Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
How to Improve Your Conversion Rate by Maximizing Search Intent
But for you to be visible in the first place, your content must be crafted the right way. It should be optimized for search intent.
In this article, we’ll discuss how you can improve your conversion rate by maximizing search intent.
- Gabe GayhartDigital Marketer & SEO
at Bruce Clay - Debi NortonInternet Strategy Consultant & Founder of BRAVO
- Jonas SicklerSEO Manager at Terakeet
- Marco GiordanoSEO & Web Analyst at Sika
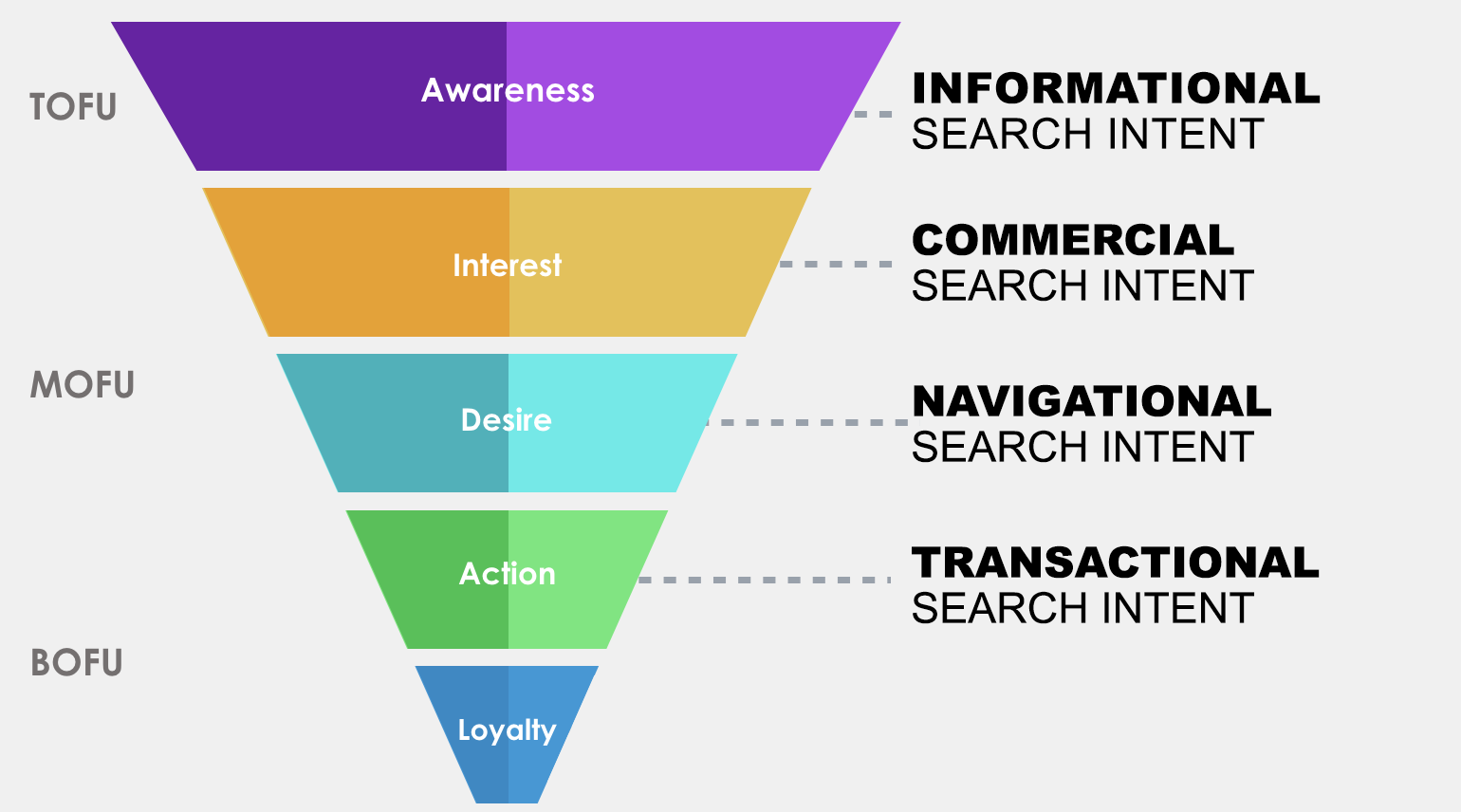
Four Different Forms of Search Intent
Online users use informational search queries to scour the web for information. So, questions such as “How big is Noah’s Ark?”. “What’s the fastest land animal?” would fall under this category.

Informational search queries can be done one after the other. A user can obtain information from their first wave of informational searches. Then, with that new information, they can perform a new wave of informational searches.
