Start Exploring Keyword Ideas
Use Serpstat to find the best keywords for your website
Complete Guide To Improving Your Email Deliverability

Issues with sender's IP address
The following are possible problems with a sender's IP address:
 |  |
Among other parameters that influence your sending reputation, there are send volume, warmed up IP address, blacklist appearances, previous spam sent, number of delivery errors and further attempts to deliver the rejected messages.
How to deal with these issues?
1. Choose an appropriate type of IP address
If you send different types of email campaigns, you would be wise to use several IP addresses and register separate email addresses for each of them. For example, send informational emails from info@domain.com, while technical ones from tech@domain.com.
Shared IP address: is used by multiple senders. In this case, you cannot control the actions of other senders. You can only rely on their fair practices. Shared IP is a good option for those who send few campaigns with a frequency of less than 30 days. Thanks to the activity of other senders, such an IP address won't be considered cold.
It's best to register a separate IP address to send important email campaigns. This precautionary measure ensures higher deliverability. Moreover, other senders with lower reputations won't impact your sender score and create problems for you.
2. Warm up a new IP address
How to warm up your IP address:
- Remove inactive subscribers from the list.
- Divide your mailing list into five groups of 10,000 users each.
- Send an email every day to the recipients in group one during the first week. For the second week, add another group to your mailing list.
3. Configure authentication settings
If you send email campaigns from your personal server, configure DNS and the following essential types of authentication:
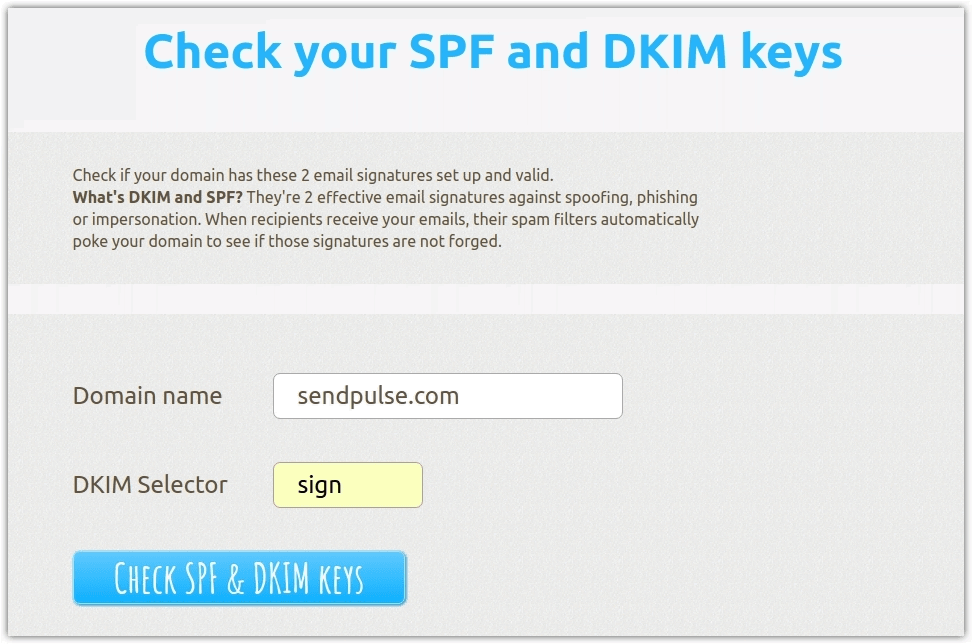
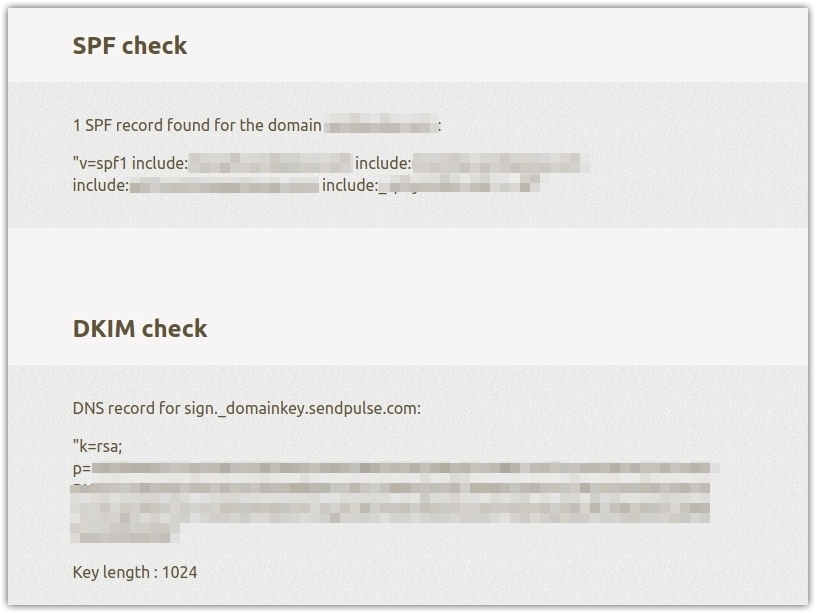
SPF (Sender Policy Framework). This is an email authentication protocol. SPF verifies the "from" address and compares it to the address indicated by the sender in the DNS record.
