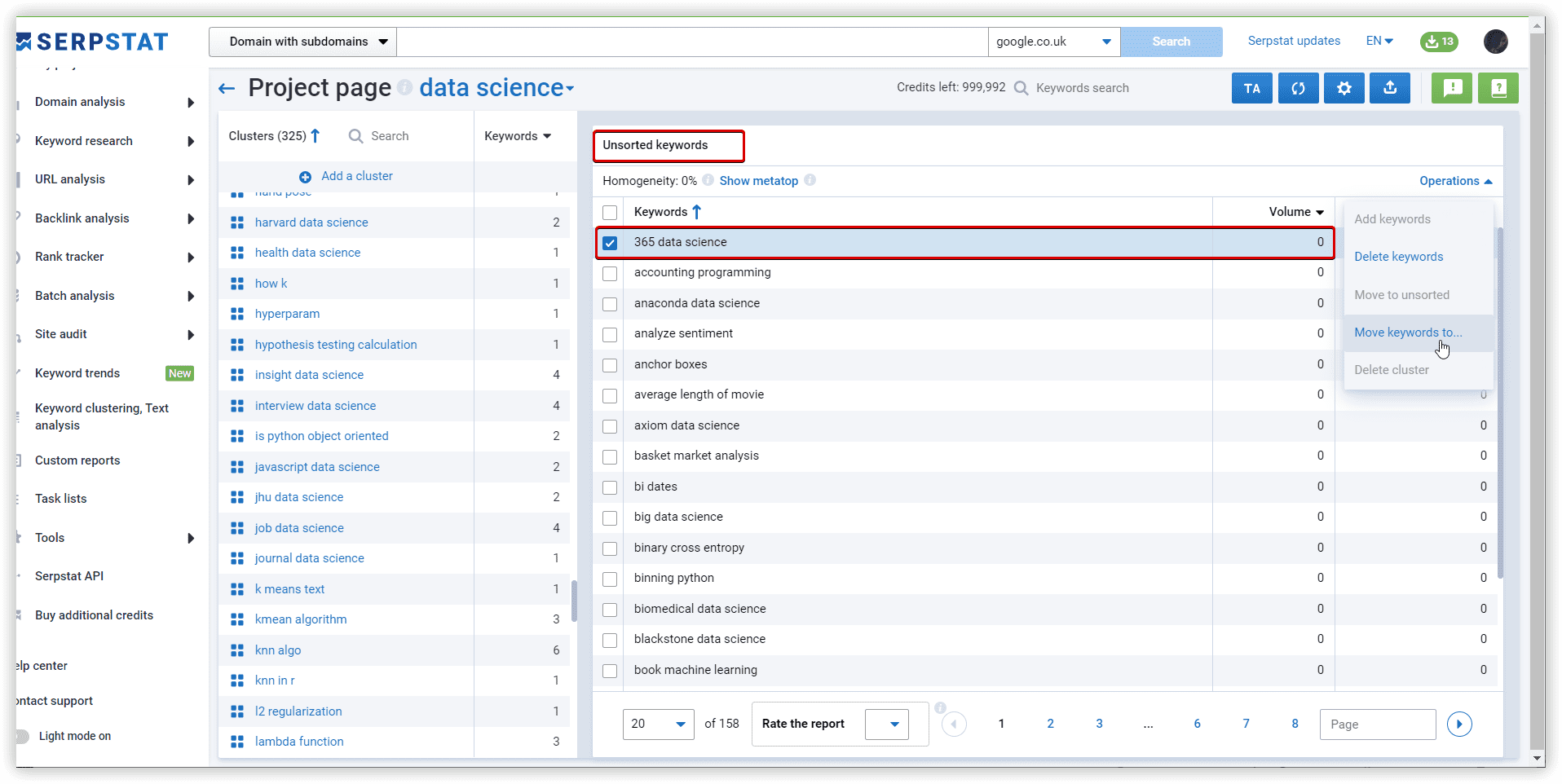
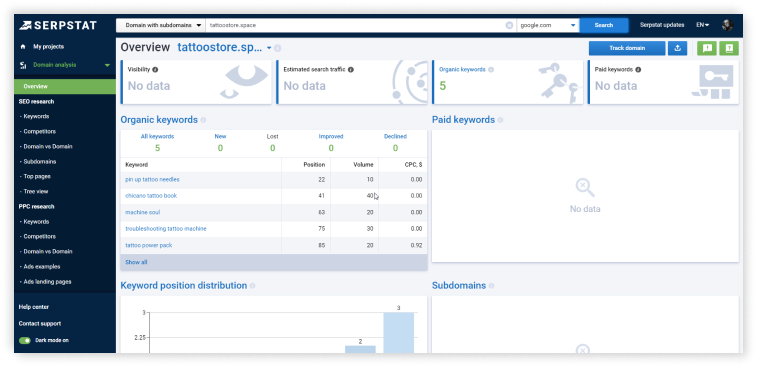
Results
