Malicious Link Checker
To maintain a strong SEO site reputation, it is crucial to avoid any affiliation with spam or harmful sites. Google provides guidelines for detecting and eliminating such links. Save time and resources by efficiently gathering information on malicious links with our tool.
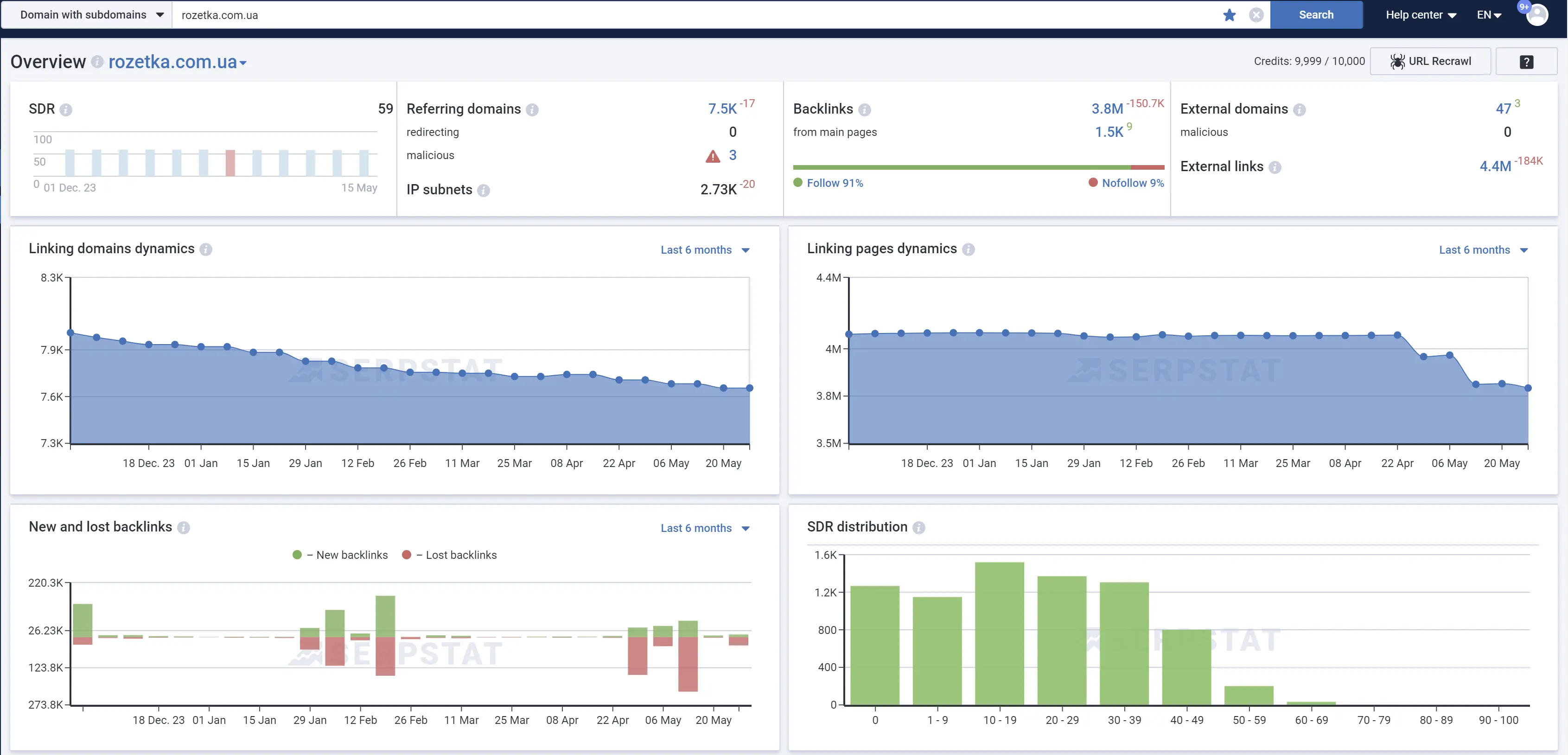






Backlink Profile
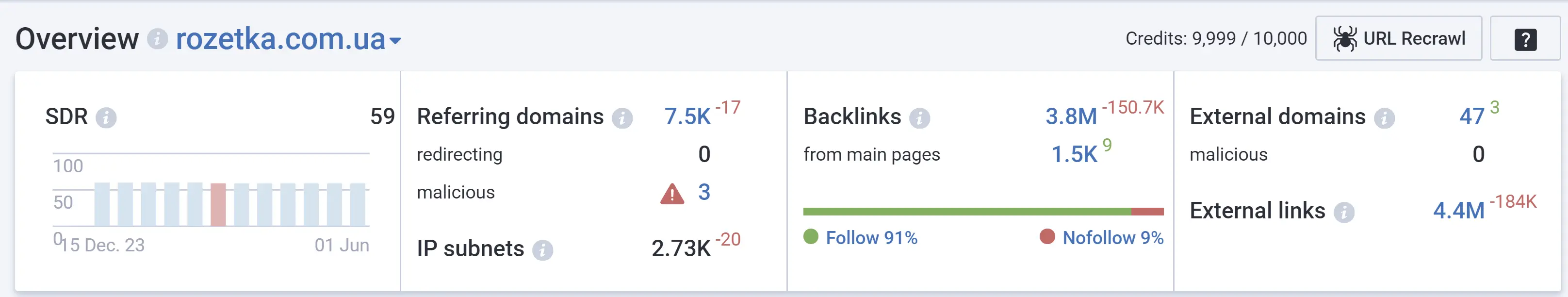
To avoid negative impact from poor quality links, it is important to review your backlink profile and assess the quality rating using Serpstat Domain Rank (SDR), which evaluates domain authority using all backlinks.