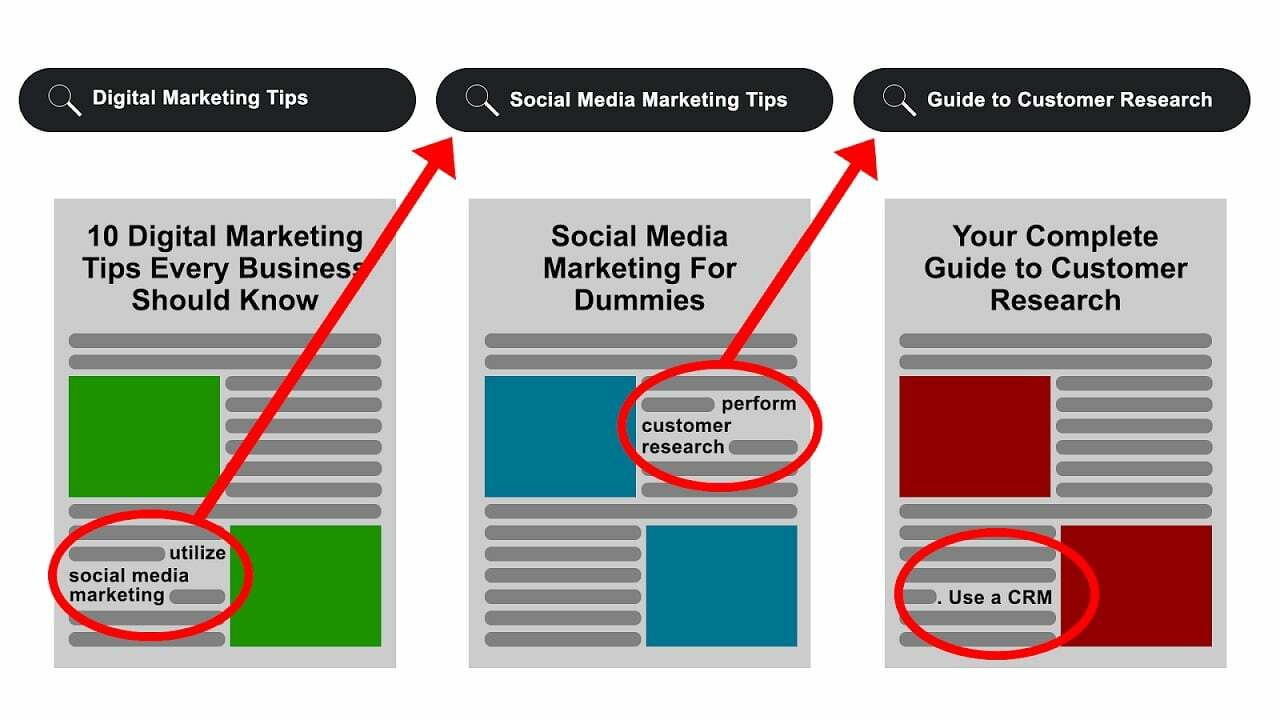
Users perform commercial searches to look for different service providers for a product/service.
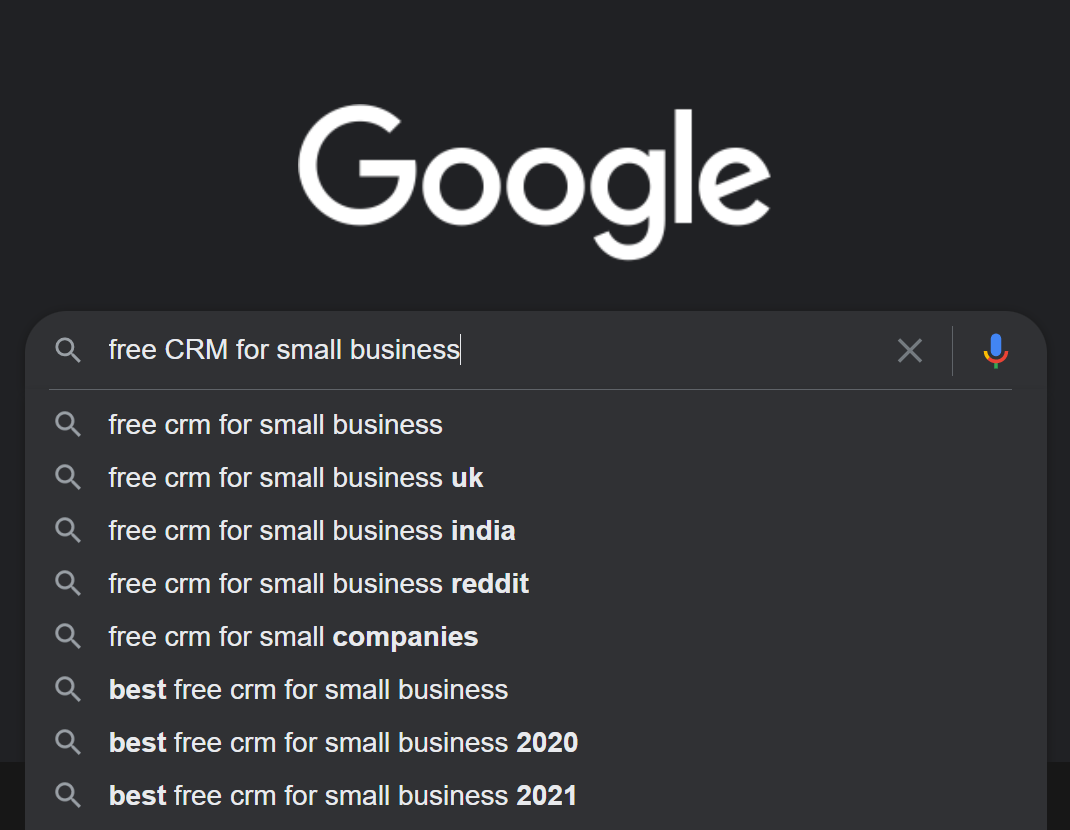
In the case of a B2B client who’s in the market for a CRM solution, they could perform a search for “free CRMs,” “budget CRMs,” or “top CRMs for small businesses.”