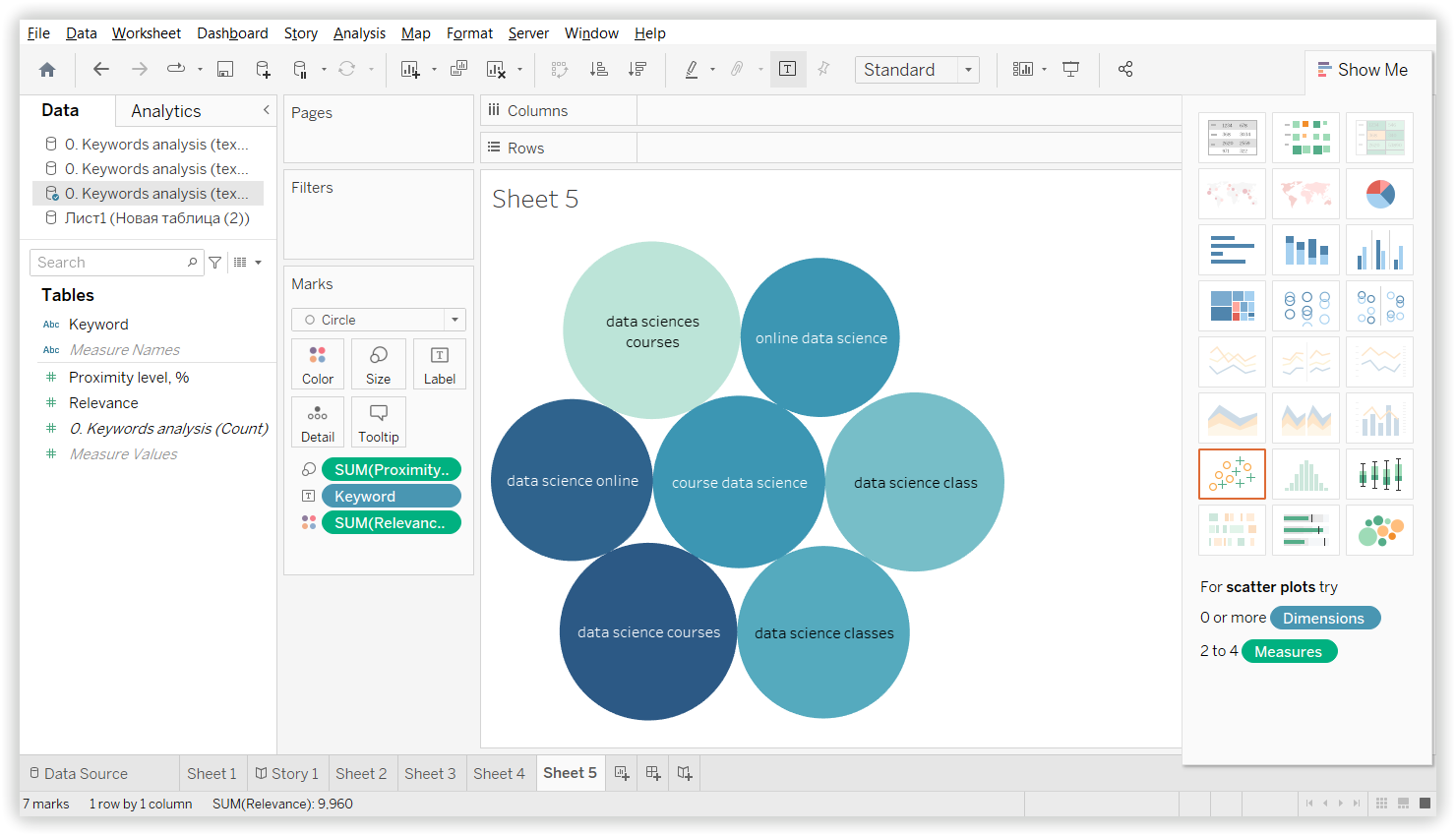
Than, we moved least 8 keywords to Spy SERP cluster.
