Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
How To Carry Out An Internal Website Optimization: Diving Into Details

We will go over all the key points that will ensure the successful promotion of your website. And I will try to make it understandable even for a beginner. Let's go!
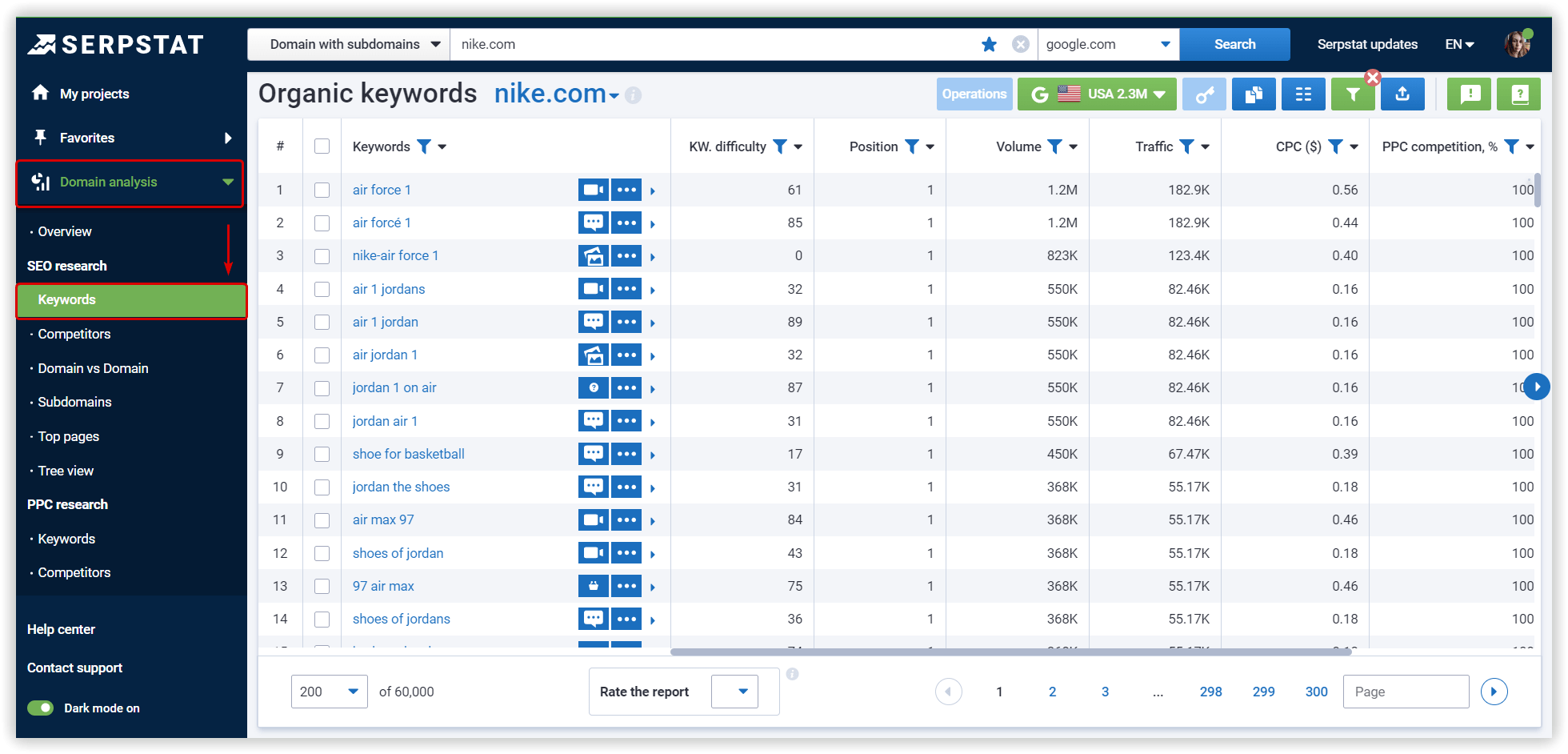
When I compiled a rating of SEO agencies, I found a pair to show as an example: the first agency is old, expensive, and well-known (let's call it D&G), and the second is young and less known (for example, Zara). Both agencies are in the top 10, but D&G ranks much better. Domain age, backlinks, even website quality - everything works in favor of D&G. But the most fascinating thing is that D&G has just as much traffic as Zara. What's the secret? Zara has more keywords, and they are better worked out: higher average CPC and lower difficulty.
You can use 2 methods to collect high-quality keywords:
Internal links are links within the same website (when a page from one domain links to another page of the same domain). External links connect pages from different domains. In terms of SEO, they have significant differences. The backlink affects page ranking as a whole (the authority) as well as the link anchor (the link factor).