When you know about a brand but don’t know its exact domain, you’d likely perform a search for the brand name to look for its website.

- The business domain;
- The business’ various social media platforms, such as Instagram and Facebook pages;
- A combination of those previously mentioned.
For example, a B2B client looking for CRM software comes across an option that fits their budget. They learned about this option when they scrolled down a top 10 CRMs list. They now search for the mentioned brand name, leading them to that chosen CRM’s webpage.
Navigational intent searches are typically performed by those already aware of your brand. The traffic coming from these search queries is an aware audience who is likely to convert.
Transactional intent searches are performed by those willing to convert.
These searches lead the user to a conversion action, such as a purchase, a lead magnet download, a sign-up for a free trial, or a registration for a free webinar.
Now that you know these four categories of search terms, the question is, how are they relevant to improving your conversion rate?
At least that's how I kinda understand it.
How to Make Your Content Search Intent-Friendly
The more visible you are to users, the more likely they will convert.
How do you make your content search intent-friendly? Follow these steps:
Select relevant keywords
Create a list of these base keywords. When you know these keywords, you can get an idea of your ideal search queries. Your list of search queries will give you an extensive list of topics to write about.
There are many ways you can search for the keywords you can rank for.
This method doesn’t require any keyword research tool. Simply input a keyword on Google. Google will give you suggested search queries revolving around that word. Take note of these suggestions.
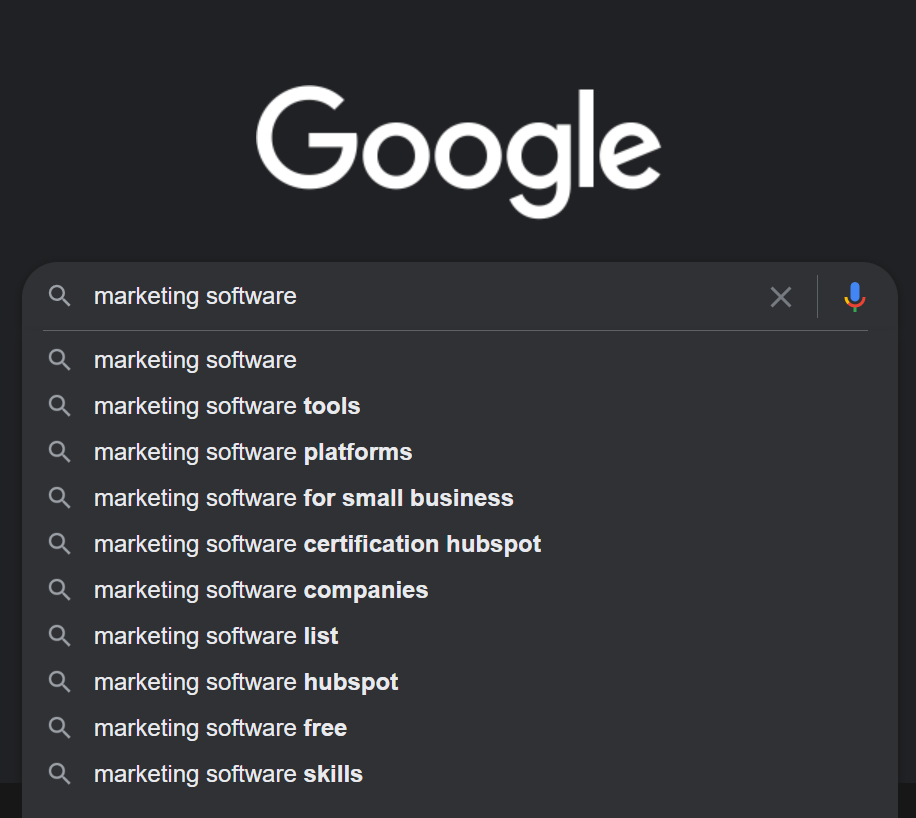
Are they about learning, doing, or buying? Sometimes there's mixed intent, so you can choose how to craft the content based on your content strategy.