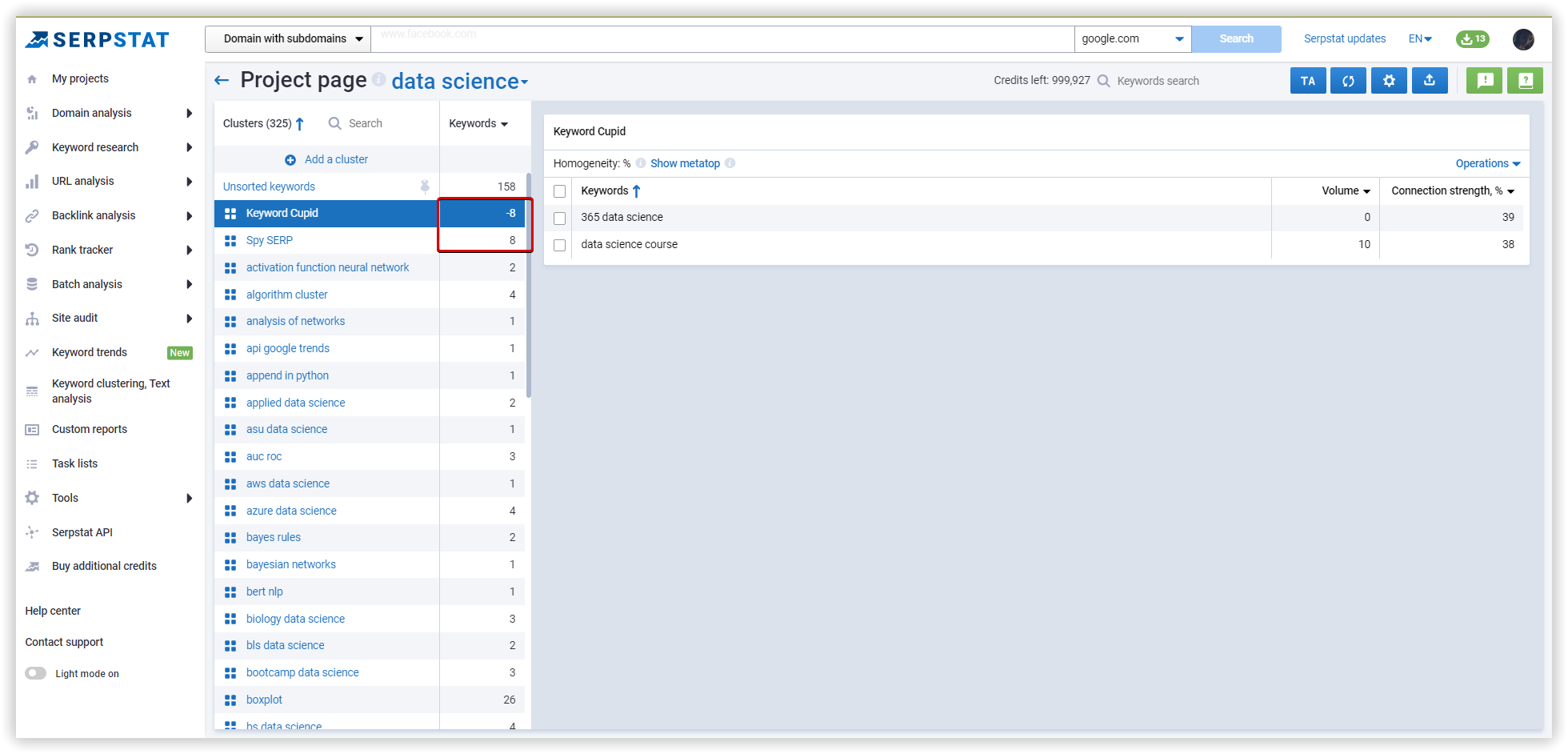
As a result:
Features of Serpstat Clustering
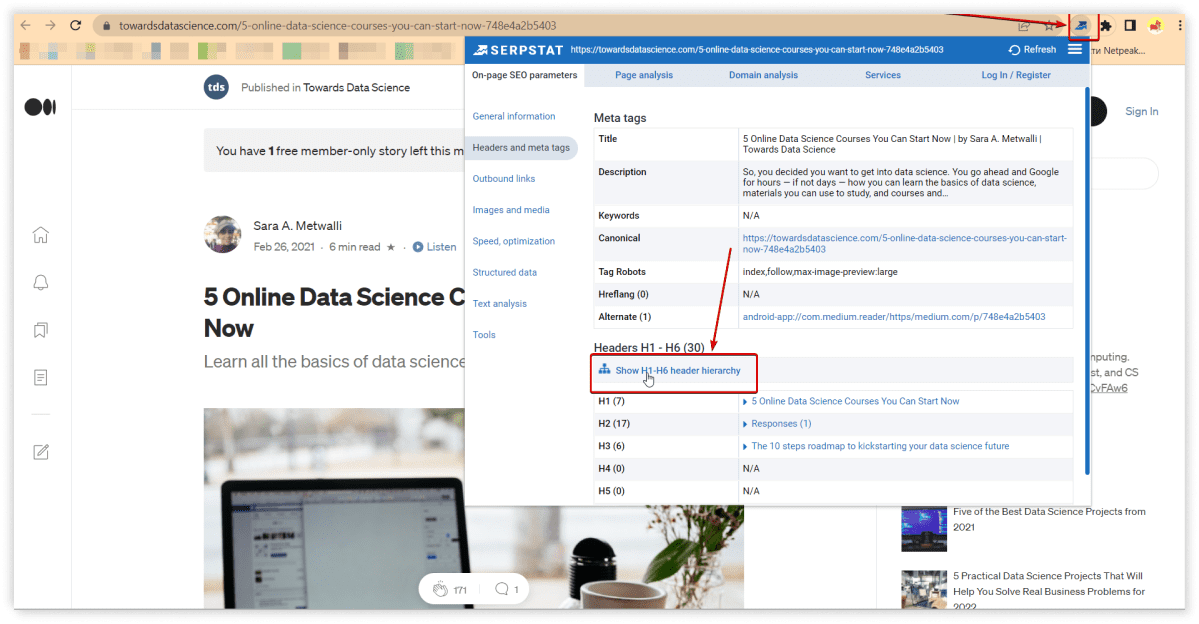
Further, you can double-check this