The link factor is the influence of the text (anchor) of a link to positions on requests close to the link text.
Page authority (Page Rank) is the influence of the link on the positions for all keywords. The page authority doesn't depend on the search query. If the text of the page is not relevant to the query, the authority itself cannot bring the page to the top. Otherwise, for all queries, the main page of Wikipedia or Google would be ranked first.
Internal links don't provide link ranking. They carry link juice, that is, anchors (texts) of internal links are not necessary. Although, what is taken into account:
I haven't heard about any filters or penalties of search engines for internal links. The relevance of linked pages is hardly accounted for internal links. For external links, this option helps Google filter out purchased links, but internal links are never bought. Although, indirectly, through user behavior factors, the relevance of the link can affect the equity it transfers.
In general, forget what you know about external links when arranging internal links. The point of optimizing internal links is to increase the page authority you need. Link texts and page relevance are not important for internal links.
Ever since the link, user behavior, and domain age factors came out, the role of link juice has declined. But still, page authority is one of the essential ranking factors.
The PageRank algorithm considers the expected number of page visits with the following calculations:
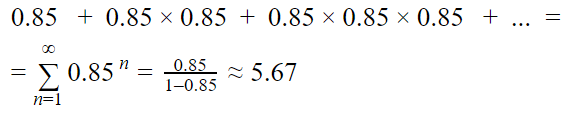
Now let's move on to the arrangement of internal links during optimization:
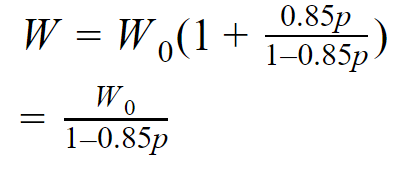
If we take the base authority of the website for 1, we get the following graph:
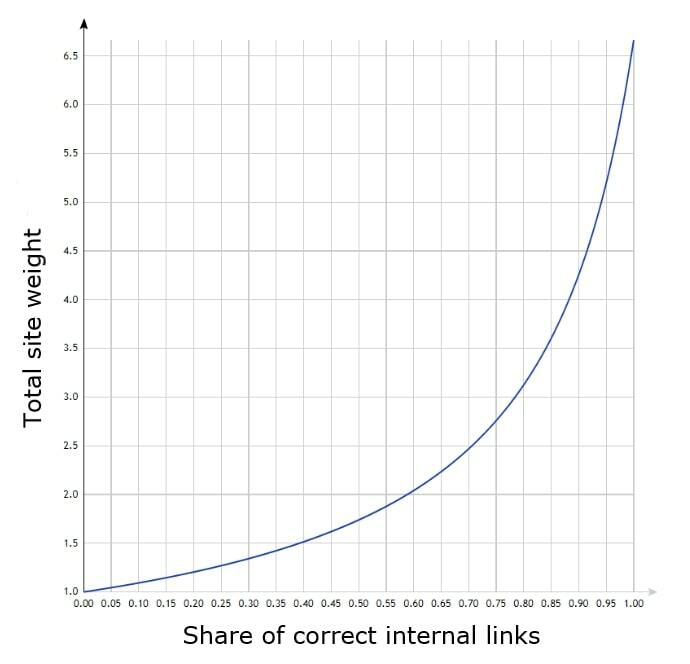
- the first link receives more of the equity than the second;
- links from the main menu get more link juice;
- links in bold receive more link juice;
- behavioral factors can be taken into account: the more often the link is clicked, the better.
However, I doubt that other algorithms are used that are fundamentally different from PageRank since the calculation of PageRank is very well suited for calculating large, constantly changing data.
In terms of link juice, this is just a broken link. This helps combat SEO spammers in the comments: they don't need to add nofollow links. Internal links are best avoided with this attribute.
In most online stores, the H1 category page matches the category name. Let's say you have a category "sneakers" on your website. You get the most traffic for queries that contain the words "men" or "women". And if you don't have separate pages "men's sneakers" and "women's sneakers," then it is worth making H1 "Men's and women's sneakers."
Such text shouldn't be displayed on the second page of the category so that search engines don't consider it as a part of the website template or filter the website for duplicate content.
You can check the quality of the text on the page using Serpstat Text Analytics tool. Read more:
Pages that can potentially bring in a lot of traffic need more authority than pages that cannot. For example, a page with contact information is in the website menu and therefore receives a lot of authority, but doesn't bring traffic.
Let's suppose:
Perhaps you need to remove some internal links from the website template. The effect of this is 5 times lower than if the link would be external, since our pages transfer up to 85% of their link equity to other pages of the website.