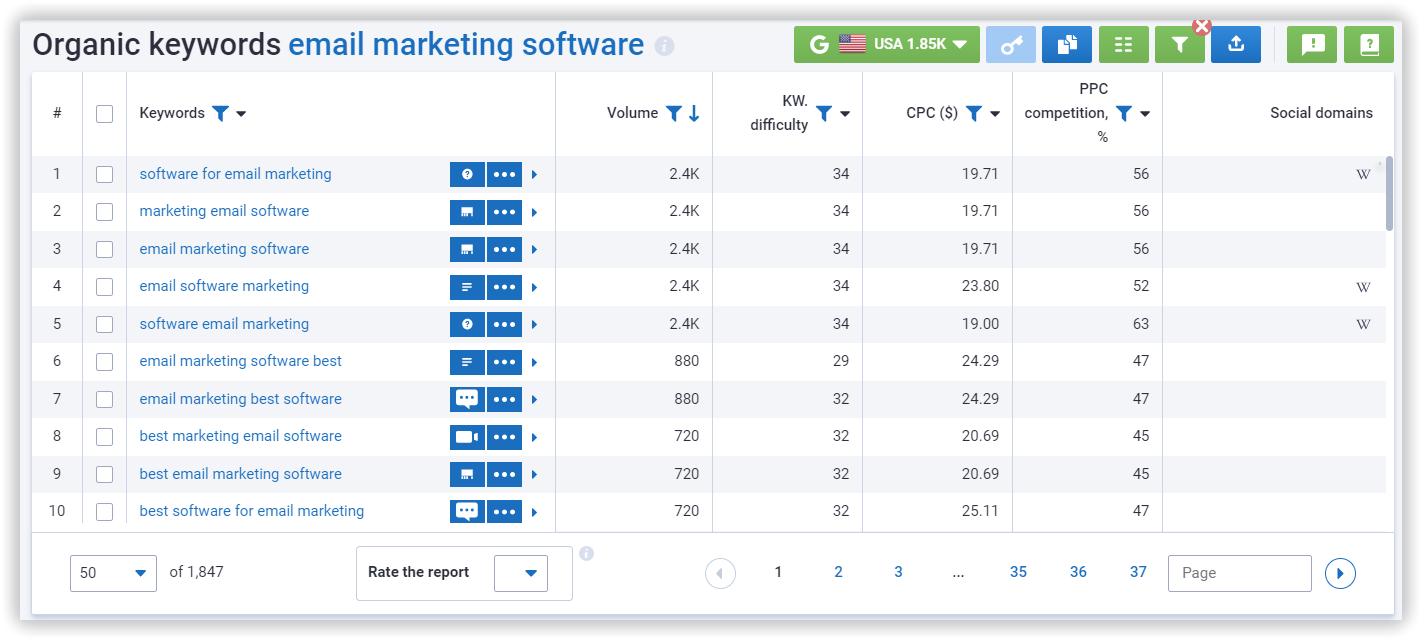
A keyword research tool fetches all search terms containing your set keywords. The software compiles all the results and includes critical data, such as:
- search volume, which is the number of times a phrase is searched for within a given period;
- cost per click, which is the cost of using the Pay-Per-Click model to advertise in the SERPs of that specific query;
- return rate, which is the average number of times a user searches for the same term again within 30 days, and many more.
Short-tail queries tend to be more general, making it harder to compete for ranking on these queries (i.e., digital marketing tips).
On the other hand, long-tail queries are more specific and less competitive, making it easier to competitively rank for these queries (i.e., how to create a social media campaign for under $100?). Long-tail queries are also higher-converting since they are more specific in addressing problems.
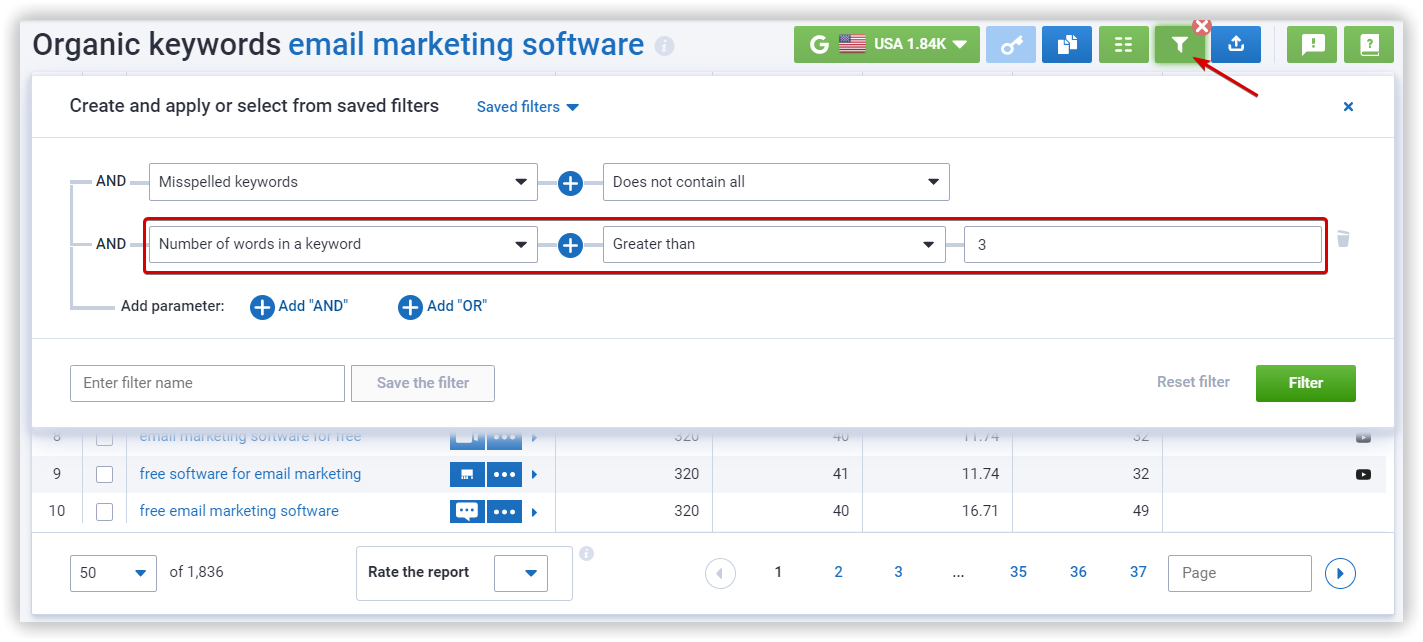
In Serpstat Keyword Research, you can generate a list of long-tail keywords. To do this, click on the filter button, and set the "Number of words in a keyword" to "greater than" three, or "between" three to five, etc.
Pick your method of searching for relevant keywords. Of the two, of course, the best way is the second method, since manual work takes up a lot of your time. Automated tools can make your life easier.