issue within our extension, Serpstat SEO Checker:
Use-case from author’s practice
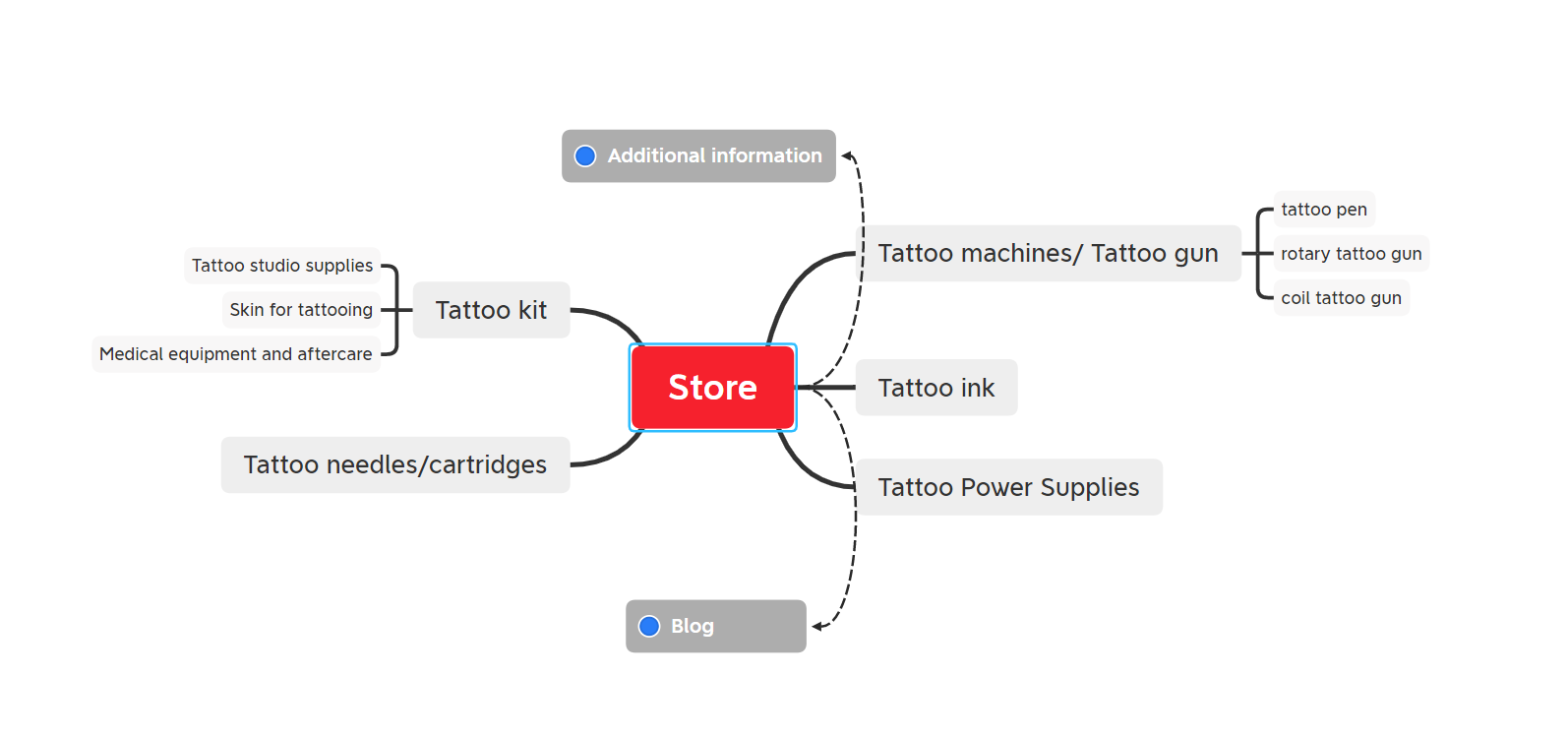
What goals have I set?
This structure should be followed to ensure that content ranks well in Google US by focusing on high-volume and relevant keywords.
How exactly does Serpstat help to achieve the goals?