An SPF record contains information on email servers that are allowed to send emails and the sender's level of trust. This data enables email clients to determine whether the email can be accepted or not. You can find out how to create and set your SPF record in the SendPulse knowledge base.
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail). This is a sender's authentication method that requires a cryptographic signature. Refer to the SendPulse knowledge base for a detailed guide on how to configure the DKIM record.
Transport Layer Security. This ensures a secure email delivery without snooping or data spoofing.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance). This verifies the incoming emails of the given domain. Moreover, it determines what to do with email that doesn't pass the SPF/DKIM authentication, or what to do if a domain or sender's email address doesn't match the confirmed address. In this case, an email will be placed in the spam folder or simply won't be accepted. Thanks to DMARC, mailbox providers recognize emails from spoofed IP addresses that are disguised as senders with a good reputation.
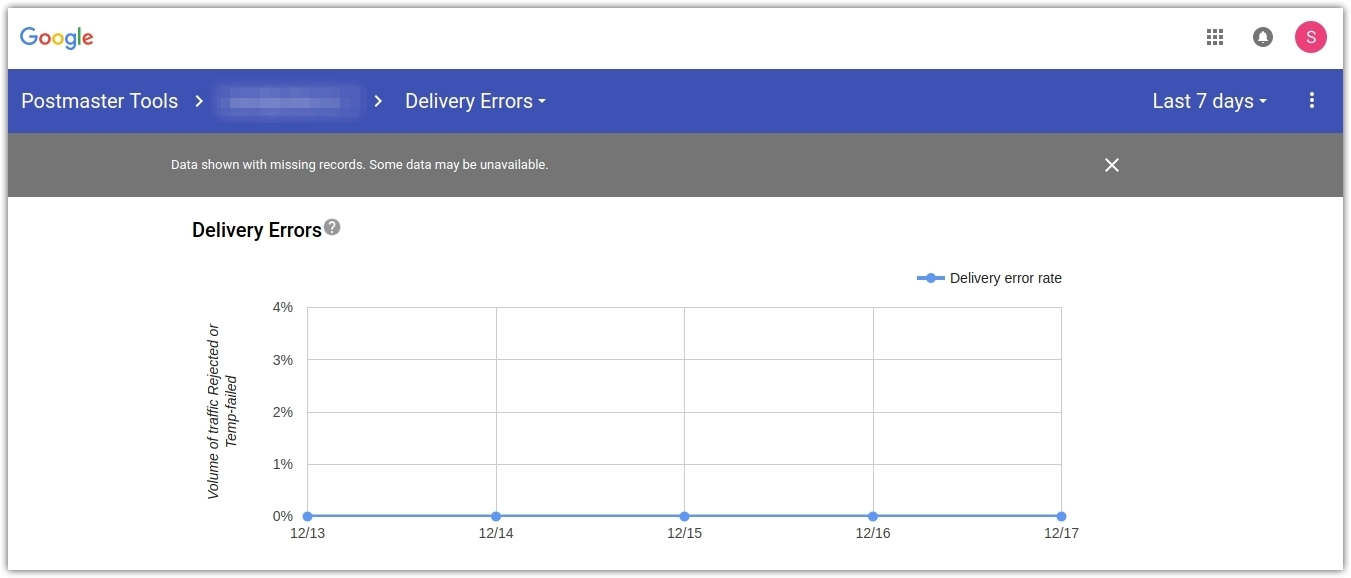
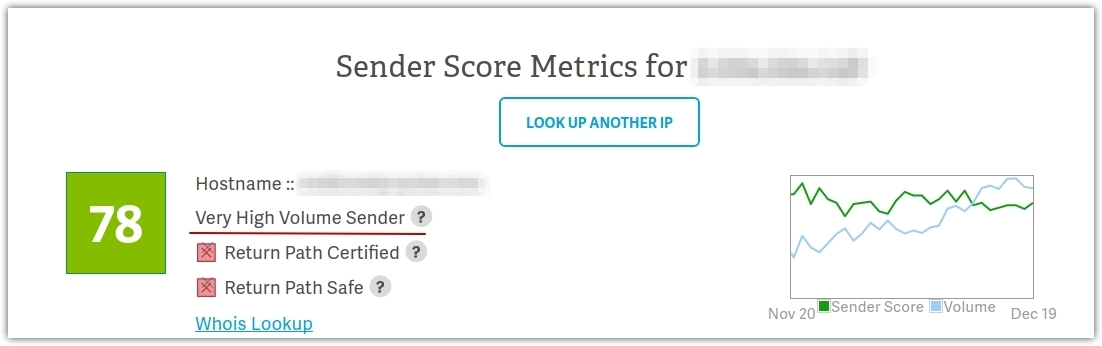
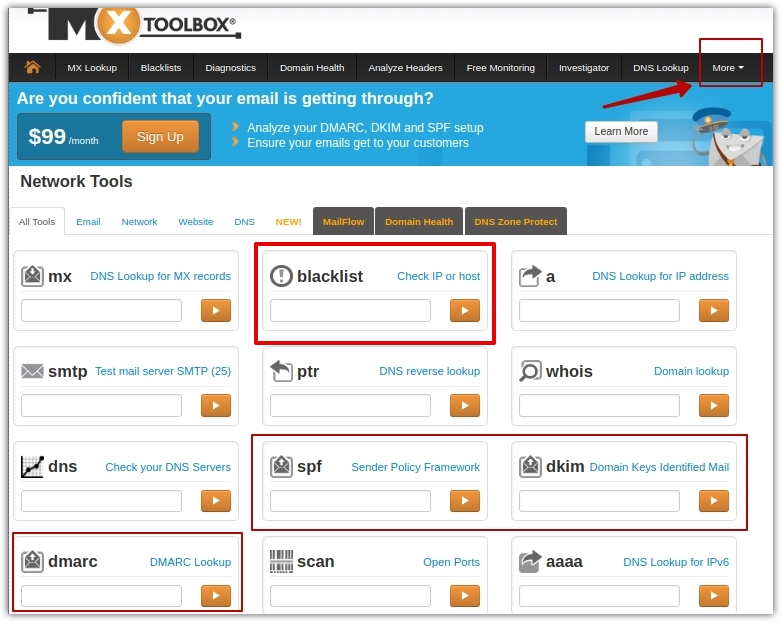
4. Check your sender score regularly
If the majority of your mailing list uses Gmail, you should track your sender reputation with dedicated online tools like Google Postmaster Tools. Once you have registered your IP address on Gmail Postmaster Tools, you can check the following parameters:
5. Sign up for feedback loop
Here is an example of a feedback report from AOL.
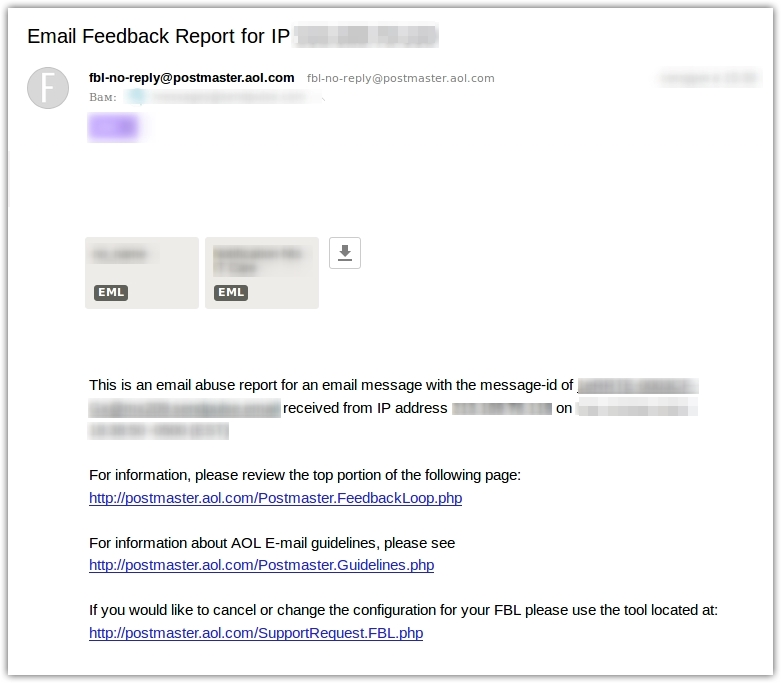
A feedback loop is an important and useful feature that helps you to take necessary measures to improve your sender score. For example, remove subscribers who complain from your mailing list, improve segmentation, or completely redo the content of your email. Some email service providers accept and process FBL reports from all available mailbox providers and subscribers are marked as "reported spam" in personal accounts.