Examine the results of related searches
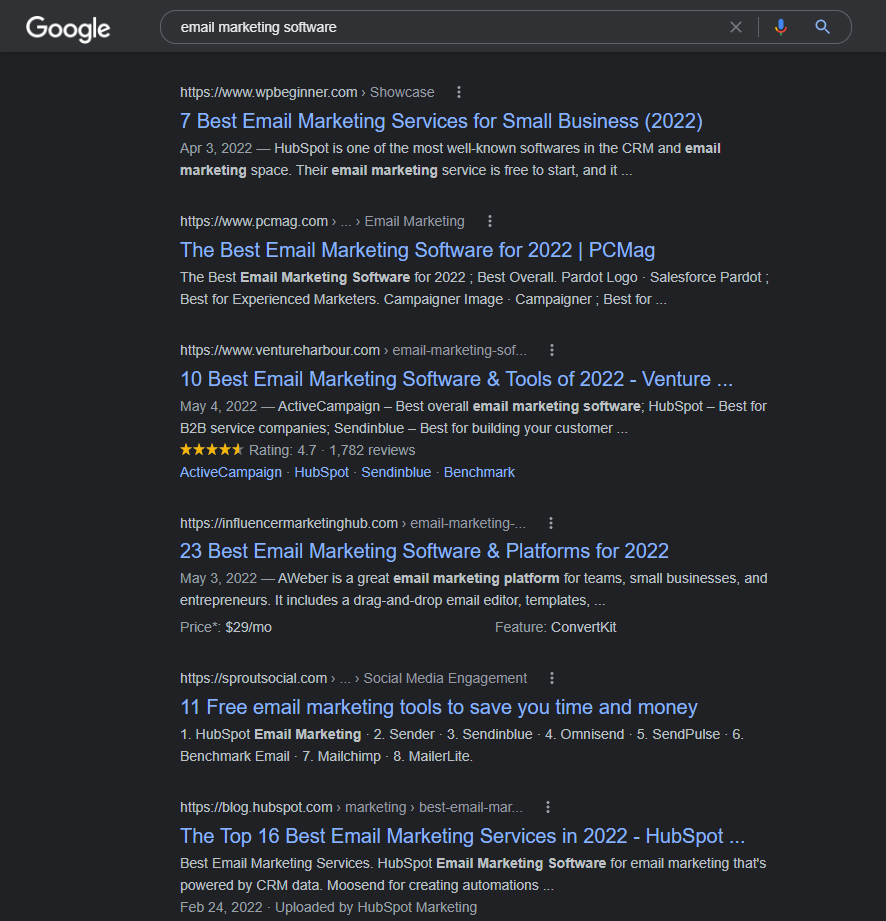
There are certain elements you need to look at when analyzing these ranking results. Do the following in your analysis:
Write your titles well, and you’ll likely rank higher than those that just ignore the titles of their blog posts. Besides, you want to give potential customers a good impression. The titles are the first things that people see when reading your blog posts since they usually come in bigger font.
Headers help search engines understand what the text underneath them is about. So, in creating your content, later on, you’d need to place the necessary keywords in the headers of your content. Looking at how the top results in SERPs use their headers can give you an idea of what to write. You may then formulate your own outline from these outlines later.
The higher the domain rating (DR) of the domain's ranking in the first SERP, the harder it will be to compete for that query.
This is because Google prioritizes domains with a higher DR. A DR basically tells you how authoritative a website is. The DR is calculated based on its backlink profile.
You can check any website's Domain Authority (SDR) and backlink profile in the Serpstat Backlink Analysis tool:
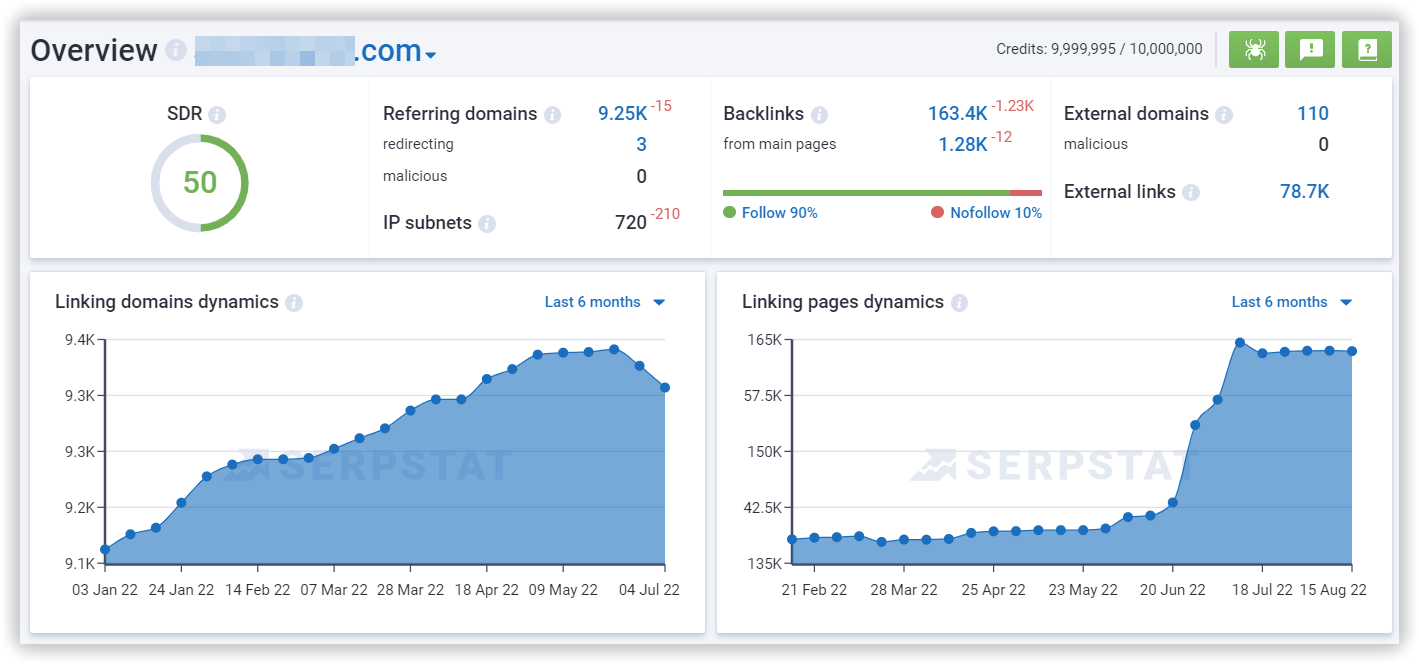
1. Guest posting for a content website with a high domain rank. More on guest posting later.
Analyze your competitors
If you don’t know who your competitors are, you may use keyword research and SEO tools, such as Serpstat. These tools determine your competitors based on the domains targeting your desired keywords, domains with relatively the same traffic as you have, or whatever baseline the tool sees fit.
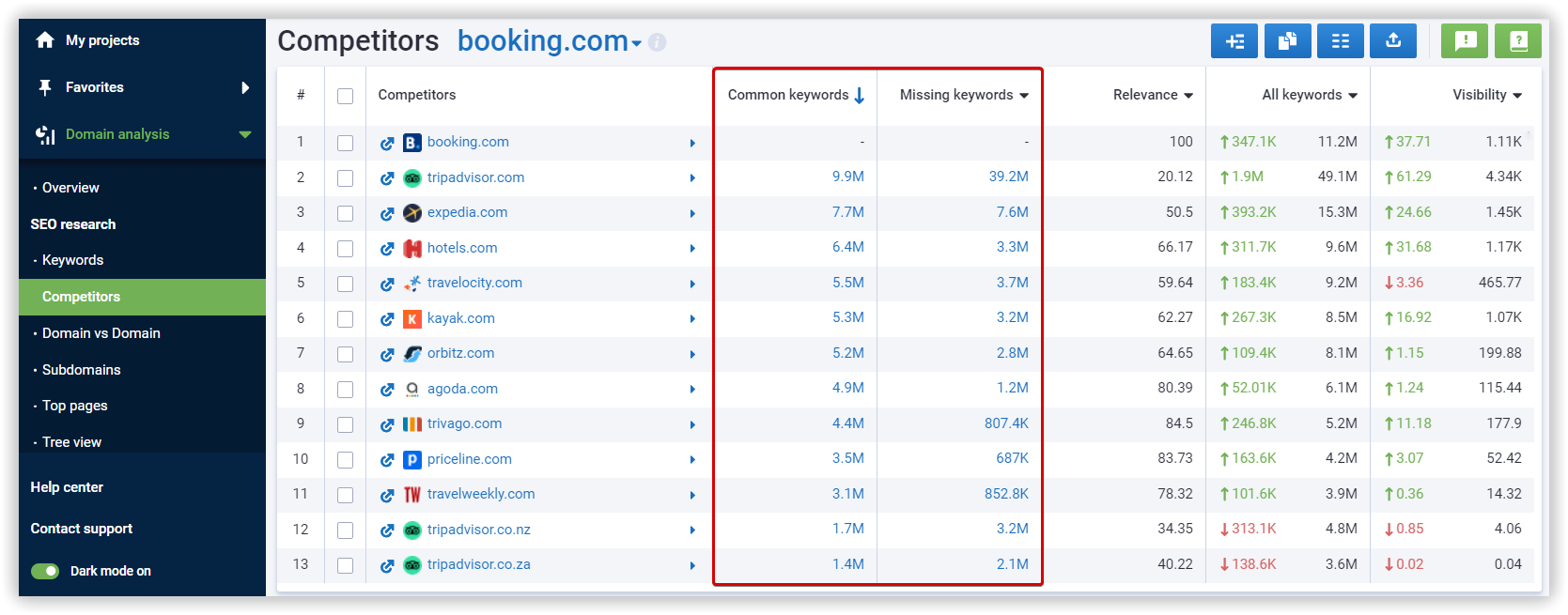
- Search traffic;
- Backlinks;
- Referring domains/DR;
- Keywords they’re ranking for.
Having an overview of the above data from your competitors will establish a baseline for you. It will give you an idea of how you should be performing to stay ahead of the competition.
Don’t just look at your competitor’s profile. Look at its content, too. Read through a few pieces of your competitor’s content. Assess how they flow from a website visitor’s perspective.
You’d want to take note of the following as well:
- What headers do they use?
- How many words are on their blog?
- How many images do they use?
Let's brainstorm it!
Join #serpstat_chat to discuss the questions of practical SEO, trends, and updates with SEO experts.
We conduct them every Thursday at 2 pm ET | 11 am PT on our Twitter channel by hashtag #serpstat_chat.