Results
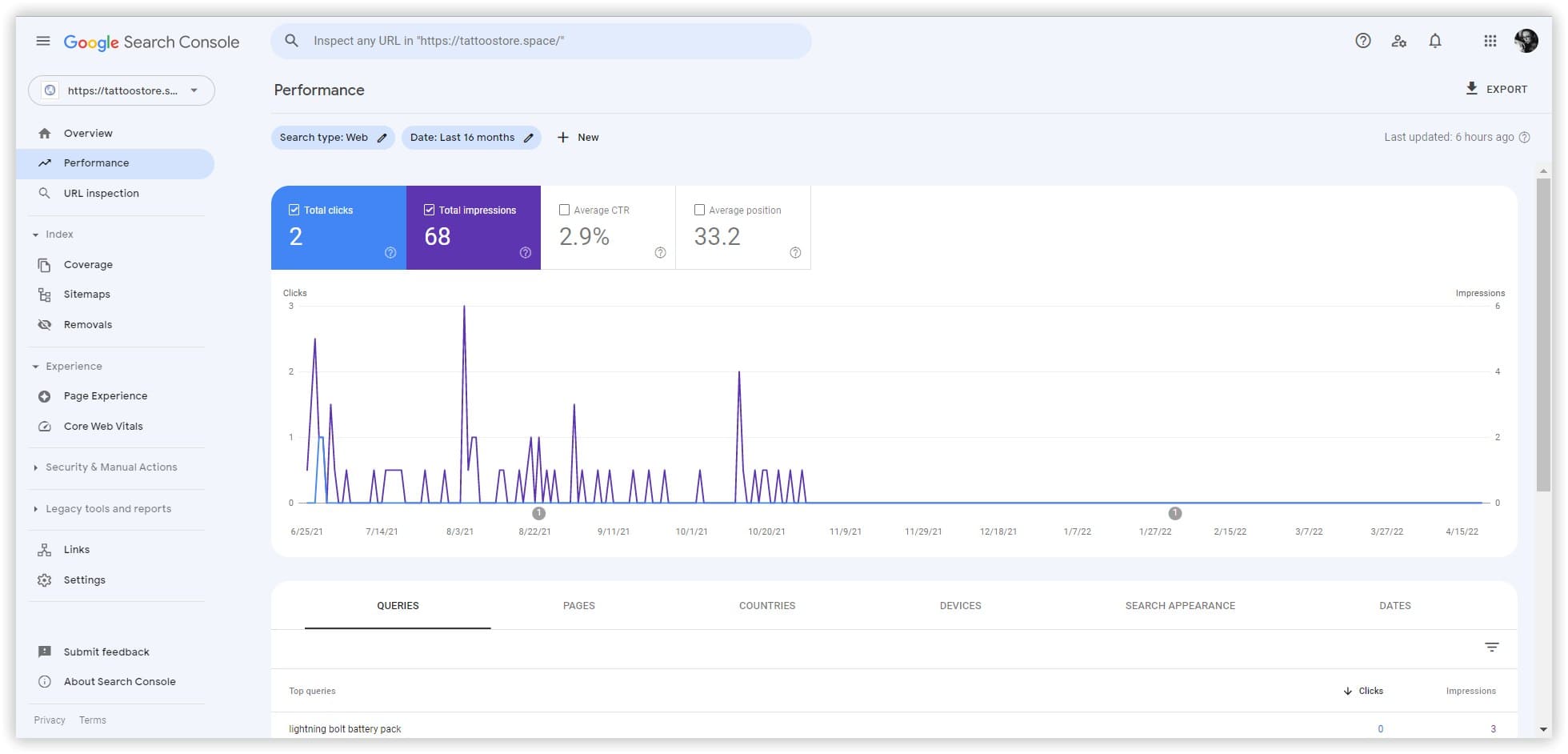
I got the result I expected and even more just prototyping a website for fun.
FAQ
How to create a keyword cluster?
To create a keyword cluster, sort your keywords by similarity, and group all related keywords or use Serpstat Keyword Clustering Tool.
What is keyword grouping?
Keyword grouping is a process of creating groups with related keywords.
How to group keywords?
Sort keywords by similarity and group related keywords in one cluster or use Serpstat Keyword Clustering Tool.
Conclusions
In addition to increasing organic traffic through useful and well-structured content, clustering can also help organize internal linking more efficiently, and expand the keywords' pool in a certain niche easier.
Keyword Clustering is the easiest way to optimize one page for multiple keywords with the same search intent. For quick and easy work with the site's keyword pool, you can group up to 50K keywords into clusters using Serpstat. With keyword clustering, you will be able to conduct more accurate keyword research and save time.
Keyword clustering assists in planning and optimizing content that targets several related keywords on one web page. Based on matching search intent, this data grouping uses machine learning algorithms.
Using text analytics, you can improve the relevance of your content on top of the clusters and take into account the top 15 results in the region.
We investigated the clustering processes in the context of machine learning and compared the results using Text analytics. With similar SERP-based algorithms, we evaluated the relevance of each cluster created by the same dataset to improve your content.
Keyword clustering requires site owners to think bigger about their content.
Speed up your search marketing growth with Serpstat!
Keyword and backlink opportunities, competitors' online strategy, daily rankings and SEO-related issues.
A pack of tools for reducing your time on SEO tasks.
Recommended posts
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.