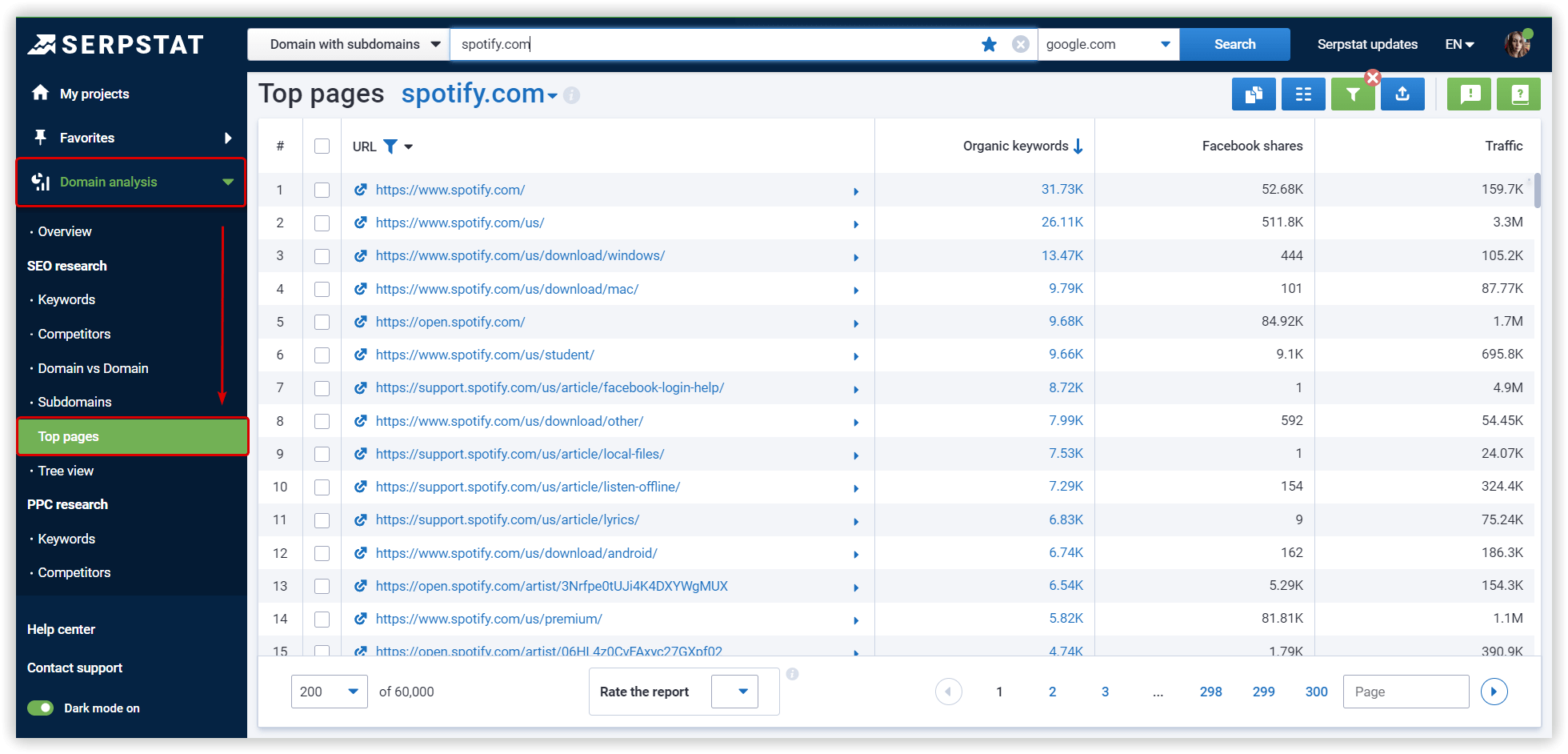
You need to link more to pages that can potentially bring more traffic. Depending on the situation, you can figure out how to organically fit them into your website. You can find them with Top Pages report at Serpstat. Enter your domain into the form below:
An audit is often carried out when the website is under the sanctions of search engines: positions decrease, and traffic drops sharply. In this case, an audit allows you to find errors, fix them, and return to the previous position.
You also need an SEO audit when everything is fine with the website: traffic is growing, and positions are gradually increasing. You can further speed up the growth of the website by identifying and correcting technical issues.
Even if you don't have errors right now, this doesn't mean that they will not appear. To prevent their occurrence, set up a permanent audit.
Load modal dialogs (pop-ups) through AJAX, or try to show search engines as much as possible that this is a modal dialogue:
<div class=”myModal”>
…
</div>
<!--noindex--><div class=”myModal modal popup” style=”display:none”>
…
</div><!--/noindex-->You can do it using Serpstat. Just enter a keyword or domain into this form:
The recommended title length is 70 characters, and the word order is essential. Therefore, the name of the organization (if present in the title) should be at the end. Alt tags and image file names strongly affect image search and organic display.
