Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
Configuring Redirects On A Website: How To Avoid Mistakes

This article will be useful for both, and hopefully, help them find common ground :)
What Is A Redirect?
Duplicate pages tend to worsen the website's rankings in search results, and
redirects help to deal with them.
They are also helpful when you need to create a new page to replace an existing one while maintaining search rankings and traffic.
There are 9 types of redirects, but only three of them are actively used in SEO: 301 Moved Permanently, 302 Moved Temporarily, and 307 Temporary Redirect. More on that later.
Why Do You Need Redirects?
Most Common Redirect-Related Mistakes You Should Avoid:
- multi-step redirects ("redirect chains") to pages where redirects are already configured. The redirect should lead to the target page without a subsequent redirection;
- redirects to irrelevant pages. Redirects should lead to the content requested by a user. You must not configure redirects to a page that has significant differences from the original one, for example, to a completely different product in an online store;
- redirects to deleted or inactive pages. You can only configure redirects to pages with a successful server response (200 OK) which indicates their correct operation;
- redirects for doorways, i.e. websites that are optimized for a number of search queries and have no value for users. These websites are created specifically for redirecting users to other websites and their use contradicts Google's webmaster guidelines;
- configuring a redirect instead of rel=canonical. If the page content is duplicated, for example, in print or mobile versions, it is preferable to specify a canonical address;
- a very significant mistake is to configure a "302" redirect instead of a "301" redirect when changing a domain, deleting a page, or changing a URL.
Redirect Types
- 300 Multiple Choices — multiple choices. There are several addresses to which a user is redirected depending on their choice or the browser settings:
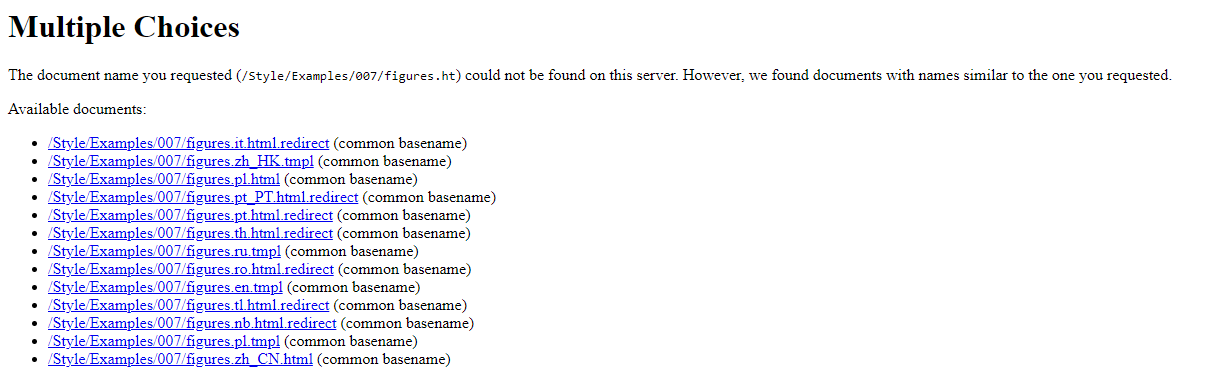
- 301 Moved Permanently is a permanent redirect to a new address. This is the most popular redirect type removing the old address from the index, but retaining all its parameters and passing them to the new one. This option is also suitable for removing duplicates. You can apply it if you no longer need to use the current page or domain;
- 302 Found is a temporary redirect to another address. A "302" redirect is leading you to a new page that is not indexed, and all results stay at the old URL. This type is not suitable if you change a domain;
- 303 See Other is a redirect to a page that uses the GET method to display it. This redirect indicates that the document was found, but you need to use the GET request method to go to it even if the HEAD or POST were originally used. It is rarely used, for example, when one document was found as a result of a user search on a website. In this case, you can immediately redirect the visitor to it using a "303" redirect without showing the search results separately;
- 304 Not Modified is a redirect indicating that the document has not been changed. This is a response the browser receives when it re-accesses a page that has not been modified. In this case, it must be downloaded from the browser cache;
- 305 Use Proxy is a redirect to a page, performed through a proxy; its address is transmitted to the browser;
- 306 Switch Proxy is not used at the moment. This redirect previously meant that future requests should occur through the transmitted proxy;
- 307 Temporary Redirect is a redirect similar to a "302" redirect by its activity. It also temporarily replaces the address of the original version which is not removed from the index. Unlike a "302" redirect, it eliminates the ambiguity about whether to change the document request method.
How To Configure Redirects
We will go over three main options:
- using the .htaccess file in the root directory of the website;
- setting up redirects on the page of a website using JS, PHP, or HTML code;
- configuring redirects in the control panel of the hosting provider.
How To Specify 301 Redirects In .htaccess
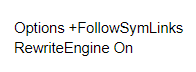