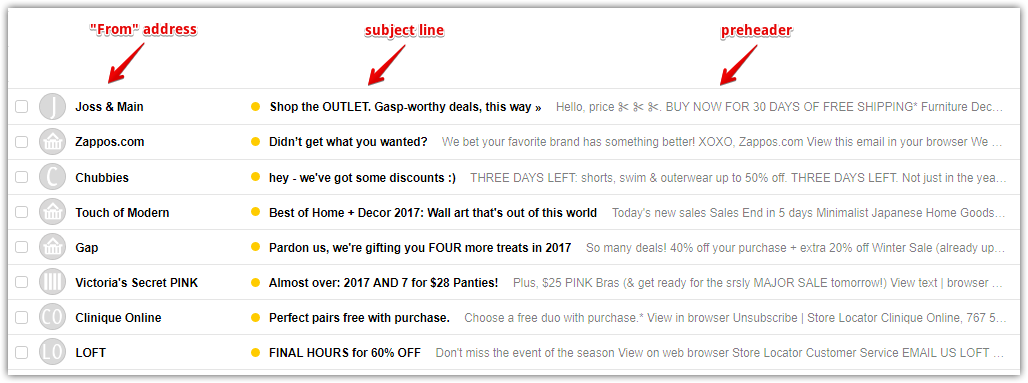
6. Fill in the "From" address
A well-known and permanent "from" address is more important for your deliverability than a subject line or preheader.
Issues with a mailing list
No express permission to email
You cannot email:
- Participants of contests or workshops, unless they have agreed to receive your messages during registration.
- Members of groups or subscribers in social networks.
- Customers of online or retail stores, unless they have agreed to receive your messages in the application for a discount or during registration on a website.
No double opt-in form
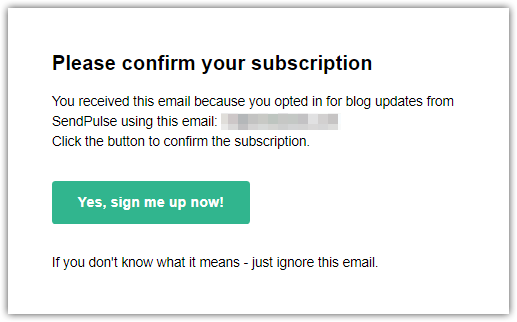
High complaint rate
The following are possible reasons for complaints:
- Subscribers can't find the unsubscribe link, or it is simply not included. They will subsequently mark such email as spam in order to receive nothing else from the sender.
- Subscribers opt out but still receive emails, or the subscriber hasn't received a notification that unsubscribing will take several days. The time lag annoys recipients.
- The subscriber is required to visit their personal account on the website to unsubscribe.
- A customer wasn't informed about being subscribed to the newsletter. For example, there was no welcome email. In this case, your first email can be a surprise to him/her.
- Email content doesn't correspond to subscribers' expectations. For example, a recipient has subscribed to an educational email series, but instead, they receive transactional emails.
- Subscribers receive emails too often or too rarely. In the first case, subscribers are irritated by persistence, while in the second one, they have simply forgotten about opting in.
Numerous delivery errors
- the subscriber's mailbox is full;
- the mailbox hasn't been used for a long time;
- the server is down.
Theoretically, a soft-bounced email can still be delivered once the problems are addressed.
Hard bounces, in turn, happen due to the following reasons:
- nonexistent email address or recipient domain;
- syntax errors in email addresses;
- recipient's mail transfer agent blocked the delivery.
If you ignore repeated delivery errors to the same subscribers and don't remove such email addresses, your deliverability rate will decrease to 20%. The accepted level of soft and hard bounces that doesn't affect the sender's reputation is
2–3%. The best way to improve it is to use double opt-in and remove inactive addresses from your list every six months.
Email hits a spam trap
The theory is that validators and verifiers of mailing lists can help you to avoid spam traps, but that doesn't correspond to reality.
Emails go to unengaged subscribers
When assessing audience engagement, email clients consider the following:
- The percentage of emails read. The more emails that are read, the higher are the chances that the subscriber is interested in your email campaigns.
- The number of emails marked as not spam or those moved to the inbox folder. For example, Gmail considers this to be a sign that the email campaigns are desired.
- The quantity of emails forwarded is another indicator that subscribers value your emails and are ready to share them.
- Emails replied to. This relates to personal emails.