You can do this in two ways:
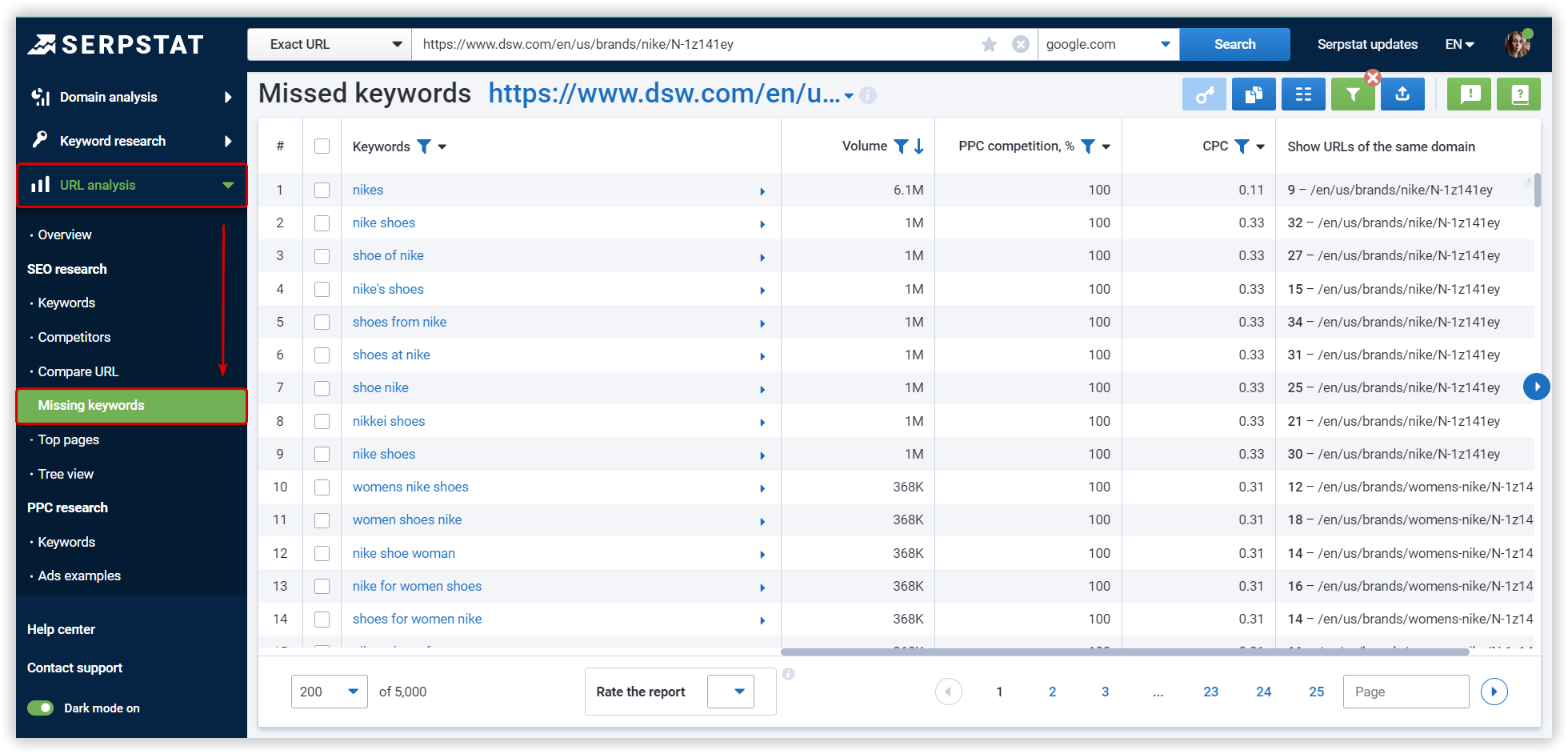
To go to this report, enter your domain in the form below:
- Quick links. In Google, they are formed from breadcrumbs of other pages.
This concludes my guide to internal website optimization. What tricks do you use? Write in the comments under the article;)
Speed up your search marketing growth with Serpstat!
Keyword and backlink opportunities, competitors' online strategy, daily rankings and SEO-related issues.
A pack of tools for reducing your time on SEO tasks.
Discover More SEO Tools
Backlink Cheсker
Backlinks checking for any site. Increase the power of your backlink profile
API for SEO
Search big data and get results using SEO API
Competitor Website Analytics
Complete analysis of competitors' websites for SEO and PPC
Keyword Rank Checker
Google Keyword Rankings Checker - gain valuable insights into your website's search engine rankings
Recommended posts
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.