Produce optimized content
Use the necessary keywords you chose to rank higher for relevant search terms. You can do that by using an SEO writing tool. These tools also give you suggestions on what other keywords to include in your content. They help you keep track of how many times you’ve used the keywords. This software also gives suggestions on how many headers, paragraphs, and images your content should contain.
Also, write for people, not just the ranking algorithm. You may use a grammar tool like Grammarly to give the finishing touches to your content. Make sure you’re avoiding buzzwords, too. Don’t use the phrases “groundbreaking SEO software” or “B2B solution that disrupts the market.” You’ll just come off as pretentious. You also won’t add value to your content.
It’s not just your writing that you should optimize. You should also look at your images, page load speed, and metadata. Those are things Google also looks at. So, you need to follow these tips:

Increase your load speed. Google gives importance to web pages that are quick to load. Google prioritizes the user experience in ranking. A slow or unresponsive page is a negative ranking factor that will affect your visibility in the SERPs.
Optimize your metadata: Your metadata determines what appears in front of users as they scroll through the SERPs. If your metadata isn’t engaging or enticing, you wouldn’t get a decent click-through rate, even if you’re the #1 ranking for a query.
- the keywords you’re aiming to rank for;
- general information about the page;
- the business name.
The meta description isn’t as frequently read as the title tag, but it should still provide users with ample information.
Your meta description shouldn’t be stuffed with keywords. Rather, elaborate on how your page relates to that keyword. Does your page provide tips around that keyword (i.e., a list of digital marketing best practices that small businesses should observe)?
Does your page sell X, which is that keyword (i.e., buy the longest-lasting wireless mouse on the market right now)?
Be short and brief. You should follow the ideal meta description length.
But one post isn’t enough. You’d want to create optimized content for each type of search intent.
Informational intent:
Informational queries often come in the form of questions. Informational keywords include “what,” “who,” “why,” “where,” “when,” and “how,” in addition to relevant keywords.
Produce content for general, high search volume (competitive) queries. Also, create pieces for specific, low search volume (less competitive) queries.
Your high search volume blogs should contain keywords that can push the reader to search for more specific, low-volume queries. Website traffic from low-volume keywords may be less, but this is traffic that is more likely to convert.

From simply being interested in leveling up their style, the user now has an acquired interest in mechanical watches and performs a search on mechanical watches. This mechanical watch niche is a more specific market.
Another example would be a marketer searching for “email marketing tips,” and then seeing the importance of sending recurring emails. After that, they search for guides on creating a follow-up email.
When the user sees lower volume search terms in a post, they can use these to perform other queries. The more they do this, the more they become part of a more specific niche, which makes it easier for you to convert them.
Commercial intent:
Commercial intent keywords include adjectives such as “best,” “top,” and “most affordable.” These are in addition to the relevant keywords for your business. The types of content optimized for this intent include top 10 lists, product comparisons, and product reviews. Create these types of content for commercial intent.
For commercial search intent, you should leverage both your blog and third-party articles.
You can ask to be featured or mentioned in third-party articles. You can have a website try out your product, for example.
Furthermore, you may also guest blog. Guest blogging is the process of writing as a guest author for a third-party site—typically one with a significantly higher DR than yours. Reach out to these websites and make your pitch for collaboration via email. Just make sure you use an email checker before sending to ensure your emails reach the intended recipients. You can create listicles that feature your product for the website, which also needs content.
Another benefit of guest blogging is that you can include a link in that other website’s article to your chosen URL. By building backlinks to your website through guest blogging, you also improve your website’s DR. This process positively affects your ranking on SERPs.