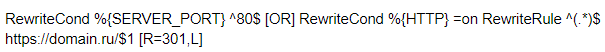

Configuring 301 Redirects Via Scripts
To redirect the entire website, the following code must be placed in the index.php file:
<?php
header("HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently");
header("Location: https://www.new-site.ru");
exit();
?>JS Redirect
You can use various JavaScript functions to configure redirects. Regardless of the implementation you choose, you must place the code inside the <script> </script> tags on the HTML page. A JS redirect requires that the source page from which the redirect is configured continues to exist. Here are the options of the redirect functions:
- document.location="https://www.new-site.com";
- window.location.replace("https://www.new-site.com");
- window.location.reload("https://www.new-site.com");
- document.location.replace("https://www.new-site.com");
- location="https://www.new-site.com/";
- a redirect after 10 seconds with a redirect message to a user:
function Redirect()
{
window.location="https://www.new-site.com";
}
document.write("Our website has a new address, you will be redirected to it in 10 seconds");
setTimeout('Redirect()', 10000);The code is written in the <head> element; a redirect occurs in 5 seconds:
<head>
<meta http-equiv="refresh"="5;URL=https://www.new-site.ru" />
</head>Configuring Redirects In The Hosting Control Panel
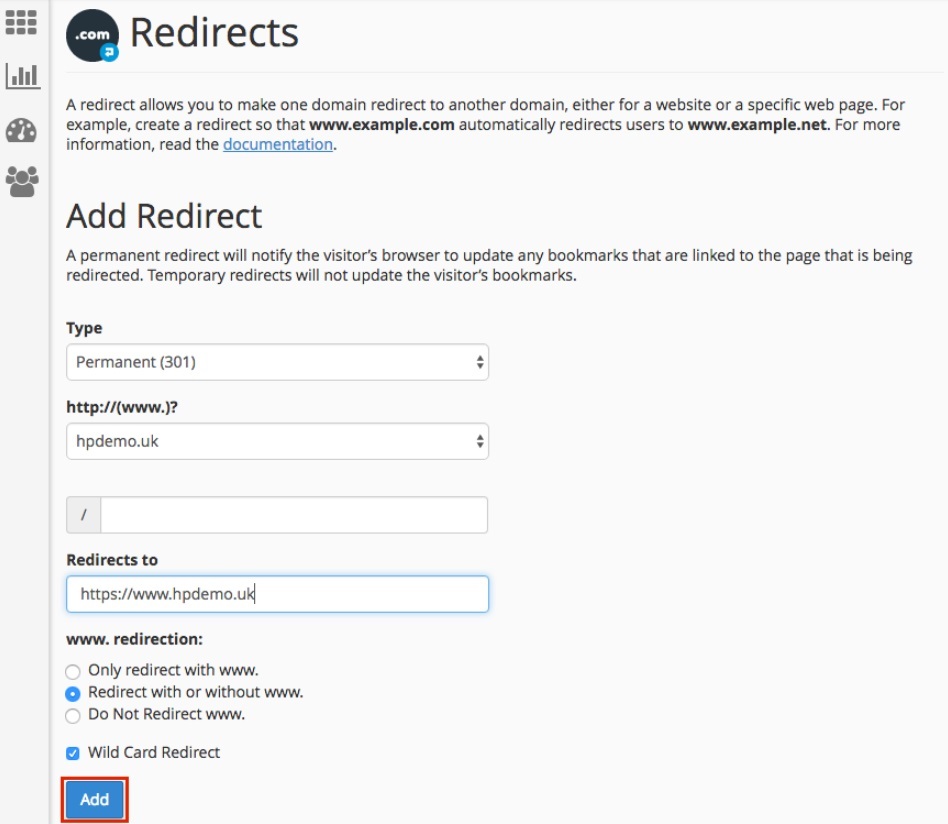
Conclusion
- Using redirects allows you to redirect visitors when changing a domain, set redirects to similar products in the online store, and fight duplicate content;
- Most often a "301" redirect is used for search engine optimization, as well as a "302" and a "307";
- Technically you can implement redirects using the .htaccess file, or by placing the necessary HTML, JS, or PHP codes on the website pages.

| Run Site Audit |
Speed up your search marketing growth with Serpstat!
Keyword and backlink opportunities, competitors' online strategy, daily rankings and SEO-related issues.
A pack of tools for reducing your time on SEO tasks.
Discover More SEO Tools
Tools for Keywords
Keywords Research Tools – uncover untapped potential in your niche
Serpstat Features
SERP SEO Tool – the ultimate solution for website optimization
Keyword Difficulty Tool
Stay ahead of the competition and dominate your niche with our keywords difficulty tool
Check Page for SEO
On-page SEO checker – identify technical issues, optimize and drive more traffic to your website
Recommended posts
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.