- Senders added to contacts. If subscribers trust these addresses, emails incoming from them can be placed in the inbox.
- Emails deleted without reading. This is a clear sign which emails are interesting for subscribers and which are not.
How to deal with these issues?
1. Avoid spam traps
Recycled. These addresses once belonged to a real person but became abandoned. If you send email to such an address, you will receive error message 550: invalid recipient. Repeatedly sending to these addresses worsen your sender reputation, so remove them from the list ASAP.
Pristine spam traps or honeypots. These addresses are published on public websites and are created solely to capture spammers and senders with low-quality mailing lists. A double opt-in form is the best way not to end up in these types of spam traps.
Syntax errors and typos in domain names. Examples of this are gmial.com or hotmai.com. No matter whether a user misspelled it or it was an error of the email marketer who collected the addresses, sending to mistaken recipients will significantly reduce your deliverability rate.
2. Collect a quality mailing list
This requires the following actions:
- Ensure that email addresses of new subscribers are valid. Don't rush to send a welcome email in order to avoid hard bounces.
- Use a double opt-in form.
- Set expectations in your subscription form or welcome email; review your email frequency and the content subscribers will receive.
3. Email your list regularly
4. Monitor subscribers' activity
Issues with email content
The following are possible problems with email content:
- Email contains more images than text. Your email is a single large image.
- Email programming code is broken or complex – PHP, JavaScript, Java, ActiveX, ASP.
- Links lead to domains that are blacklisted.
- There are spam words in subject line or email text.
- Email contains files for download instead of links.
- Email size is too large due to visual elements.
How to deal with these issues?
1. Avoid spam words, excess punctuation and uppercase letters in your subject line
2. Watch your email structure
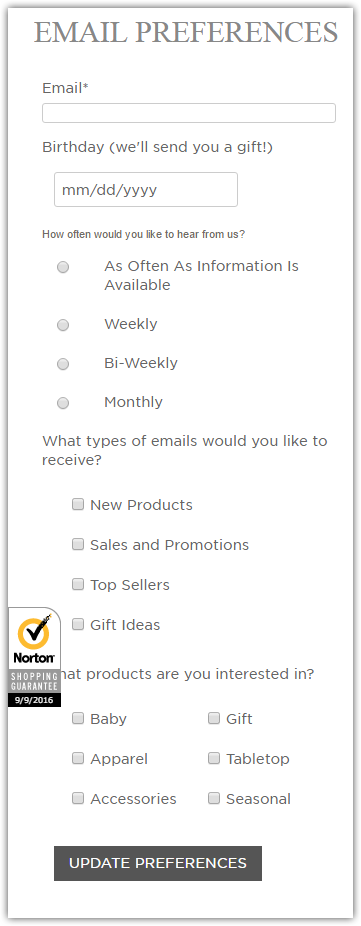
Add a link to your preference center. Your subscribers will have the opportunity to indicate the content they'd like to receive, email frequency and get unsubscribed. Below is an example of the preference center from Mud Pie. A link to it is in the footer of every email. It is a good practice, as it helps to segment the list, and, as a result, to send relevant content.
Include both plain text and web versions of your email. If visual elements aren't displayed, subscribers will still be able to review your email. Moreover, spam filters are more loyal to such messages.
When you add links to your email, create a call-to-action button or anchor link with appropriate text instead of shortening it.
3. Improve email content
Files for downloading should be provided as links instead of attachments. Emails with embedded attachments along with large visual elements are more likely to end up in a spam folder.
Check all the links to make sure they aren't on blacklists. If the link leads to an external source, check it for reliability and authenticity. Never engage spammers to promote your website, as it will negatively impact your deliverability rate.
4. Check email content using anti-spam tools
Check your email for the following points before sending:
- Bad HTML code in your template;
- Image-to-text ratio;
- Quality of URLs and IP addresses;
- Missing the unsubscribe link;
- Inclusion of spam words.
Bottom line
The following are a summary of the suggestions to avoid ending up in a spam folder:
Discover More SEO Tools
Domain Analysis Tools
SEO Domain Analysis – gain insights into your website's strengths and weaknesses
URL Inspection Tool
Uncover hidden SEO opportunities with our powerful URL Inspection Tool
Keyword Rank Checker
Google Keyword Rankings Checker – gain valuable insights into your website's search engine rankings
Competitor Website Analytics
Complete analysis of competitors' websites for SEO and PPC
Cases, life hacks, researches, and useful articles
Don’t you have time to follow the news? No worries! Our editor will choose articles that will definitely help you with your work. Join our cozy community :)
By clicking the button, you agree to our privacy policy.