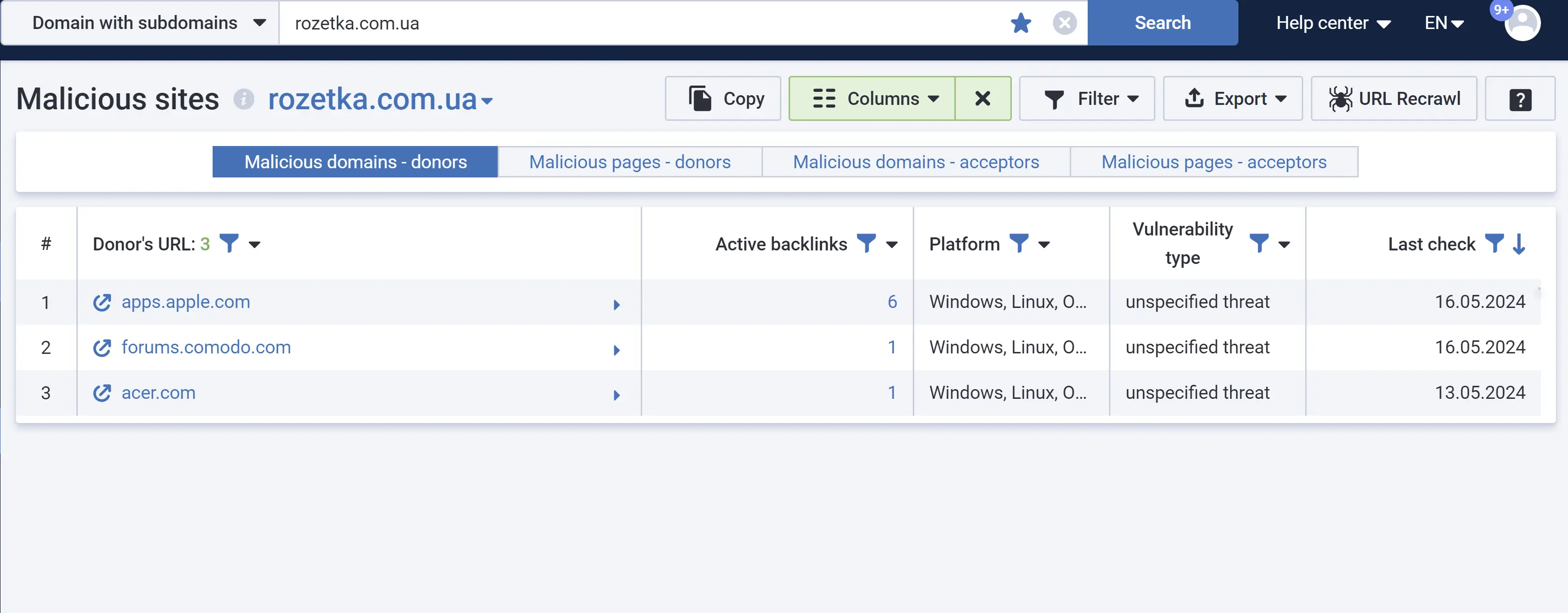
Malicious sites
Discover which of your domain's referring sites are flagged as malicious by Google Chrome.
- Get a ready-made list of malicious sites, data on the number of referring links, as well as the types of possible vulnerabilities.
- Protect your site by removing or closing every malicious link that appears in the report.
Malicious Links Checker Advantages
Checking the backlink profile quality and the domain authority level
Investigating dynamics of the backlink profile and finding low-quality links
Analysis of the list of anchors and search for spam links
Automatic links collection that Chrome marks as malicious
Use the Right Data
1.46B
Domains
7.03B
Keywords
1.1T
Backlinks
4.54B
Keywords suggestions
230
Countries
1.97B
Keywords in SERPs
Protect your website with malicious links checker
Quickly find malicious links, block them and protect your site from threats. Analyze anchors and identify spammy links which should be blocked.
Experience our tool at no cost for a week and identify malicious links that can negatively impact your search engine ranking.
Malicious Links Checker FAQ
How to find malicious links on a site?
You can find malicious links using specialized tools like Serpstat. Simply enter your URL into the search box and find the ready report in th Malicious sites section.
What is a Site Backlink Profile?
A site's backlink profile is a collection of all links and anchors that lead to this site. The link profile of the site consists of both its organic (natural) and artificial links. If the site has information that is useful and interesting for users, other sites will refer to it, so it will develop a natural backlink profile. An artificial backlink profile is created when links to the site are bought or rented on specialized platforms.
What are the signs of a malicious link?
Signs of malicious links on a website include unexpected redirects to unrelated or suspicious pages, warnings from antivirus software or browsers about unsafe content, and unusual pop-ups prompting you to download software or enter personal information.
Malicious links on a website can impact SEO negatively. Search engines may penalize sites with links to known malware, phishing, or spammy sites, leading to lower rankings or even removal from search results. It's crucial for website owners to regularly monitor and audit their links to maintain SEO health and user trust.