The point is, that you touch base multiple times with researching consumers if you’re mentioned on multiple websites. So, when they make a commercial intent query, you can appear in SERPs.
Navigational intent:
Leads and prospects that already know about your brand will likely already search for your brand name.
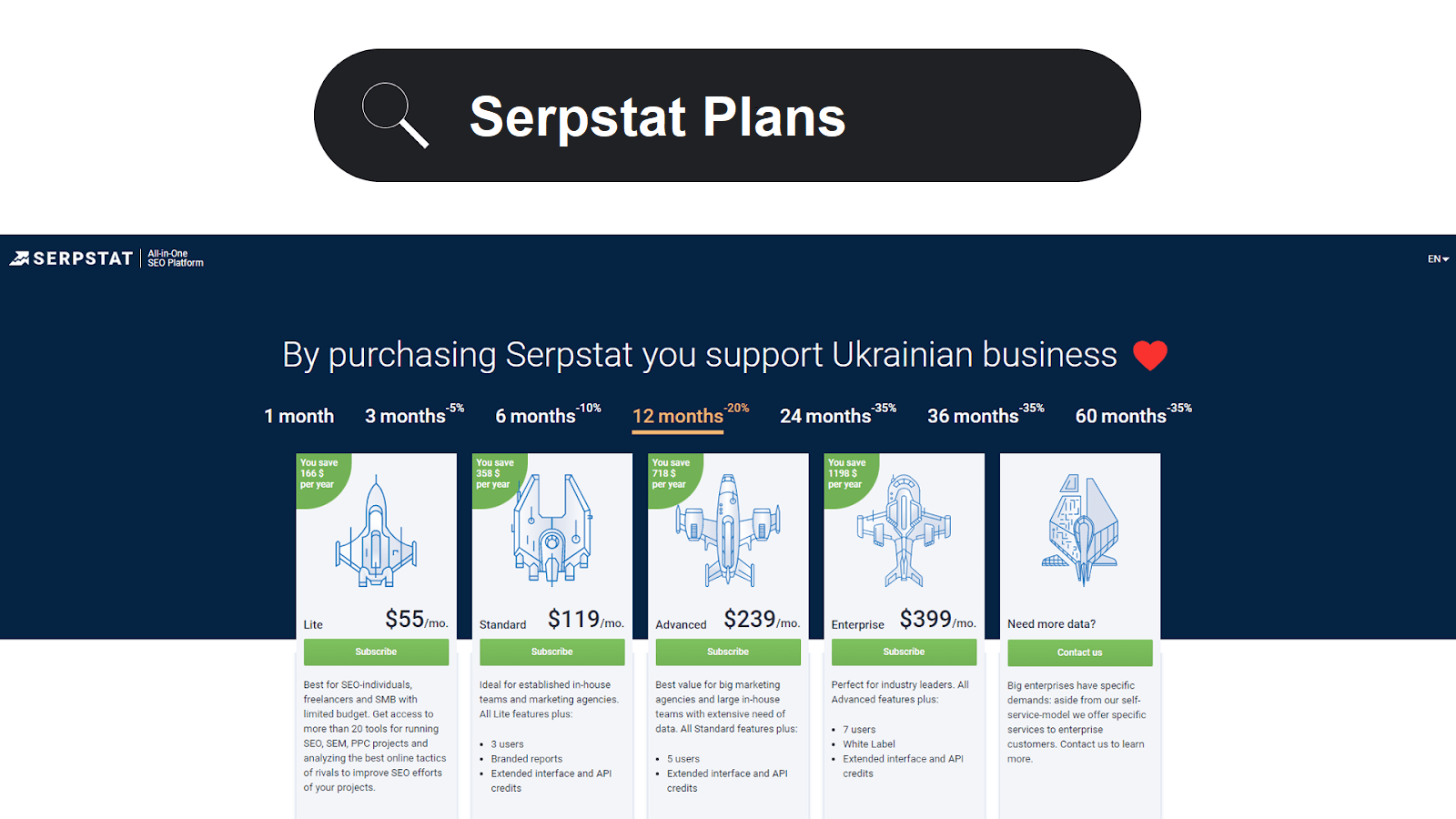
Transactional intent:
Transactional keywords include “buy,” “order,” “purchase,” “plans,” etc., in addition to the relevant keywords for your business. Create product pages since this is content that is optimized for these keywords.
- An audience that knows about your brand and is looking to purchase from your brand;
- An audience that knows about a specific service/product but isn’t necessarily aware of your brand.
The second type of audience is considered to have commercial/transactional intent. This audience is in the market for a product but is ready to make a purchase then and there. Some common examples of this audience are those browsing through Amazon. Or, those who search Google for “buy + *product type*” (i.e., buy a wireless mouse).
You can optimize for the second type of audience by including keywords for the service or product you’re selling. Don’t just insert the model name. If you’re running a promo, it helps to include the discount on your copy (i.e., Shop Wireless Mice, 50% Off).
Once you have the content optimized for all four search intent types, your content strategy can help you convert your audience since your content will act as a marketing funnel.
Some other tools are already available as free Streamlit apps, so you don't even have to code!
Review the results
Here are some of the things you should measure when it comes to your website:
- DR: Have you built (or earned) enough backlinks for your DR to improve?
- Target keywords: Are you ranking for the relevant keywords you’ve indicated in your keyword plan? You will know what queries you’re ranking for using Google Search Console.
- Organic traffic: Is there increased traffic to your site due to organic searches?
- Ranking: What position does your website rank for your select keywords? Keyword research tools will help you determine this metric.
There are other metrics you should consider. For instance, bounce rate is also an important metric. Your page may be ranking. But is your content engaging enough for people to stay and linger?
Purchases are also a critical factor. You need to see if your sales actually went up due to higher content engagement. Look at your conversions as well. Have more people downloaded your lead magnet, applied for a free trial, etc.?
You can have other metrics. These will ultimately depend on your marketing and business goals.
Link to relevant pages where it makes the most sense for readers and is topically relevant within the page. Also, use keywords in the anchor you want your target page to rank for.
Furthermore, map out your topic cluster in advance, and assign ideal anchor text variations to each URL for internal links.
Don't link to different pages with the same anchor. And think of internal links like wires in a house. https://terakeet.com/blog/internal-linking/
Wrapping Up
The key is to optimize your content so that you appear for each of these types of search intent.
Select the keywords most relevant to your business. Examine the search results for queries containing your selected keywords to see how you can create your content. Create content optimized for each search intent using informational, commercial, navigational, and transactional keywords.
Optimize your metadata to improve your click-through rate, too. Assess your competitors to establish a baseline for how you should be performing. Finally, measure your results against this baseline after your efforts.
If you follow this guide, you’ll ultimately mediate every stage of the buyer’s journey with your content. As a result, you can improve your brand awareness and conversion rate.
Speed up your search marketing growth with Serpstat!
Keyword and backlink opportunities, competitors' online strategy, daily rankings and SEO-related issues.
A pack of tools for reducing your time on SEO tasks.
Discover More SEO Tools
Backlink Cheсker
Backlinks checking for any site. Increase the power of your backlink profile
API for SEO
Search big data and get results using SEO API
Competitor Website Analytics
Complete analysis of competitors' websites for SEO and PPC
Keyword Rank Checker
Google Keyword Rankings Checker - gain valuable insights into your website's search engine rankings
Recommended posts
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.



